Abstract
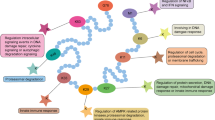
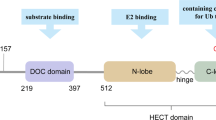
Accumulating evidence suggests that E3 ubiquitin ligases play important roles in cancer development. In this article, we provide a comprehensive summary of the roles of the Nedd4-like family of E3 ubiquitin ligases in human cancer. There are nine members of the Nedd4-like E3 family, all of which share a similar structure, including a C2 domain at the N-terminus, two to four WW domains in the middle of the protein, and a homologous to E6-AP COOH terminus domain at the C-terminus. The assertion that Nedd4-like E3s play a role in cancer is supported by the overexpression of Smurf2 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, WWP1 in prostate and breast cancer, Nedd4 in prostate and bladder cancer, and Smurf1 in pancreatic cancer. Because Nedd4-like E3s regulate ubiquitin-mediated trafficking, lysosomal or proteasomal degradation, and nuclear translocation of multiple proteins, they modulate important signaling pathways involved in tumorigenesis like TGFβ, EGF, IGF, VEGF, SDF-1, and TNFα. Additionally, several Nedd4-like E3s directly regulate various cancer-related transcription factors from the Smad, p53, KLF, RUNX, and Jun families. Interestingly, multiple Nedd4-like E3s show ligase independent function. Furthermore, Nedd4-like E3s themselves are frequently regulated by phosphorylation, ubiquitination, translocation, and transcription in cancer cells. Because the regulation and biological output of these E3s is such a complex process, study of the role of these E3s in cancer development poses some challenges. However, understanding the oncogenic potential of these E3s may facilitate the identification and development of biomarkers and drug targets in human cancer.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pickart, C. M. (2004). Back to the future with ubiquitin. Cell, 116, 181–90.
Pickart, C. M., & Fushman, D. (2004). Polyubiquitin chains: Polymeric protein signals. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 8, 610–16.
Hicke, L., & Dunn, R. (2003). Regulation of membrane protein transport by ubiquitin and ubiquitin-binding proteins. Annual Review of Cell and Developmental Biology, 19, 141–72.
Nalepa, G., Rolfe, M., & Harper, J. W. (2006). Drug discovery in the ubiquitin-proteasome system. Nature Reviews. Drug Discovery, 5, 596–13.
Chen, C., Seth, A. K., & Aplin, A. E. (2006). Genetic and expression aberrations of e3 ubiquitin ligases in human breast cancer. Molecular Cancer Research, 4, 695–07.
Kumar, S., Harvey, K. F., Kinoshita, M., Copeland, N. G., Noda, M., & Jenkins, N. A. (1997). cDNA cloning, expression analysis, and mapping of the mouse Nedd4 gene. Genomics, 40, 435–43.
Plant, P. J., Yeger, H., Staub, O., Howard, P., & Rotin, D. (1997). The C2 domain of the ubiquitin protein ligase Nedd4 mediates Ca2+-dependent plasma membrane localization. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 272, 32329–2336.
Seo, S. R., Lallemand, F., Ferrand, N., Pessah, M., L’Hoste, S., Camonis, J., et al. (2004). The novel E3 ubiquitin ligase Tiul1 associates with TGIF to target Smad2 for degradation. EMBO Journal, 23, 3780–792.
Lu, P. J., Zhou, X. Z., Shen, M., & Lu, K. P. (1999). Function of WW domains as phosphoserine- or phosphothreonine-binding modules. Science, 283, 1325–328.
Ingham, R. J., Gish, G., & Pawson, T. (2004). The Nedd4 family of E3 ubiquitin ligases: Functional diversity within a common modular architecture. Oncogene, 23, 1972–984.
Harvey, K. F., & Kumar, S. (1999). Nedd4-like proteins: An emerging family of ubiquitin-protein ligases implicated in diverse cellular functions. Trends in Cell Biology, 9, 166–69.
Staub, O., Abriel, H., Plant, P., Ishikawa, T., Kanelis, V., Saleki, R., et al. (2000). Regulation of the epithelial Na+ channel by Nedd4 and ubiquitination. Kidney International, 57, 809–15.
Shearwin-Whyatt, L., Dalton, H. E., Foot, N., & Kumar, S. (2006). Regulation of functional diversity within the Nedd4 family by accessory and adaptor proteins. Bioessays, 28, 617–28.
Lin, X., Liang, M., & Feng, X. H. (2000). Smurf2 is a ubiquitin E3 ligase mediating proteasome-dependent degradation of Smad2 in transforming growth factor-beta signaling. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 275, 36818–6822.
Kavsak, P., Rasmussen, R. K., Causing, C. G., Bonni, S., Zhu, H., Thomsen, G. H., et al. (2000). Smad7 binds to Smurf2 to form an E3 ubiquitin ligase that targets the TGF beta receptor for degradation. Molecular Cell, 6, 1365–375.
Fukuchi, M., Fukai, Y., Masuda, N., Miyazaki, T., Nakajima, M., Sohda, M., et al. (2002). High-level expression of the Smad ubiquitin ligase Smurf2 correlates with poor prognosis in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Research, 62, 7162–165.
Zhang, H., & Cohen, S. N. (2004). Smurf2 up-regulation activates telomere-dependent senescence. Genes & Development, 18, 3028–040.
