Abstract
Purpose
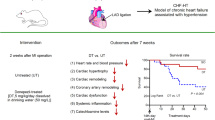
Pharmacological modulation of parasympathetic activity with donepezil, an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, improves the long-term survival of rats with chronic heart failure (CHF) after myocardial infarction (MI). However, its mechanism is not well understood. The α7-nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (α7-nAChR) reportedly plays an important role in the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway. The purpose of this study was to examine whether blockade of α7-nAChR, either centrally or peripherally, affects cardioprotection by donepezil during CHF.
Methods
One-week post-MI, the surviving rats were implanted with an electrocardiogram or blood pressure transmitter to monitor hemodynamics continuously. Seven days after implantation, the MI rats (n = 74) were administered donepezil in drinking water or were untreated (UT). Donepezil-treated MI rats were randomly assigned to the following four groups: peripheral infusion of saline (SPDT) or an α7-nAChR antagonist methyllycaconitine (α7PDT), and brain infusion of saline (SBDT) or the α7-nAChR antagonist (α7BDT).
Results
After the 4-week treatment, the role of α7-nAChR was evaluated using hemodynamic parameters, neurohumoral states, and histological and morphological assessment. Between the peripheral infusion groups, α7PDT (vs. SPDT) showed significantly increased heart weight and cardiac fibrosis, deteriorated hemodynamics, increased plasma neurohumoral and cytokine levels, and significantly decreased microvessel density (as assessed by anti-von Willebrand factor–positive cells). In contrast, between the brain infusion groups, α7BDT (vs. SBDT) showed no changes in either cardiac remodeling or hemodynamics.
Conclusion
Peripheral blockade of α7-nAChR significantly attenuated the cardioprotective effects of donepezil in CHF rats, whereas central blockade did not. This suggests that peripheral activation of α7-nAChR plays an important role in cholinergic pharmacotherapy for CHF.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Desai MY, Watanabe MA, Laddu AA, Hauptman PJ. Pharmacologic modulation of parasympathetic activity in heart failure. Heart Fail Rev. 2011;16(2):179–93. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10741-010-9195-1.
Yancy CW, Jessup M, Bozkurt B, Butler J, Casey DE Jr, Colvin MM, et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/HFSA focused update of the 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of heart failure: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on clinical practice guidelines and the heart failure society of America. J Card Fail. 2017;23:628–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cardfail.2017.04.014.
Pfeffer MA, Pfeffer JM, Steinberg C, Finn P. Survival after an experimental myocardial infarction: beneficial effects of long-term therapy with captopril. Circulation. 1985;72(2):406–12. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.cir.72.2.406.
Milavetz JJ, Raya TE, Johnson CS, Morkin E, Goldman S. Survival after myocardial infarction in rats: captopril versus losartan. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1996;27(3):714–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/0735-1097(95)00506-4.
Ahmet I, Morrell C, Lakatta EG, Talan MI. Therapeutic efficacy of a combination of a beta1-adrenoreceptor (AR) blocker and beta2-AR agonist in a rat model of postmyocardial infarction dilated heart failure exceeds that of a beta1-AR blocker plus angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2009;331(1):178–85. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.109.157107.
Kawada T, Li M, Zheng C, et al. Chronic vagal nerve stimulation improves baroreflex neural arc function in heart failure rats. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2014;116(10):1308–14. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.00140.2014.
De Jong MJ, Randall DC. Heart rate variability analysis in the assessment of autonomic function in heart failure. J Cardiovasc Nurs. 2005;20(3):186–95. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005082-200505000-00010.
Segovia V, Manterola C, Gonzalez M, Rodriguez-Nunez I. The exercise training restores the heart rate variability in heart failure patients. A systematic review. Arch Cardiol Mex. 2017;87(4):326–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acmx.2016.12.002.
Li M, Zheng C, Sato T, Kawada T, Sugimachi M, Sunagawa K. Vagal nerve stimulation markedly improves long-term survival after chronic heart failure in rats. Circulation. 2004;109(1):120–4. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.CIR.0000105721.71640.DA.
Li M, Zheng C, Inagaki M, Kawada T, Sunagawa K, Sugimachi M. Chronic vagal stimulation decreased vasopressin secretion and sodium ingestion in heart failure rats after myocardial infarction. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2005;4:3962–5. https://doi.org/10.1109/IEMBS.2005.1615329.
Li M, Zheng C, Kawada T, Inagaki M, Uemura K, Shishido T, et al. Donepezil markedly improves long-term survival in rats with chronic heart failure after extensive myocardial infarction. Circ J. 2013;77(10):2519–25. https://doi.org/10.1253/circj.cj-13-0476.
