Abstract
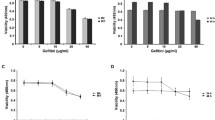
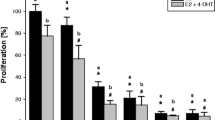
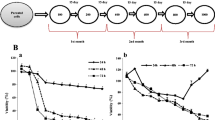
Endocrine therapy is an important therapeutic approach for the treatment of oestrogen receptor (ER)-positive breast cancer. However, a number of these endocrine therapies can fail when the tumour loses its ER expression during treatment. To date, few studies have explored the potential clinical significance of traditional Chinese medicine in inducing the reversal of resistance to endocrine therapy in breast cancers. We used the ERα-negative MCF7 breast cancer cell line to create a tamoxifen (TAM)-resistant cell line, MCF7/TAM cells. After treating MCF7/TAM cells with ELE to induce the re-expression of ERα, we investigated the role and molecular mechanisms by which elemene (ELE) promotes the reversal of resistance to endocrine therapy. We discovered that treatment with 10 μg/ml ELE restored the sensitivity of MCF7/TAM cells to TAM. RT-PCR analysis revealed that ELE treatment upregulated ERα mRNA levels in MCF7/TAM cells, and immunohistochemistry confirmed the upregulation of ERα expression. Western blot analysis revealed that ELE treatment decreased the protein expression levels of Ras, MEK1/2 and p-ERK1/2 in MCF7/TAM cells. The loss of ERα expression was the primary reason for TAM resistance in MCF7 cells. The ELE-induced reversal of TAM resistance was mediated by the upregulation of ERα mRNA and the re-expression of ERα through the MAPK pathway.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Johnston SR (1997) Acquired tamoxifen resistance in human breast cancer-potential mechanisms and clinical implications. Anticancer Drugs 8:911–930
Harvey JM, Clark GM, Osborne CK, Allred DC (1999) Estrogen receptor status by immunohistochemistry is superior to the ligand-binding assay for predicting response to adjuvant endocrine therapy in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 17:1474–1481
Ali S, Coombes RC (2002) Endocrine-responsive breast cancer and strategies for combating resistance. Nat Rev Cancer 2:101–112
Gee JM, Harper ME, Hutcheson IR, Madden TA, Barrow D, Knowlden JM, McClelland RA, Jordan N, Wakeling AE, Nicholson RI (2003) The antiepidermal growth factor receptor agent gefitinib (ZD1839/Iressa) improves antihormone response and prevents development of resistance in breast cancer in vitro. Endo Crinol 144:5105–5117
Johnston SR (2009) Enhancing the efficacy of hormonal agents with selected targeted agents. Clin Breast Cancer 9:28–36
Zhang F, Xu L, Qu X, Zhao M, Jin B, Kang J, Liu Y, Hu X (2011) Synergistic antitumor effect of β-elemene and etoposide is mediated via induction of cell apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in non-small cell lung carcinoma cells. Mol Med Report 4:1189–1193
Wang G, Li X, Huang F, Zhao J, Ding H, Cunningham C, Coad JE, Flynn DC, Reed E, Li QQ (2005) Antitumor effect of beta-elemene in non-small-cell lung cancer cells is mediated via induction of cell cycle arrest and apoptotic cell death. Cell Mol Life Sci 62:881–893
Li G, Xie B, Li X, Chen Y, Wang Q, Xu Y, Xu-Welliver M, Zou L (2012) Down-regulation of survivin and hypoxia-inducible factor-1α by β-elemene enhances the radiosensitivity of lung adenocarcinoma xenograft. Cancer Biother Radiopharm 27:56–64
Hu J, Jin W, Yang PM (2004) Reversal of resistance to adriamycin in human breast cancer cell line MCF-7/ADM by beta-elemene. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi 26:268–270
Ma HL, Zhou XJ, Liu J (2008) Experimental study on β-elemene combined with tamoxifen inhibiting the apoptosis of breast cancer cell strain MCF-7. Mod Oncol 116:510–514
