Abstract
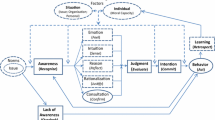
Based on evidence from press articles covering 39 corporate fraud cases that went public during the period 1992–2005, the objective of this article is to examine the role of managers’ behavior in the commitment of the fraud. This study integrates the fraud triangle (FT) and the theory of planned behavior (TPB) to gain a better understanding of fraud cases. The results of the analysis suggest that personality traits appear to be a major fraud-risk factor. The analysis was further validated through a quantitative analysis of keywords which confirmed that keywords associated with the attitudes/rationalizations component of the integrated theory were predominately found in fraud firms as opposed to a sample of control firms. The results of the study suggest that auditors should evaluate the ethics of management through the components of the TPB: the assessment of attitude, subjective norms, perceived behavioral control and moral obligation. Therefore, it is potentially important that the professional standards that are related to fraud detection strengthen the emphasis on managers’ behavior that may be associated with unethical behavior.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott, L. J., S. Parker, and G. F. Peters: 2004, ‘Audit Committee Characteristics and Restatements’, Auditing: A Journal of Practice and Theory 23(1), 69-87.
Abernethy, M. A., and E. Vagnoni: 2004, ‘Power, Organization Design and Managerial Behaviour’, Accounting, Organizations and Society 29(3-4), 207-225.
Ackerman, E. and C. Kang: 2001, ‘Silicon Valley Software Company Sinks Under Its Own Ambition’, Knight Ridder Tribune Business News, February 15.
Agrawal, A., and S. Chadha: 2005, ‘Corporate Governance and Accounting Scandals’, Journal of Law and Economics 48(2), 371-406.
Ahrens, F.: 2002, ‘History of Conflict for Ex-Rite Aid Chief; Indictment Paints Picture of Grass as an Arrogant Bully’, The Washington Post, June 22, E1.
AICPA: 1988, Statement on Auditing Standards (SAS) No. 53: The Auditor’s Responsibility to Detect and Report Errors and Irregularities (American Institute of Certified Public Accountants, Durham).
AICPA: 1997, Statement on Auditing Standards (SAS) No. 82: Consideration of Fraud in a Financial Statement Audit (American Institute of Certified Public Accountants, Durham).
AICPA: 2002, Statement on Auditing Standards (SAS) No. 99: Consideration of Fraud in a Financial Statement Audit (American Institute of Certified Public Accountants, Durham).
Ajzen, I. 1985, From intentions to actions: A theory of planned behavior. In Action-control: From cognition to behavior, Eds, Kuhl, J. and Beckmann, J., Springer, Heidelberg, 11-39.
Ajzen, I.: 1988, Attitudes, personality, and behavior (Dorsey Press, Chicago).
Ajzen, I.: 1991, ‘The theory of planned behavior’, Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes 50(2), 179-211.
Ajzen, I.: 2001, ‘Nature and operation of attitudes’, Annual Review of Psychology 52(1), 27-58.
Ajzen, I., and B. L. Driver: 1992, ‘Contingent value measurement: On the nature and meaning of willingness to pay’, Journal of Consumer Psychology 1(4), 297.
Ajzen, I., and M. Fishbein: 1974, ‘Factors influencing intentions and the intention-behavior relation’, Human Relations 27(1), 1-15.
Ajzen, I., and M. Fishbein: 1980, Understanding attitudes and predicting social behavior (Prentice-Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ).
Albrecht, W. S., C. C. Albrecht, and C. O. Albrecht: 2004, ‘Fraud and corporate executives: Agency, stewardship and broken trust’, Journal of Forensic Accounting 5, 109–130.
Albrecht, W. S., and M. B. Romney: 1986, ‘Red-flagging management fraud: A validation’, Advances in Accounting 3, 323-333.
Albrecht, W. S., M. B. Romney, D. J. Cherrington, I. R. Payne, and A. J. Roe: 1982, How to detect and prevent business fraud (Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ).
Alphonso, C.: 2000, ‘A Man of Apparent Contradictions – Software Tycoon Devoted to Charities’, The Globe and Mail, August 8, B9.
Anonymous: 2000, ‘Accept Tech as a Part of Business’, Business Times Singapore, April 24.
Anonymous: 2002. ‘Adelphia Founder Reports Health Woes’, AP Online, June 30.
Bailey, A. A.: 2006, ‘Retail employee theft: A theory of planned behavior perspective’, International Journal of Retail & Distribution Management 34(11), 802-816.