Chen, C., Sun, X., Guo, P., Dong, X. Y., Sethi, P., Zhou, W., et al. (2007). Ubiquitin E3 ligase WWP1 as an oncogenic factor in human prostate cancer. Oncogene, 26, 2386–394.
Chen, C., Zhou, Z., Ross, J. S., Zhou, W., & Dong, J. T. (2007). The amplified WWP1 gene is a potential molecular target in breast cancer. International Journal of Cancer, 121, 2834–841.
Martin-Serrano, J., Eastman, S. W., Chung, W., & Bieniasz, P. D. (2005). HECT ubiquitin ligases link viral and cellular PPXY motifs to the vacuolar protein-sorting pathway. Journal of Cell Biology, 168, 89–01.
Huang, K., Johnson, K. D., Petcherski, A. G., Vandergon, T., Mosser, E. A., Copeland, N. G., et al. (2000). A HECT domain ubiquitin ligase closely related to the mammalian protein WWP1 is essential for Caenorhabditis elegans embryogenesis. Gene, 252, 137–45.
Loukopoulos, P., Shibata, T., Katoh, H., Kokubu, A., Sakamoto, M., Yamazaki, K., et al. (2007). Genome-wide array-based comparative genomic hybridization analysis of pancreatic adenocarcinoma: Identification of genetic indicators that predict patient outcome. Cancer Science, 98, 392–00.
Kwei, K. A., Maitra, A., Van de Rijn, M., Montgomery, K., Pollack, J. R. (2007). Role of Smurf1 amplification in pancreatic oncogenesis. AACR Annual Meeting 2007 Proceedings, 48, 1051.
Wang, X., Trotman, L. C., Koppie, T., Alimonti, A., Chen, Z., Gao, Z., et al. (2007). NEDD4– is a proto-oncogenic ubiquitin ligase for PTEN. Cell, 128, 129–39.
Staub, O., Dho, S., Henry, P., Correa, J., Ishikawa, T., McGlade, J., et al. (1996). WW domains of Nedd4 bind to the proline-rich PY motifs in the epithelial Na+ channel deleted in Liddle’s syndrome. EMBO Journal, 15, 2371–380.
Shi, P., Sweezer, E., Kinney, T. S., Williams, N., Volk, K., et al. (2007). Nedd4l null mice are defective in downregulating ENAC and have salt-sensitive hypertension. Keystone Symposia: Ubiquitin and Signaling, 84.
Izzi, L., & Attisano, L. (2006). Ubiquitin-dependent regulation of TGFbeta signaling in cancer. Neoplasia, 8, 677–88.
Akhurst, R. J., & Derynck, R. (2001). TGF-beta signaling in cancer—a double-edged sword. Trends in Cell Biology, 11, S44’S51.
Ebisawa, T., Fukuchi, M., Murakami, G., Chiba, T., Tanaka, K., Imamura, T., et al. (2001). Smurf1 interacts with transforming growth factor-beta type I receptor through Smad7 and induces receptor degradation. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 276, 12477–2480.
Yamaguchi, T., Kurisaki, A., Yamakawa, N., Minakuchi, K., & Sugino, H. (2006). FKBP12 functions as an adaptor of the Smad7’Smurf1 complex on activin type I receptor. Journal of Molecular Endocrinology, 36, 569–79.
Kuratomi, G., Komuro, A., Goto, K., Shinozaki, M., Miyazawa, K., Miyazono, K., et al. (2005). NEDD4– (neural precursor cell expressed, developmentally down-regulated 4–) negatively regulates TGF-beta (transforming growth factor-beta) signalling by inducing ubiquitin-mediated degradation of Smad2 and TGF-beta type I receptor. Biochemical Journal, 386, 461–70.
Komuro, A., Imamura, T., Saitoh, M., Yoshida, Y., Yamori, T., Miyazono, K., et al. (2004). Negative regulation of transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) signaling by WW domain-containing protein 1 (WWP1). Oncogene, 23, 6914–923.
Lallemand, F., Seo, S. R., Ferrand, N., Pessah, M., L’Hoste, S., Rawadi, G., et al. (2005). AIP4 restricts transforming growth factor-beta signaling through a ubiquitination-independent mechanism. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 280, 27645–7653.
Murakami, G., Watabe, T., Takaoka, K., Miyazono, K., & Imamura, T. (2003). Cooperative inhibition of bone morphogenetic protein signaling by Smurf1 and inhibitory Smads. Molecular Biology of the Cell, 14, 2809–817.
Maillard, I., & Pear, W. S. (2003). Notch and cancer: Best to avoid the ups and downs. Cancer Cell, 3, 203–05.
Weng, A. P., & Aster, J. C. (2004). Multiple niches for Notch in cancer: Context is everything. Current Opinion in Genetics & Development, 14, 48–4.
Qiu, L., Joazeiro, C., Fang, N., Wang, H. Y., Elly, C., Altman, Y., et al. (2000). Recognition and ubiquitination of Notch by Itch, a hect-type E3 ubiquitin ligase. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 275, 35734–5737.
McGill, M. A., & McGlade, C. J. (2003). Mammalian numb proteins promote Notch1 receptor ubiquitination and degradation of the Notch1 intracellular domain. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 278, 23196–3203.