Nordstrom P, Religa D, Wimo A, Winblad B, Eriksdotter M. The use of cholinesterase inhibitors and the risk of myocardial infarction and death: a nationwide cohort study in subjects with Alzheimer’s disease. Eur Heart J. 2013;34(33):2585–91. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/eht182.
Li M, Zheng C, Kawada T, Inagaki M, Uemura K, Sugimachi M. Chronic vagal nerve stimulation exerts additional beneficial effects on the beta-blocker-treated failing heart. J Physiol Sci. 2019;69(2):295–303. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12576-018-0646-0.
Li M, Zheng C, Kawada T, Inagaki M, Uemura K, Sugimachi M. Adding the acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, donepezil, to losartan treatment markedly improves long-term survival in rats with chronic heart failure. Eur J Heart Fail. 2014;16(10):1056–65. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejhf.164.
Kjekshus J, Apetrei E, Barrios V, Böhm M, Cleland JG, Cornel JH, et al. Rosuvastatin in older patients with systolic heart failure. N Engl J Med. 2007;357(22):2248–61. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa0706201.
Torre-Amione G, Anker SD, Bourge RC, Colucci WS, Greenberg BH, Hildebrandt P, et al. Results of a non-specific immunomodulation therapy in chronic heart failure (ACCLAIM trial): a placebo-controlled randomised trial. Lancet. 2008;371(9608):228–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60134-8.
Zhao M, Sun L, Liu JJ, Wang H, Miao Y, Zang WJ. Vagal nerve modulation: a promising new therapeutic approach for cardiovascular diseases. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2012;39(8):701–5. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1681.2011.05644.x.
Mann DL. Tumor necrosis factor-induced signal transduction and left ventricular remodeling. J Card Fail. 2002;8(6 Suppl):S379–86. https://doi.org/10.1054/jcaf.2002.129253.
Borovikova LV, Ivanova S, Zhang M, Yang H, Botchkina GI, Watkins LR, et al. Vagus nerve stimulation attenuates the systemic inflammatory response to endotoxin. Nature. 2000;405(6785):458–62. https://doi.org/10.1038/35013070.
Guarini S, Altavilla D, Cainazzo MM, Giuliani D, Bigiani A, Marini H, et al. Efferent vagal fibre stimulation blunts nuclear factor-kappaB activation and protects against hypovolemic hemorrhagic shock. Circulation. 2003;107(8):1189–94. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.cir.0000050627.90734.ed.
Bernik TR, Friedman SG, Ochani M, DiRaimo R, Ulloa L, Yang H, et al. Pharmacological stimulation of the cholinergic antiinflammatory pathway. J Exp Med. 2002;195(6):781–8. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20011714.
Wang H, Yu M, Ochani M, Amella CA, Tanovic M, Susarla S, et al. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor alpha7 subunit is an essential regulator of inflammation. Nature. 2003;421(6921):384–8. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01339.
Pavlov VA, Parrish WR, Rosas-Ballina M, Ochani M, Puerta M, Ochani K, et al. Brain acetylcholinesterase activity controls systemic cytokine levels through the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway. Brain Behav Immun. 2009;23(1):41–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2008.06.011.
Heeschen C, Weis M, Aicher A, Dimmeler S, Cooke JP. A novel angiogenic pathway mediated by non-neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. J Clin Invest. 2002;110(4):527–36. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI14676.
Moore C, Wang Y, Ramage AG. Nicotine’s central cardiovascular actions: receptor subtypes involved and their possible physiological role in anaesthetized rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 2011;668(1–2):177–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2011.06.055.
Turek JW, Kang CH, Campbell JE, Arneric SP, Sullivan JP. A sensitive technique for the detection of the alpha 7 neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor antagonist, methyllycaconitine, in rat plasma and brain. J Neurosci Methods. 1995;61(1–2):113–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-0270(95)00032-p.
Li M, Zheng C, Kawada T, Inagaki M, Uemura K, Sugimachi M. Intracerebroventricular infusion of donepezil prevents cardiac remodeling and improves the prognosis of chronic heart failure rats. J Physiol Sci. 2020;70(1):11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12576-020-00739-0.
Rosas-Ballina M, Tracey KJ. Cholinergic control of inflammation. J Intern Med. 2009;265(6):663–79. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2796.2009.02098.x.
Anzai T. Post-infarction inflammation and left ventricular remodeling: a double-edged sword. Circ J. 2013;77(3):580–7. https://doi.org/10.1253/circj.cj-13-0013.
Su X, Lee JW, Matthay ZA, Mednick G, Uchida T, Fang X, et al. Activation of the alpha7 nAChR reduces acid-induced acute lung injury in mice and rats. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2007;37(2):186–92. https://doi.org/10.1165/rcmb.2006-0240OC.