Bamberg, S., I. Ajzen, and P. Schmidt: 2003, ‘Choice of travel mode in the theory of planned behavior: The roles of past behavior, habit, and reasoned action’, Basic & Applied Social Psychology 25(3), 175.
Barboza, D: 1998, ‘He’s Dazzled Wall Street, But the Ghosts of his Company may Haunt his Future’. The New York Times, May 10, 1.
Beasley, M. S.: 1996, ‘An empirical analysis of the relation between the board of director composition and financial statement fraud’, The Accounting Review 71(4), 443-465.
Beck, L., and I. Ajzen: 1991, ‘Predicting dishonest actions using the theory of planned behavior’, Journal of Research in Personality 25(3), 285-301.
Bell, T. B., and J. V. Carcello: 2000, ‘A decision aid for assessing the likelihood of fraudulent financial reporting.’, Auditing: A Journal of Practice and Theory 19(1), 169-184.
Bergstresser, D., and T. Philippon: 2006, ‘CEO incentives and earnings management’, Journal of Financial Economics 80(3), 511-529.
Brennan, N. M., and M. McGrath: 2007, ‘Financial statement fraud: Some lessons from US and European case studies’, Australian Accounting Review 17(2), 49-61.
Carpenter, T. D., and J. L. Reimers: 2005, ‘Unethical and fraudulent financial reporting: Applying the theory of planned behavior’, Journal of Business Ethics 60(2), 115–129.
Caruso, D. B.: 2002. ‘For Years, Rigas Treated Adelphia Like a Family Business’, Associated Press Newswires, May 25.
Caster, P., D. W. Massey, and A. M. Wright: 2000, ‘Research on the nature, characteristics, and causes of accounting errors: The need for a multi-method approach’, Journal of Accounting Literature 19, 60.
Chad Terhune, C. and J. S. Lublin: 2002, ‘Unlike Others, Dollar General Issues a Mea Culpa – Amid Enron, Other Scandals, Discount Retailer Apologizes for Its Accounting Problems’, The Wall Street Journal, January 17, B1.
Cheng, Q., and T. D. Warfield: 2005, ‘Equity incentives and earnings management’, The Accounting Review 80(2), 441-476.
Choo, F., and K. Tan: 2007, ‘An “American dream” Theory of corporate executive fraud’, Accounting Forum 31(2), 203-215.
Coffee, J. C.: 2005, ‘A theory of corporate scandals: Why the USA and Europe differ’, Oxford Review of Economic Policy 21(2), 198-211.
Cohen, J. R., L. Holder-Webb, D. J. Sharp, and L. W. Pant: 2007, ‘The effects of perceived fairness on opportunistic behavior’, Contemporary Accounting Research 24(4), 1119-1138.
Cohen, J. R., G. Krishnamoorthy, and A. M. Wright: 2010, ‘Corporate governance in the post Sarbanes-Oxley era: Auditors’ experiences’, Contemporary Accounting Research 27(3), 751-786.
Cohen, J. R., and N. Martinov Bennie: 2006, ‘The applicability of a contingent factors model to accounting ethics research’, Journal of Business Ethics 68(1), 1-18.
Comer, M. J.: 1977, Corporate fraud (McGraw-Hill, London).
Cooper, C.: 2008, Extraordinary circumstances - the journey of a corporate whistleblower (John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken, New Jersey).
Cressey, D. R.: 1953, Other people’s money: A study in the social psychology of embezzlement (The Free Press, Glencoe, Illinois).
Denis, D. J., P. Hanouna, and A. Sarin: 2006, ‘Is there a dark side to incentive compensation?’, Journal of Corporate Finance 12(3), 467-488.
Doll, J., and I. Ajzen: 1992, ‘Accessibility and stability of predictors in the theory of planned behavior’, Journal of Personality & Social Psychology 63(5), 754-765.
Dyck, A., A. Morse, and L. Zingales: 2010, ‘Who blows the whistle on corporate fraud?’, Journal of Finance 65(6), 2213-2253.
Dyck, A., N. Volchkova, and L. Zingales: 2008, ‘Corporate governance role of the media: Evidence from Russia’, Journal of Finance 63(3), 1093-1135.
Efendi, J., A. Srivastava, and E. P. Swanson: 2007, ‘Why do corporate managers misstate financial statements? The role of option compensation and other factors’, Journal of Financial Economics 85(3), 667-708.