Matesic, L. E., Haines, D. C., Copeland, N. G., & Jenkins, N. A. (2006). Itch genetically interacts with Notch1 in a mouse autoimmune disease model. Human Molecular Genetics Online, 15, 3485–497.
Shaye, D. D., & Greenwald, I. (2005). LIN-12/Notch trafficking and regulation of DSL ligand activity during vulval induction in Caenorhabditis elegans. Development, 132, 5081–092.
Sakata, T., Sakaguchi, H., Tsuda, L., Higashitani, A., Aigaki, T., Matsuno, K., et al. (2004). Drosophila Nedd4 regulates endocytosis of notch and suppresses its ligand-independent activation. Current Biology, 14, 2228–236.
Chastagner, P., Israel, A., & Brou, C. (2006). Itch/AIP4 mediates Deltex degradation through the formation of K29-linked polyubiquitin chains. EMBO Reports, 7, 1147–153.
Vecchione, A., Marchese, A., Henry, P., Rotin, D., & Morrione, A. (2003). The Grb10/Nedd4 complex regulates ligand-induced ubiquitination and stability of the insulin-like growth factor I receptor. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 23, 3363–372.
Miller, B. S., & Yee, D. (2005). Type I insulin-like growth factor receptor as a therapeutic target in cancer. Cancer Research, 65, 10123–0127.
Baserga, R. (2005). The insulin-like growth factor-I receptor as a target for cancer therapy. Expert Opinion on Therapeutic Targets, 9, 753–68.
Morrione, A., Plant, P., Valentinis, B., Staub, O., Kumar, S., Rotin, D., et al. (1999). mGrb10 interacts with Nedd4. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 274, 24094–4099.
Murdaca, J., Treins, C., Monthouel-Kartmann, M. N., Pontier-Bres, R., Kumar, S., Van Obberghen, E., et al. (2004). Grb10 prevents Nedd4-mediated vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 degradation. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 279, 26754–6761.
Ferrara, N. (2005). VEGF as a therapeutic target in cancer. Oncology, 69(Suppl 3), 11–6.
Marchese, A., Raiborg, C., Santini, F., Keen, J. H., Stenmark, H., & Benovic, J. L. (2003). The E3 ubiquitin ligase AIP4 mediates ubiquitination and sorting of the G protein-coupled receptor CXCR4. Developments in Cell, 5, 709–22.
Dewan, M. Z., Ahmed, S., Iwasaki, Y., Ohba, K., Toi, M., & Yamamoto, N. (2006). Stromal cell-derived factor-1 and CXCR4 receptor interaction in tumor growth and metastasis of breast cancer. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 60, 273–76.
Wang, J., Loberg, R., & Taichman, R. S. (2006). The pivotal role of CXCL12 (SDF-1)/CXCR4 axis in bone metastasis. Cancer and Metastasis Reviews, 25, 573–87.
Yarden, Y. (2001). The EGFR family and its ligands in human cancer. signalling mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. European Journal of Cancer, 37(Suppl 4), S3’S8.
Magnifico, A., Ettenberg, S., Yang, C., Mariano, J., Tiwari, S., Fang, S., et al. (2003). WW domain HECT E3s target Cbl RING finger E3s for proteasomal degradation. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 278, 43169–3177.
Katz, M., Shtiegman, K., Tal-Or, P., Yakir, L., Mosesson, Y., Harari, D., et al. (2002). Ligand-independent degradation of epidermal growth factor receptor involves receptor ubiquitylation and Hgs, an adaptor whose ubiquitin-interacting motif targets ubiquitylation by Nedd4. Traffic, 3, 740–51.
Courbard, J. R., Fiore, F., Adelaide, J., Borg, J. P., Birnbaum, D., & Ollendorff, V. (2002). Interaction between two ubiquitin-protein isopeptide ligases of different classes, CBLC and AIP4/ITCH. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 277, 45267–5275.
Angers, A., Ramjaun, A. R., & McPherson, P. S. (2004). The HECT domain ligase itch ubiquitinates endophilin and localizes to the trans-Golgi network and endosomal system. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 279, 11471–1479.
Omerovic, J., Santangelo, L., Puggioni, E. M., Marrocco, J., Dall’armi, C., Palumbo, C., et al. (2007). The E3 ligase Aip4/Itch ubiquitinates and targets ErbB-4 for degradation. FASEB Journal, DOI 10.1096/fj.06-7925com.
Arevalo, J. C., Waite, J., Rajagopal, R., Beyna, M., Chen, Z. Y., Lee, F. S., et al. (2006). Cell survival through Trk neurotrophin receptors is differentially regulated by ubiquitination. Neuron, 50, 549–59.
Dikic, I. (2003). Mechanisms controlling EGF receptor endocytosis and degradation. Biochemical Society Transactions, 31, 1178–181.
Miyake, S., Mullane-Robinson, K. P., Lill, N. L., Douillard, P., & Band, H. (1999). Cbl-mediated negative regulation of platelet-derived growth factor receptor-dependent cell proliferation. A critical role for Cbl tyrosine kinase-binding domain. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 274, 16619–6628.
Petrelli, A., Gilestro, G. F., Lanzardo, S., Comoglio, P. M., Migone, N., & Giordano, S. (2002). The endophilin-CIN85-Cbl complex mediates ligand-dependent downregulation of c-Met. Nature, 416, 187–90.