Mitra AK, Gao L, Zucker IH. Angiotensin II-induced upregulation of AT(1) receptor expression: sequential activation of NF-kappaB and Elk-1 in neurons. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2010;299(3):C561–9. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00127.2010.
Pavlov VA, Ochani M, Gallowitsch-Puerta M, Ochani K, Huston JM, Czura CJ, et al. Central muscarinic cholinergic regulation of the systemic inflammatory response during endotoxemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103(13):5219–23. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0600506103.
Ulloa L. The vagus nerve and the nicotinic anti-inflammatory pathway. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2005;4(8):673–84. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd1797.
Okazaki Y, Zheng C, Li M, Sugimachi M. Effect of the cholinesterase inhibitor donepezil on cardiac remodeling and autonomic balance in rats with heart failure. J Physiol Sci. 2010;60(1):67–74. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12576-009-0071-5.
Androne AS, Hryniewicz K, Goldsmith R, Arwady A, Katz SD. Acetylcholinesterase inhibition with pyridostigmine improves heart rate recovery after maximal exercise in patients with chronic heart failure. Heart. 2003;89(8):854–8. https://doi.org/10.1136/heart.89.8.854.
Castro RR, Porphirio G, Serra SM, Nobrega AC. Cholinergic stimulation with pyridostigmine protects against exercise induced myocardial ischaemia. Heart. 2004;90(10):1119–23. https://doi.org/10.1136/hrt.2003.028167.
Raj SR, Black BK, Biaggioni I, Harris PA, Robertson D. Acetylcholinesterase inhibition improves tachycardia in postural tachycardia syndrome. Circulation. 2005;111(21):2734–40. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.104.497594.
Burkhoff D, Sagawa K. Ventricular efficiency predicted by an analytical model. Am J Phys. 1986;250(6 Pt 2):R1021–7. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.1986.250.6R1021.
Gaballa MA, Goldman S. Ventricular remodeling in heart failure. J Card Fail. 2002;8(6 Suppl):S476–85. https://doi.org/10.1054/jcaf.2002.129270.
Kubo T, Sato T, Noguchi T, Kitaoka H, Yamasaki F, Kamimura N, et al. Influences of donepezil on cardiovascular system--possible therapeutic benefits for heart failure--donepezil cardiac test registry (DOCTER) study. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2012;60(3):310–4. https://doi.org/10.1097/FJC.0b013e3182609a74.
Khuanjing T, Palee S, Chattipakorn SC, Chattipakorn N. The effects of acetylcholinesterase inhibitors on the heart in acute myocardial infarction and heart failure: from cells to patient reports. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2019;e13396. https://doi.org/10.1111/apha.13396.
Mavropoulos SA, Khan NS, Levy ACJ, Faliks BT, Sison CP, Pavlov VA, et al. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor-mediated protection of the rat heart exposed to ischemia reperfusion. Mol Med. 2017;23:120–33. https://doi.org/10.2119/molmed.2017.00091.
Oikawa S, Kai Y, Mano A, Nakamura S, Kakinuma Y. A novel nitric oxide donor, S-nitroso-Npivaloyl-D-penicillamine, activates a non-neuronal cardiac cholinergic system to synthesize acetylcholine and augments cardiac function. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2019;52(4):922–34. https://doi.org/10.33594/000000064.
Saw EL, Kakinuma Y, Fronius M, Katare R. The non-neuronal cholinergic system in the heart: a comprehensive review. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2018;125:129–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yjmcc.2018.10.013.
Kakinuma Y, Akiyama T, Sato T. Cholinoceptive and cholinergic properties of cardiomyocytes involving an amplification mechanism for vagal efferent effects in sparsely innervated ventricular myocardium. FEBS J. 2009;276(18):5111–25. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-4658.2009.07208.x.
Availability of Data and Material
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code Availability
None.
Funding
This study was partly supported by JSPS KAKENHI (Grant Number: 17K09544, 18K08091).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ML and CZ designed the study. ML and CZ performed the measurements and statistical analyses and drafted the manuscript. TK, MI, KU, TA, and MS joined in interpreting the data. ML and CZ wrote and edited, while TK and MS reviewed the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics Approval
The care of animals and all animal experiments were performed in strict accordance with the guiding principles of the Physiological Society of Japan and the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals published by the US National Institutes of Health (NIH Publications No 85-23, revised 1996). All protocols were reviewed and approved by the Animal Subject Committee in the National Cerebral and Cardiovascular Center.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, M., Zheng, C., Kawada, T. et al. Impact of Peripheral α7-Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors on Cardioprotective Effects of Donepezil in Chronic Heart Failure Rats. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther 35, 877–888 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10557-020-07062-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10557-020-07062-1