Eilifsen, A., and W. F. Messier Jr: 2000, ‘The incidence and detection of misstatements: A review and integration of archival research’, Journal of Accounting Literature 19, 1-43.
Eilifsen, A., and W. F. Messier Jr: 2006, Auditing & assurance services - international edition (McGraw-Hill, Maidenhead).
Elias, R. Z.: 2002, ‘Determinants of earnings management ethics among accountants’, Journal of Business Ethics 40, 33-45.
Erickson, M., M. Hanlon, and E. L. Maydew: 2006, ‘Is there a link between executive equity incentives and accounting fraud?’, Journal of Accounting Research 44(1), 113-143.
Farber, D. B.: 2005, ‘Restoring trust after fraud: Does corporate governance matter?’, The Accounting Review 80(2), 539-561.
Fishbein, M., and I. Ajzen: 1975, Belief, attitude, intention, and behavior: An introduction to theory and research (Addison-Wesley, Reading, MA).
Gilbert, D. T., and P. S. Malone: 1995, ‘The correspondence bias’, Psychological Bulletin 117(1), 21-38.
Gillett, P. R., and N. Uddin: 2005, ‘CFO intentions of fraudulent financial reporting’, Auditing: A Journal of Practice and Theory 24(1), 55-75.
Heiman-Hoffman, V. B., K. P. Morgan, and J. M. Patton: 1996, ‘The warning signs of fraudulent financial reporting.’, Journal of Accountancy 182(4), 75-77.
Hess, D.: 2007, ‘A business ethics perspective on Sarbanes-Oxley and the organizational sentencing guidelines’, Michigan Law Review 105(8), 1781-1816.
IFAC (International Federation of Accountants): 2005, ‘International Standard on Auditing (ISA) 240: The Auditor’s Responsibility to Consider Fraud in an Audit of Financial Statements’, Handbook of International Auditing, Assurance, and Ethics Pronouncements (IFAC, New York).
IFAC (International Federation of Accountants): 2009, ‘International Standard on Auditing (ISA) 240 Revised: The Auditor’s Responsibility to Consider Fraud in an Audit of Financial Statements’, Handbook of International Auditing, Assurance, and Ethics Pronouncements (IFAC, New York).
Jennings, M. M.: 2006a, ‘The seven signs of ethical collapse’, European Business Forum 25(Summer), 32-38.
Jennings, M. M.: 2006b, The seven signs of ethical collapse: How to spot moral meltdowns in companies… Before it’s too late (St. Martin’s Press, New York).
Johnson, J. L., A. E. Ellstrand, D. R. Dalton, and C. M. Dalton: 2005, ‘The influence of the financial press on stockholder wealth: The case of corporate governance’, Strategic Management Journal 26(5), 461-471.
Jones, T. M.: 1991, ‘Ethical decision making by individuals in organizations: An issue-contingent model’, Academy of Management Review 16(2), 366-395.
Jones, M. J., and P. A. Shoemaker: 1994, ‘Accounting narratives: A review of empirical studies of content and readability’, Journal of Accounting Literature 13(1), 142-184.
Kabanoff, B., R. Waldersee, and M. Cohen: 1995, ‘Espoused values and organizational change themes’, Academy of Management Journal 38(4), 1075-1104.
Kinney, W. R., Z.-V. Palmrose, and S. Scholz: 2004, ‘Auditor independence, non-audit services, and restatements: Was the U.S. Government right?’, Journal of Accounting Research 42(3), 561-588.
Kohlberg, L.: 1958, ‘The Development of Modes of Moral Thinking and Choice in the Years Ten to Sixteen’, Ph.D. dissertation, University of Chicago.
Kohlberg, L.: 1979, The meaning and measurement of moral development (Clark University Press, Worcester, MA).
Loebbecke, J. K., M. M. Eining, and J. J. Willingham: 1989, ‘Auditors’ experience with material irregularities: Frequency, nature and detectability’, Auditing: A Journal of Practice and Theory 9(1), 1-28.
Martin, R. D.: 2007, ‘Through the ethics looking glass: Another view of the world of auditors and ethics’, Journal of Business Ethics 70(1), 5-14.
McCarty, J. F. and R. Schneider: 1992, ‘Team Owner Accused in $350 Million Fraud Case’, The Plain Dealer Cleveland, August 05.
Miller, G. S.: 2006, ‘The press as a watchdog for accounting fraud’, Journal of Accounting Research 44(5), 1001-1033.