Soubeyran, P., Kowanetz, K., Szymkiewicz, I., Langdon, W. Y., & Dikic, I. (2002). Cbl-CIN85-endophilin complex mediates ligand-induced downregulation of EGF receptors. Nature, 416, 183–87.
Stamenova, S. D., Dunn, R., Adler, A. S., & Hicke, L. (2004). The Rsp5 ubiquitin ligase binds to and ubiquitinates members of the yeast CIN85-endophilin complex, Sla1-Rvs167. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 279, 16017–6025.
Di Fiore, P. P., Polo, S., & Hofmann, K. (2003). When ubiquitin meets ubiquitin receptors: A signalling connection. Nature Reviews. Molecular Cell Biology, 4, 491–97.
Polo, S., Sigismund, S., Faretta, M., Guidi, M., Capua, M. R., Bossi, G., et al. (2002). A single motif responsible for ubiquitin recognition and monoubiquitination in endocytic proteins. Nature, 416, 451–55.
Woelk, T., Oldrini, B., Maspero, E., Confalonieri, S., Cavallaro, E., Di Fiore, P. P., et al. (2006). Molecular mechanisms of coupled monoubiquitination. Nature Cell Biology, 8, 1246–254.
Hoeller, D., Crosetto, N., Blagoev, B., Raiborg, C., Tikkanen, R., Wagner, S., et al. (2006). Regulation of ubiquitin-binding proteins by monoubiquitination. Nature Cell Biology, 8, 163–69.
Fallon, L., Belanger, C. M., Corera, A. T., Kontogiannea, M., Regan-Klapisz, E., Moreau, F., et al. (2006). A regulated interaction with the UIM protein Eps15 implicates parkin in EGF receptor trafficking and PI(3)K-Akt signalling. Nature Cell Biology, 8, 834–42.
Xu, L. L., Shi, Y., Petrovics, G., Sun, C., Makarem, M., Zhang, W., et al. (2003). PMEPA1, an androgen-regulated NEDD4-binding protein, exhibits cell growth inhibitory function and decreased expression during prostate cancer progression. Cancer Research, 63, 4299–304.
Harvey, K. F., Shearwin-Whyatt, L. M., Fotia, A., Parton, R. G., & Kumar, S. (2002). N4WBP5, a potential target for ubiquitination by the Nedd4 family of proteins, is a novel Golgi-associated protein. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 277, 9307–317.
Shearwin-Whyatt, L. M., Brown, D. L., Wylie, F. G., Stow, J. L., & Kumar, S. (2004). N4WBP5A (Ndfip2), a Nedd4-interacting protein, localizes to multivesicular bodies and the Golgi, and has a potential role in protein trafficking. Journal of Cell Science, 117, 3679–689.
Hongyun, L., K, M., Xu, L., Cullen, J., Dobi, A., & Srivastava, S. (2007). PMEPA1 regulates androgen receptor levels through interactions with the ubiquitin-proteasomal pathway. AACR Annual Meeting 2007 Proceedings, 48, 1027.
Kitching, R., Wong, M. J., Koehler, D., Burger, A. M., Landberg, G., Gish, G., et al. (2003). The RING-H2 protein RNF11 is differentially expressed in breast tumours and interacts with HECT-type E3 ligases. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1639, 104–12.
Subramaniam, V., Li, H., Wong, M., Kitching, R., Attisano, L., Wrana, J., et al. (2003). The RING-H2 protein RNF11 is overexpressed in breast cancer and is a target of Smurf2 E3 ligase. British Journal of Cancer, 89, 1538–544.
Burger, A., Amemiya, Y., Kitching, R., & Seth, A. K. (2006). Novel RING E3 ubiquitin ligases in breast cancer. Neoplasia, 8, 689–95.
Bache, K. G., Slagsvold, T., & Stenmark, H. (2004). Defective downregulation of receptor tyrosine kinases in cancer. EMBO Journal, 23, 2707–712.
Miyaki, M., & Kuroki, T. (2003). Role of Smad4 (DPC4) inactivation in human cancer. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 306, 799–04.
Zhu, H., Kavsak, P., Abdollah, S., Wrana, J. L., & Thomsen, G. H. (1999). A SMAD ubiquitin ligase targets the BMP pathway and affects embryonic pattern formation. Nature, 400, 687–93.
Zhang, Y., Chang, C., Gehling, D. J., Hemmati-Brivanlou, A., & Derynck, R. (2001). Regulation of Smad degradation and activity by Smurf2, an E3 ubiquitin ligase. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 98, 974–79.
Ying, S. X., Hussain, Z. J., & Zhang, Y. E. (2003). Smurf1 facilitates myogenic differentiation and antagonizes the bone morphogenetic protein-2-induced osteoblast conversion by targeting Smad5 for degradation. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 278, 39029–9036.
Shi, W., Chen, H., Sun, J., Chen, C., Zhao, J., Wang, Y. L., et al. (2004). Overexpression of Smurf1 negatively regulates mouse embryonic lung branching morphogenesis by specifically reducing Smad1 and Smad5 proteins. American Journal of Physiology. Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology, 286, L293’L300.
Bai, Y., Yang, C., Hu, K., Elly, C., & Liu, Y. C. (2004). Itch E3 ligase-mediated regulation of TGF-beta signaling by modulating smad2 phosphorylation. Molecular Cell, 15, 825–31.