Creighton CJ, Hilger AM, Murthy S, Rae JM, Chinnaiyan AM, El-Ashry D (2006) Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase in estrogen receptor alpha-positive breast cancer cells in vitro induces an in vivo molecular phenotype of estrogen receptor alpha-negative human breast tumors. Cancer Res 66:3903–3911
Oh AS, Lorant LA, Holloway JN, Miller DL, Kern FG, El-Ashry D (2001) Hyperactivation of MAPK induces loss of ERalpha expression in breast cancer cells. Mol Endocrinol 15:1344–1359
Bayliss J, Hilger A, Vishnu P, Diehl K, El-Ashry D (2007) Reversal of the estrogen receptor negative phenotype in breast cancer and restoration of antiestrogen response. Clin Cancer Res 13:7029–7036
Santen RJ, Song RX, Zhang Z, Yue W, Kumar R (2004) Adaptive hypersensitivity to estrogen: mechanism for sequential responses to hormonal therapy in breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 10:337–345
Pan GD, Yang JQ, Yan LN, Chu GP, Liu Q, Xiao Y, Yuan L (2009) Reversal of multi-drug resistance by pSUPER-shRNA-mdr1 in vivo and in vitro. World J Gastroenterol 5:431–440
Chen FP, Hsu T, Hu CH, Wang WD, Wang KC, Teng LF (2006) Expression of estrogen receptors alfa and beta mRNA and alkaline phosphatase in the differentiation of osteoblasts from elderly postmenopausal women: comparison with osteoblasts from osteosarcoma cell lines. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol 45:307–312
Fu ZY, Han JX, Zhang HY (2007) Effect s of emodin on gene expression profile in small cell lung cancer NCI-H446 cell. Chin Med J 120:1710–1715
Clark AS, West K, Streicher S, Dennis PA (2002) Constitutive and inducible Akt activity promotes resistance to chemotherapy, trastuzumab, or tamoxifen in breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther 1:707–717
Song RX, McPherson RA, Adam L, Bao Y, Shupnik M, Kumar R, Santen RJ (2002) Linkage of rap id estrogen action of MAPK activation by ERα-Shc association and Shc path-way activation. Mol Endocrinol 16:116–127
Migliaccio A, Di Domenico M, Castoria G, de Falco A, Bontempo P, Nola E, Auricchio F (1996) Tyrosine kinase/p21ras/MAP-kinase pathway activation by estradiol-receptor complex in MCF-7 cells. EMBO J 15:1292–1300
Krueger JS, Keshamouni VG, Atanaskova N, Reddy KB (2001) Temporal and quantitative regulation of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) modulates cell motility and invasion. Oncogene 20:4209–4218
Jelovac D, Sabnis G, Long BJ, Macedo L, Goloubeva OG, Brodie AM (2005) Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase in xenografts and cells during prolonged treatment with aromatase inhibitor letrozole. Cancer Res 65:5380–5389
Martin LA, Farmer I, Johnston SR, Ali S, Dowsett M (2005) Elevated ERK1/ERK2/estrogen receptor cross-talk enhances estrogen-mediated signaling during long-term estrogen deprivation. Endocr Relat Cancer 12:S75–S84
Allred DC, Mohsin SK, Fuqua SA (2001) Histological and biological evolution of human premalignant breast disease. Endocr Relat Cancer 8:47–61
Yao YQ, Xu YH, Lu J, Zhou HY, Wang YZ (2008) Effect of p38 MAPK on elemene-induced cell cycle arrest in C6 glioblastoma cells. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 88:56–58
Li L, Xu L, Qu X, Zhao M, Yu P, Kang J, Liu Y, Hu X (2011) Cbl-regulated Akt and ERK signals are involved in β-elemene-induced cell apoptosis in lung cancer cells. Mol Med Report 4:1243–1246
Gruvberger-Saal SK, Bendahl PO, Saal LH, Laakso M, Hegardt C, Edén P, Peterson C, Malmström P, Isola J, Borg A, Fernö M (2007) Estrogen receptor beta expression is associated with tamoxifen response in ERalpha-negative breast carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 13:1987–1994