Nieschwietz, R. J., J. J. Schultz Jr, and M. F. Zimbelman: 2000, ‘Empirical research on external auditors’ detection of financial statement fraud’, Journal of Accounting Literature 19, 190-246.
Pincus, K. V.: 1989, ‘The efficacy of a red flags questionnaire for assessing the possibility of fraud’, Accounting, Organizations and Society 14(1-2), 153-163.
Price Waterhouse: 1985, Challenge and opportunity for the accounting profession: Strenghthening the public’s confidence (Price Waterhouse, New York).
Ramos, M.: 2003, ‘Auditors’ responsibility for fraud detection’, Journal of Accountancy 195(1), 28-36.
Rest, J.: 1979, Development in judging moral issues (University of Minnesota Press, Minneapolis, MN).
Rezaee, Z.: 2002, Financial statement fraud: Prevention and detection (J. Wiley & Sons, dfd).
Rezaee, Z.: 2005, ‘Causes, consequences, and deterence of financial statement fraud’, Critical Perspectives on Accounting 16(3), 277-298.
Sauer, R. C.: 2002, ‘Financial statement fraud: The boundaries of liability under the federal securities laws’, The Business Lawyer 57(3), 955-997.
Schneider, G.: 2003, ‘Scrushy’s Sterling Image Tarnished; Community’s Faith in HealthSouth CEO Tested’, The Washington Post, April 9, 18, E01.
Schrand, C. M. and S. L. C. Zechman: 2007, ‘Executive overconfidence and the slippery slope to fraud’, Working Paper, University of Pennsylvania.
Shafer, W. E.: 2002, ‘Effects of materiality, risk, and ethical perceptions on fraudulent reporting by financial executives’, Journal of Business Ethics 38(3), 243-262.
Smith, J.: 2002, ‘Is troubled Qwest Missing Anschutz’s Golden Touch? Ailing Stock, SEC Probe and Management Questions are Pulling Qwest’s Billionaire Founder Away from his Sports and Entertainment Empire’, Rocky Mountain News, April 27, 1C.
Soltani, B.: 2007, Auditing - an international approach (Pearson, Harlow).
Srinivasan, S.: 2005, ‘Consequences of financial reporting failure for outside directors: Evidence from accounting restatements and audit committee members’, Journal of Accounting Research 43(2), 291-334.
Stewart, C.: 1998, ‘Live by Chainsaw, die by Chainsaw’, The Australian, June 20, 1.
Sutherland, E. H.: 1949, White-collar crime (Dryden Press, New York, NY).
Tetlock, P. C.: 2007, ‘Giving content to investor sentiment: The role of media in the stock market’, Journal of Finance 62(3), 1139-1168.
Tetlock, P. C., M. Saar-Tsechansky, and S. Macskassy: 2008, ‘More than words: Quantifying language to measure firms’ fundamentals’, Journal of Finance 63(3), 1437-1467.
Thorne, L., D. W. Massey, and M. Magnan: 2003, ‘Institutional context and auditors’ moral reasoning: A Canada-U.S. Comparison’, Journal of Business Ethics 43(4), 305-321.
Tomberlin, M.: 2003, ‘Trappings of Wealth – CEO may have Wanted the Good Life a Little too Much’, The Star-Ledger, March 27, 57.
United States General Accounting Office: 2002, Financial statements restatements – trends, market impacts, regulatory responses, and remaining challenges, GAO 03-138 (United States General Accounting Office, Washington DC).
U.S. Congress: 2002, Public Company Accounting Reform and Investor Protection Act (Sarbanes-Oxley Act) (U.S. Congress).
Uzun, H., S. H. Szewczyk, and R. Varma: 2004, ‘Board composition and corporate fraud’, Financial Analysts Journal 60(3), 33-43.
Wilks, T. J., and M. F. Zimbelman: 2004, ‘Decomposition of fraud-risk assessments and auditors’ sensitivity to fraud cues’, Contemporary Accounting Research 21(3), 719-745.
Wood, A.: 1993, ‘Monus Confidant: Everyone Knew Everything’, Business Journal of the Five-County Region, August 15, 3.
Zandstra, G.: 2002, ‘Enron, board governance and moral failings’, Corporate Governance 2(2), 16-19.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cohen, J., Ding, Y., Lesage, C. et al. Corporate Fraud and Managers’ Behavior: Evidence from the Press. J Bus Ethics 95 (Suppl 2), 271–315 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-011-0857-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-011-0857-2