Han, G., Li, A. G., Liang, Y. Y., Owens, P., He, W., Lu, S., et al. (2006). Smad7-induced beta-catenin degradation alters epidermal appendage development. Developments in Cell, 11, 301–12.
Moren, A., Imamura, T., Miyazono, K., Heldin, C. H., & Moustakas, A. (2005). Degradation of the tumor suppressor Smad4 by WW and HECT domain ubiquitin ligases. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 280, 22115–2123.
Bonni, S., Wang, H. R., Causing, C. G., Kavsak, P., Stroschein, S. L., Luo, K., et al. (2001). TGF-beta induces assembly of a Smad2’Smurf2 ubiquitin ligase complex that targets SnoN for degradation. Nature Cell Biology, 3, 587–95.
Shen, R., Chen, M., Wang, Y. J., Kaneki, H., Xing, L., O’Keefe R, J., et al. (2006). Smad6 interacts with Runx2 and mediates Smad ubiquitin regulatory factor 1-induced Runx2 degradation. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 281, 3569–576.
Feng, L., Guedes, S., & Wang, T. (2004). Atrophin-1-interacting protein 4/human Itch is a ubiquitin E3 ligase for human enhancer of filamentation 1 in transforming growth factor-beta signaling pathways. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 279, 29681–9690.
Levine, A. J. (1997). p53, the cellular gatekeeper for growth and division. Cell, 88, 323–31.
Levrero, M., De Laurenzi, V., Costanzo, A., Gong, J., Wang, J. Y., & Melino, G. (2000). The p53/p63/p73 family of transcription factors: overlapping and distinct functions. Journal of Cell Science, 113(Pt 10), 1661–670.
Watson, I. R., & Irwin, M. S. (2006). Ubiquitin and ubiquitin-like modifications of the p53 family. Neoplasia, 8, 655–66.
Willis, A. C., Pipes, T., Zhu, J., & Chen, X. (2003). p73 can suppress the proliferation of cells that express mutant p53. Oncogene, 22, 5481–495.
Helton, E. S., Zhu, J., & Chen, X. (2006). The unique NH2-terminally deleted (DeltaN) residues, the PXXP motif, and the PPXY motif are required for the transcriptional activity of the DeltaN variant of p63. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 281, 2533–542.
Harris, S. L., & Levine, A. J. (2005). The p53 pathway: Positive and negative feedback loops. Oncogene, 24, 2899–908.
Brooks, C. L., & Gu, W. (2003). Ubiquitination, phosphorylation and acetylation: The molecular basis for p53 regulation. Current Opinion in Cell Biology, 15, 164–71.
Laine, A., & Ronai, Z. (2007). Regulation of p53 localization and transcription by the HECT domain E3 ligase WWP1. Oncogene, 26(10), 1477–483.
Li, M., Brooks, C. L., Wu-Baer, F., Chen, D., Baer, R., & Gu, W. (2003). Mono- versus polyubiquitination: Differential control of p53 fate by Mdm2. Science, 302, 1972–975.
Miyazaki, K., Ozaki, T., Kato, C., Hanamoto, T., Fujita, T., Irino, S., et al. (2003). A novel HECT-type E3 ubiquitin ligase, NEDL2, stabilizes p73 and enhances its transcriptional activity. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 308, 106–13.
Rossi, M., De Laurenzi, V., Munarriz, E., Green, D. R., Liu, Y. C., Vousden, K. H., et al. (2005). The ubiquitin-protein ligase Itch regulates p73 stability. EMBO Journal, 24, 836–48.
Oberst, A., Rossi, M., Salomoni, P., Pandolfi, P. P., Oren, M., Melino, G., et al. (2005). Regulation of the p73 protein stability and degradation. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 331, 707–12.
Levy, D., Adamovich, Y., Reuven, N., & Shaul, Y. (2007). The Yes-associated protein 1 stabilizes p73 by preventing Itch-mediated ubiquitination of p73. Cell Death and Differentiation, 14, 743–51.
Bakkers, J., Camacho-Carvajal, M., Nowak, M., Kramer, C., Danger, B., & Hammerschmidt, M. (2005). Destabilization of DeltaNp63alpha by Nedd4-mediated ubiquitination and Ubc9-mediated sumoylation, and its implications on dorsoventral patterning of the zebrafish embryo. Cell Cycle, 4, 790–00.
Melino, G., Knight, R. A., & Cesareni, G. (2006). Degradation of p63 by Itch. Cell Cycle, 5, 1735–739.
Rossi, M., Aqeilan, R. I., Neale, M., Candi, E., Salomoni, P., Knight, R. A., et al. (2006). The E3 ubiquitin ligase Itch controls the protein stability of p63. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 103, 12753–2758.
Rossi, M., De Simone, M., Pollice, A., Santoro, R., La Mantia, G., Guerrini, L., et al. (2006) Itch/AIP4 associates with and promotes p63 protein degradation. Cell Cycle, 5, 1816–822.
Black, A. R., Black, J. D., & Azizkhan-Clifford, J. (2001). Sp1 and kruppel-like factor family of transcription factors in cell growth regulation and cancer. Journal of Cellular Physiology, 188, 143–60.
Safe, S., & Abdelrahim, M. (2005). Sp transcription factor family and its role in cancer. European Journal of Cancer, 41, 2438–448.