Paech K, Webb P, Kuiper GG, Nilsson S, Gustafsson J, Kushner PJ, Scanlan TS (1997) Differential ligand activation of estrogen receptors ERalpha and ERbeta at AP1 sites. Science 277:1508–1510
Hodges LC, Cook JD, Lobenhofer EK, Li L, Bennett L, Bushel PR, Aldaz CM, Afshari CA, Walker CL (2003) Tamoxifen functions as a molecular agonist inducing cell cycle-associated genes in breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer Res 1:300–311
Ström A, Hartman J, Foster JS, Kietz S, Wimalasena J, Gustafsson JA (2004) Estrogen receptor β inhibits 17beta-estradiol-stimulated proliferation of the breast cancer cell line T47D. Proc Natl Acad Sci 101:1566–1571
Borgquist S, Holm C, Stendahl M, Anagnostaki L, Landberg G, Jirström K (2008) Oestrogen receptors alpha and beta show different associations to clinicopathological parameters and their co-expression might predict a better response to endocrine treatment in breast cancer. J Clin Pathol 61:197–203
Hopp TA, Weiss HL, Parra IS, Cui Y, Osborne CK, Fuqua SA (2004) Low levels of estrogen receptor beta protein predict resistance to tamoxifen therapy in breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 10:7490–7499
Iwao K, Miyoshi Y, Egawa C, Ikeda N, Tsukamoto F, Noguchi S (2000) Quantitative analysis of estrogen receptor-alpha and -beta messenger RNA expression in breast carcinoma by real-time polymerase chain reaction. Cancer 89:1732–1738
Lapidus RG, Nass SJ, Butash KA, Parl FF, Weitzman SA, Graff JG, Herman JG, Davidson NE (1998) Mapping of ER gene CpG island methylation-specific polymerase chain reaction. Cancer Res 58(12):2515–2519
Ottaviano YL, Issa JP, Parl FF, Smith HS, Baylin SB, Davidson NE (1994) Methylation of the estrogen receptor gene CpG island marks loss of estrogen receptor expression in human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 54:2552–2555
Zhao L, Wang L, Jin F, Ma W, Ren J, Wen X, He M, Sun M, Tang H, Wei M (2009) Silencing of estrogen receptor alpha(ERalpha) gene by promoter hypermethylation is a frequent event in Chinese women with sporadic breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 117:253–259
Kawai H, Li H, Avraham S, Jiang S, Avraham HK (2003) Overexpression of histone deacetylase HDAC1 modulates breast cancer progression by negative regulation of estrogen receptor alpha. Int J Cancer 107:353–358
Fan J, Yin WJ, Lu JS, Wang L, Wu J, Wu FY, Di GH, Shen ZZ, Shao ZM (2008) ER alpha negative breast cancer cells restore response to endocrine therapy by combination treatment with both HDAC inhibitor and DNMT inhibitor. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 134:883–890
El-Osta A, Wolffe AP (2000) DNA methylation and histone deacetylation in the control of gene expression: basic biochemistry to human development and disease. Gene Expr 9:63–75
Fuks F, Hurd PJ, Wolf D, Nan X, Bird AP, Kouzarides T (2003) The methyl-CpG-binding protein MeCP2 links DNA methylation to histone methylation. J Biol Chem 278:4035–4040
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Chaohui Wang, Ling Li and Yan Wang from the Central Laboratory of the Second Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University for providing technical consultation for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Zhang Bin and Zhang Xia contributed equally to this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, B., Zhang, X., Tang, B. et al. Investigation of elemene-induced reversal of tamoxifen resistance in MCF-7 cells through oestrogen receptor α (ERα) re-expression. Breast Cancer Res Treat 136, 399–406 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-012-2263-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-012-2263-6