Wu, J., & Lingrel, J. B. (2004). KLF2 inhibits Jurkat T leukemia cell growth via upregulation of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21WAF1/CIP1. Oncogene, 23, 8088–096.
Chen, C., Benjamin, M. S., Sun, X., Otto, K. B., Guo, P., Dong, X. Y., et al. (2006). KLF5 promotes cell proliferation and tumorigenesis through gene regulationin the TSU-Pr1 human bladder cancer cell line. International Journal of Cancer, 118, 1346–355.
Conkright, M. D., Wani, M. A., & Lingrel, J. B. (2001). Lung Kruppel-like factor contains an autoinhibitory domain that regulates its transcriptional activation by binding WWP1, an E3 ubiquitin ligase. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 276, 29299–9306.
Bhattacharya, R., Senbanerjee, S., Lin, Z., Mir, S., Hamik, A., Wang, P., et al. (2005). Inhibition of vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor-mediated angiogenesis by the Kruppel-like factor KLF2. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 280, 28848–8851.
Wang, F., Zhu, Y., Huang, Y., McAvoy, S., Johnson, W. B., Cheung, T. H., et al. (2005). Transcriptional repression of WEE1 by Kruppel-like factor 2 is involved in DNA damage-induced apoptosis. Oncogene, 24, 3875–885.
Chen, C., Sun, X., Ran, Q., Wilkinson, K. D., Murphy, T. J., Simons, J. W., et al. (2005). Ubiquitin-proteasome degradation of KLF5 transcription factor in cancer and untransformed epithelial cells. Oncogene, 24, 3319–327.
Chen, C., Sun, X., Guo, P., Dong, X. Y., Sethi, P., Cheng, X., et al. (2005). Human Kruppel-like factor 5 is a target of the E3 ubiquitin ligase WWP1 for proteolysis in epithelial cells. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 280, 41553–1561.
Pratap, J., Lian, J. B., Javed, A., Barnes, G. L., van Wijnen, A. J., Stein, J. L., et al. (2006). Regulatory roles of Runx2 in metastatic tumor and cancer cell interactions with bone. Cancer and Metastasis Reviews, 25, 589–00.
Zhao, M., Qiao, M., Oyajobi, B. O., Mundy, G. R., & Chen, D. (2003). E3 ubiquitin ligase Smurf1 mediates core-binding factor alpha1/Runx2 degradation and plays a specific role in osteoblast differentiation. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 278, 27939–7944.
Kaneki, H., Guo, R., Chen, D., Yao, Z., Schwarz, E. M., Zhang, Y. E., et al. (2006). Tumor necrosis factor promotes Runx2 degradation through up-regulation of Smurf1 and Smurf2 in osteoblasts. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 281, 4326–333.
Jones, D. C., Wein, M. N., Oukka, M., Hofstaetter, J. G., Glimcher, M. J., & Glimcher, L. H. (2006). Regulation of adult bone mass by the zinc finger adapter protein Schnurri-3. Science, 312, 1223–227.
Zhao, M., Qiao, M., Harris, S. E., Oyajobi, B. O., Mundy, G. R., & Chen, D. (2004). Smurf1 inhibits osteoblast differentiation and bone formation in vitro and in vivo. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 279, 12854–2859.
Yamashita, M., Ying, S. X., Zhang, G. M., Li, C., Cheng, S. Y., Deng, C. X., et al. (2005). Ubiquitin ligase Smurf1 controls osteoblast activity and bone homeostasis by targeting MEKK2 for degradation. Cell, 121, 101–13.
Li, Q. L., Ito, K., Sakakura, C., Fukamachi, H., Inoue, K., Chi, X. Z., et al. (2002).Causal relationship between the loss of RUNX3 expression and gastric cancer. Cell, 109, 113–24.
Jin, Y. H., Jeon, E. J., Li, Q. L., Lee, Y. H., Choi, J. K., Kim, W. J., et al. (2004). Transforming growth factor-beta stimulates p300-dependent RUNX3 acetylation, which inhibits ubiquitination-mediated degradation. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 279, 29409–9417.
Fang, D., Elly, C., Gao, B., Fang, N., Altman, Y., Joazeiro, C., et al. (2002). Dysregulation of T lymphocyte function in itchy mice: A role for Itch in TH2 differentiation. Nature Immunology, 3, 281–87.
Gao, M., Labuda, T., Xia, Y., Gallagher, E., Fang, D., Liu, Y. C., et al. (2004). Jun turnover is controlled through JNK-dependent phosphorylation of the E3 ligase Itch. Science, 306, 271–75.
Li, B., Tournier, C., Davis, R. J., & Flavell, R. A. (1999). Regulation of IL-4 expression by the transcription factor JunB during T helper cell differentiation. EMBO Journal, 18, 420–32.
Gao, B., Lee, S. M., & Fang, D. (2006). The tyrosine kinase c-Abl protects c-Jun from ubiquitination-mediated degradation in T cells. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 281, 29711–9718.
Oliver, P. M., Cao, X., Worthen, G. S., Shi, P., Briones, N., MacLeod, M., et al. (2006). Ndfip1 protein promotes the function of itch ubiquitin ligase to prevent T cell activation and T helper 2 cell-mediated inflammation. Immunity, 25, 929–40.
Jonk, L. J., Itoh, S., Heldin, C. H., ten Dijke, P., & Kruijer, W. (1998). Identification and functional characterization of a Smad binding element (SBE) in the JunB promoter that acts as a transforming growth factor-beta, activin, and bone morphogenetic protein-inducible enhancer. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 273, 21145–1152.
Mosser, E. A., Kasanov, J. D., Forsberg, E. C., Kay, B. K., Ney, P. A., & Bresnick, E. H. (1998). Physical and functional interactions between the transactivation domain of the hematopoietic transcription factor NF-E2 and WW domains. Biochemistry, 37, 13686–3695.
Chen, X., Wen, S., Fukuda, M. N., Gavva, N. R., Hsu, D., Akama, T. O., et al. (2001). Human ITCH is a coregulator of the hematopoietic transcription factor NF-E2. Genomics, 73, 238–41.
Di Marcotullio, L., Ferretti, E., Greco, A., De Smaele, E., Screpanti, I., & Gulino, A. (2007). Multiple ubiquitin-dependent processing pathways regulate hedgehog/gli signaling: Implications for cell development and tumorigenesis. Cell Cycle, 6, 390–93.
Xu, H. M., Liao, B., Zhang, Q. J., Wang, B. B., Li, H., Zhong, X. M., et al. (2004). Wwp2, an E3 ubiquitin ligase that targets transcription factor Oct-4 for ubiquitination. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 279, 23495–3503.
Imhof, M. O., & McDonnell, D. P. (1996). Yeast RSP5 and its human homolog hRPF1 potentiate hormone-dependent activation of transcription by human progesterone and glucocorticoid receptors. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 16, 2594–605.
Maehama, T., & Dixon, J. E. (1998). The tumor suppressor, PTEN/MMAC1, dephosphorylates the lipid second messenger, phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 273, 13375–3378.
Shen, W. H., Balajee, A. S., Wang, J., Wu, H., Eng, C., Pandolfi, P. P., et al. (2007). Essential role for nuclear PTEN in maintaining chromosomal integrity. Cell, 128, 157–70.
Li, J., Yen, C., Liaw, D., Podsypanina, K., Bose, S., Wang, S. I., et al. (1997). PTEN, a putative protein tyrosine phosphatase gene mutated in human brain, breast, and prostate cancer. Science, 275, 1943–947.
Wu, W., Wang, X., Zhang, W., Reed, W., Samet, J. M., Whang, Y. E., et al. (2003). Zinc-induced PTEN protein degradation through the proteasome pathway in human airway epithelial cells. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 278, 28258–8263.
Trotman, L. C., Wang, X., Alimonti, A., Chen, Z., Teruya-Feldstein, J., Yang, H., et al. (2007). Ubiquitination regulates PTEN nuclear import and tumor suppression. Cell, 128, 141–56.
Miyazaki, K., Fujita, T., Ozaki, T., Kato, C., Kurose, Y., Sakamoto, M., et al. (2004). NEDL1, a novel ubiquitin-protein isopeptide ligase for dishevelled-1, targets mutant superoxide dismutase-1. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 279, 11327–1335.
Chang, L., Kamata, H., Solinas, G., Luo, J. L., Maeda, S., Venuprasad, K., et al. (2006). The E3 ubiquitin ligase itch couples JNK activation to TNFalpha-induced cell death by inducing c-FLIP(L) turnover. Cell, 124, 601–13.
Micheau, O., Lens, S., Gaide, O., Alevizopoulos, K., & Tschopp, J. (2001). NF-kappaB signals induce the expression of c-FLIP. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 21, 5299–305.
Perry, W. L., Hustad, C. M., Swing, D. A., O’Sullivan, T. N., Jenkins, N. A., & Copeland, N. G. (1998). The itchy locus encodes a novel ubiquitin protein ligase that is disrupted in a18H mice. Nature Genetics, 18, 143–46.
Wang, H. R., Zhang, Y., Ozdamar, B., Ogunjimi, A. A., Alexandrova, E., Thomsen, G. H., et al. (2003). Regulation of cell polarity and protrusion formation by targeting RhoA for degradation. Science, 302, 1775–779.
Ozdamar, B., Bose, R., Barrios-Rodiles, M., Wang, H. R., Zhang, Y., & Wrana, J. L. (2005). Regulation of the polarity protein Par6 by TGFbeta receptors controls epithelial cell plasticity. Science, 307, 1603–609.
Boyer, L., Turchi, L., Desnues, B., Doye, A., Ponzio, G., Mege, J. L., et al. (2006). CNF1-induced ubiquitylation and proteasome destruction of activated RhoA is impaired in Smurf1−−cells. Molecular Biology of the Cell, 17, 2489–497.
Sahai, E., Garcia-Medina, R., Pouyssegur, J., & Vial, E. (2007). Smurf1 regulates tumor cell plasticity and motility through degradation of RhoA leading to localized inhibition of contractility. Journal of Cell Biology, 176, 35–2.
Nefsky, B., & Beach, D. (1996). Pub1 acts as an E6-AP-like protein ubiquitiin ligase in the degradation of cdc25. EMBO Journal, 15, 1301–312.
Donzelli, M., & Draetta, G. F. (2003). Regulating mammalian checkpoints through Cdc25 inactivation. EMBO Reports, 4, 671–77.
Donzelli, M., Squatrito, M., Ganoth, D., Hershko, A., Pagano, M., & Draetta, G. F. (2002). Dual mode of degradation of Cdc25 A phosphatase. EMBO Journal, 21, 4875–884.
Aqeilan, R. I., Donati, V., Palamarchuk, A., Trapasso, F., Kaou, M., Pekarsky, Y., et al. (2005). WW domain-containing proteins, WWOX and YAP, compete for interaction with ErbB-4 and modulate its transcriptional function. Cancer Research, 65, 6764–772.
Yang, C., Zhou, W., Jeon, M. S., Demydenko, D., Harada, Y., Zhou, H., et al. (2006). Negative regulation of the E3 ubiquitin ligase itch via Fyn-mediated tyrosine phosphorylation. Molecular Cell, 21, 135–41.
Gallagher, E., Gao, M., Liu, Y. C., & Karin, M. (2006). Activation of the E3 ubiquitin ligase Itch through a phosphorylation-induced conformational change. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 103, 1717–722.
Snyder, P. M., Olson, D. R., Kabra, R., Zhou, R., & Steines, J. C. (2004) cAMP and serum and glucocorticoid-inducible kinase (SGK) regulate the epithelial Na(+) channel through convergent phosphorylation of Nedd4–. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 279, 45753–5758.
Bhalla, V., Daidie, D., Li, H., Pao, A. C., LaGrange, L. P., Wang, J., et al. (2005). Serum- and glucocorticoid-regulated kinase 1 regulates ubiquitin ligase neural precursor cell-expressed, developmentally down-regulated protein 4– by inducing interaction with 14-3-3. Molecular Endocrinology, 19, 3073–084.
Slagsvold, T., Marchese, A., Brech, A., & Stenmark, H. (2006). CISK attenuates degradation of the chemokine receptor CXCR4 via the ubiquitin ligase AIP4. EMBO Journal, 25, 3738–749.
Harvey, K. F., Harvey, N. L., Michael, J. M., Parasivam, G., Waterhouse, N., Alnemri, E. S., et al. (1998). Caspase-mediated cleavage of the ubiquitin-protein ligase Nedd4 during apoptosis. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 273, 13524–3530.
Flasza, M., Nguyen Huu, N. S., Mazaleyrat, S., Clemence, S., Villemant, C., Clarke, R., et al. (2006). Regulation of the nuclear localization of the human Nedd4-related WWP1 protein by Notch. Molecular Membrane Biology, 23, 269–76.
Peruzzi, F., Prisco, M., Morrione, A., Valentinis, B., & Baserga, R. (2001). Anti-apoptotic signaling of the insulin-like growth factor-I receptor through mitochondrial translocation of c-Raf and Nedd4. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 276, 25990–5996.
Hamilton, M. H., Tcherepanova, I., Huibregtse, J. M., & McDonnell, D. P. (2001). Nuclear import/export of hRPF1/Nedd4 regulates the ubiquitin-dependent degradation of its nuclear substrates. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 276, 26324–6331.
Tajima, Y., Goto, K., Yoshida, M., Shinomiya, K., Sekimoto, T., Yoneda, Y., et al. (2003). Chromosomal region maintenance 1 (CRM1)-dependent nuclear export of Smad ubiquitin regulatory factor 1 (Smurf1) is essential for negative regulation of transforming growth factor-beta signaling by Smad7. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 278, 10716–0721.
Umemura, M., Ishigami, T., Tamura, K., Sakai, M., Miyagi, Y., Nagahama, K., et al. (2006). Transcriptional diversity and expression of NEDD4L gene in distal nephron. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 339, 1129–137.
Wood, J. D., Yuan, J., Margolis, R. L., Colomer, V., Duan, K., Kushi, J., et al. (1998). Atrophin-1, the DRPLA gene product, interacts with two families of WW domain-containing proteins. Molecular and Cellular Neurosciences, 11, 149–60.
Flasza, M., Gorman, P., Roylance, R., Canfield, A. E., & Baron, M. (2002). Alternative splicing determines the domain structure of WWP1, a Nedd4 family protein. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 290, 431–37.
Qi, H., Grenier, J., Fournier, A., & Labrie, C. (2003). Androgens differentially regulate the expression of NEDD4L transcripts in LNCaP human prostate cancer cells. Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology, 210, 51–2.
Ohashi, N., Yamamoto, T., Uchida, C., Togawa, A., Fukasawa, H., Fujigaki, Y., et al. (2005) Transcriptional induction of Smurf2 ubiquitin ligase by TGF-beta. FEBS Letters, 579, 2557–563.
Judge, A. R., Koncarevic, A., Hunter, R. B., Liou, H. C., Jackman, R. W., & Kandarian, S. C. (2007). Role for IkappaBalpha, but not c-Rel, in skeletal muscle atrophy. American Journal of Physiology. Cell Physiology, 292, C372’C382.
Gu, Z., Rubin, M. A., Yang, Y., Deprimo, S. E., Zhao, H., Horvath, S., et al. (2005). Reg IV: A promising marker of hormone refractory metastatic prostate cancer. Clinical Cancer Research, 11, 2237–243.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, C., Matesic, L.E. The Nedd4-like family of E3 ubiquitin ligases and cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev 26, 587–604 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-007-9091-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-007-9091-x