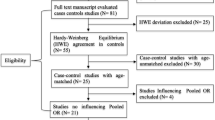
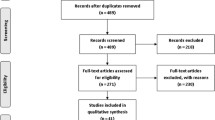
Abstract
p53 is a tumor suppressor gene and plays an important role in the etiology of breast cancer. However, studies on the association between p53 polymorphisms and breast cancer risk have yielded conflicting results. We performed a meta-analysis to investigate the association between breast cancer and the p53 polymorphisms codon 72 (27,046 cases and 30,998 controls), IVS3 16 bp (3,332 cases and 3,700 controls) and IVS6+62A>G (8,787 cases and 9,869 controls) in different inheritance models. When all the eligible studies of codon 72 polymorphism were pooled into this meta-analysis, there was no evidence of significant association between breast cancer risk and p53 codon 72 polymorphism in any genetic model. However, in the stratified analysis for Indian population, significantly association was observed in additive model (OR = 0.62, 95% CI = 0.46–0.82, P value of heterogeneity test [P h] = 0.153) and recessive model (OR = 0.70, 95% CI = 0.50–0.92, P h = 0.463). IVS3 16 bp was significantly associated with breast cancer risk in a pooled 15 studies dataset (dominant model: OR = 1.14, 95% CI = 1.02–1.27, P h = 0.30; recessive model: OR = 1.61, 95% CI = 1.21–2.25, P h = 0.25; additive model: OR = 1.66, 95% CI = 1.24–2.21, P h = 0.28). No significant association was found between IVS6+62A>G polymorphism and breast cancer risk in a total of 14 studies. In summary, these results indicate that IVS3 16 bp is likely an important genetic marker contributing to susceptibility of breast cancer, and codon 72 homozygous mutants may be associated with decreased breast cancer risk in Indian population.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berns EM, van Staveren IL, Look MP, Smid M, Klijn JGM, Foekens JA (1998) Mutations in residues of TP53 that directly contact DNA predict poor outcome in human primary breast cancer. Br J Cancer 77:1130–1136
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J et al (2001) Estimating the world cancer burden: Globocan 2000. Int J Cancer 94:153–156
Veronesi U, Boyle P, Golsdhirsch A, Orecchia R, Viale G (2005) Breast cancer. Lancet 365:1727–1741
Yager JD, Davidson NE (2006) Mechanism of disease: estrogen carcinogenesis in breast cancer. N Engl J Med 354:270–282
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2000) The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 100:57–70
Dumitrescu RG, Cotarla I (2005) Understanding breast cancer risk—where do we stand in 2005? J Cell Mol Med 9:208–221
Hollstein M, Sidransky D, Vogelstein B et al (1991) p53 mutations in human cancers. Science 253:49–53
Oren M (2003) Decision making by p53: life, death and cancer. Cell Death 10:431–442
Denehower LA (2005) p53 guardian and suppressor of longevity? Exp Gerontol 40:7–9
Dumont P, Leu JI, Della Pietra ACIII et al (2003) The codon 72 polymorphic variants of p53 have markedly different apoptotic potential. Nat Genet 33:357–365
Zhang Z, Wang M, Wu D, Wang M, Tong N, Tian Y, Zhang Z (2010) P53 codon 72 polymorphism contributes to breast cancer risk: a meta-analysis based on 39 case–control studies. Breast Cancer Res Treat 120(2):509–517
Hu Z, Li X, Yuan R, Ring BZ, Su L (2010) Three common TP53 polymorphisms in susceptibility to breast cancer, evidence from meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Res Treat 120(3):705–714
Ma Y, Yang J, Liu Z, Zhang P, Yang Z, Wang Y, Qin H (2011) No significant association between the TP53 codon 72 polymorphism and breast cancer risk: a meta-analysis of 21 studies involving 24,063 subjects. Breast Cancer Res Treat 125(1):201–205
Francisco G, Menezes PR, Eluf-Neto J, Chammas R (2010) Arg72Pro TP53 polymorphism and cancer susceptibility: a comprehensive meta-analysis of 302 case-control studies. Int J Cancer. doi:10.1002/ijc.25710
Kawajiri K, Nakachi K, Imai K, Watanabe J, Hayashi S (1993) Germ line polymorphisms of p53 and CYP1A1 genes involved in human lung cancer. Carcinogenesis 14:1085–1089
Sjalander A, Birgander R, Hallmans G, Cajander S, Lenner P, Athlin L, Beckman G, Beckman L (1996) p53 polymorphisms and haplotypes in breast cancer. Carcinogenesis 17:1313–1316
Weston A, Pan CF, Ksieski HB, Wallenstein S, Berkowitz GS, Tartter PI, Bleiweiss IJ, Brower ST, Senie RT, Wolff MS (1997) p53 haplotype determination in breast cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 6:105–112
Helland A, Langerod A, Johnsen H, Olsen AO, Skovlund E, Borresen-Dale AL (1998) p53 polymorphism and risk of cervical cancer. Nature 396:530–531
Wang-Gohrke S, Rebbeck TR, Besenfelder W et al (1998) p53 germline polymorphisms are associated with an increased risk for breast cancer in German women. Anticancer Res 18:2095–2099
Khaliq S, Hameed A, Khaliq T et al (2000) P53 mutations, polymorphisms, and haplotypes in Pakistani ethnic groups and breast cancer patients. Genet Test 4:23–29
Papadakis EN, Dokianakis DN, Spandidos DA (2000) p53 codon 72 polymorphism as a risk factor in the development of breast cancer. Mol Cell Biol Res Commun 3:389–392
Li T, Lu ZM, Guo M, Wu QJ, Chen KN, Xing HP, Mei Q, Ke Y (2002) p53 codon 72 polymorphism (C/G) and the risk of human papillomavirus-associated carcinomas in China. Cancer 95:2571–2576
Wang-Gohrke S, Becher H, Kreienberg R, Runnebaum IB, Chang-Claude J (2003) Intron 3 16 bp duplication polymorphism of p53 is associated with an increased risk for breast cancer by the age of 50 years. Pharmacogenetics 12:269–272
Buyru N, Tigli H, Dalay N (2003) P53 codon 72 polymorphism in breast cancer. Oncol Rep 10:711–714
Mabrouk I, Baccouche S, El-Abed R, Mokdad-Gargouri R, Mosbah A, Saïd S, Daoud J, Frikha M, Jlidi R, Gargouri A (2003) No evidence of correlation between p53 codon 72 polymorphism and risk of bladder or breast carcinoma in Tunisian patients. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1010:764–770
Huang XE, Hamajima N, Katsuda N, Matsuo K, Hirose K, Mizutani M, Iwata H, Miura S, Xiang J, Tokudome S, Tajima K (2003) Association of p53 codon Arg72Pro and p73 G4C14-to-A4T14 at exon 2 genetic polymorphisms with the risk of Japanese breast cancer. Breast Cancer 10:307–311
Katiyar S, Thelma BK, Murthy NS, Hedau S, Jain N, Gopalkrishna V, Husain SA, Das BC (2003) Polymorphism of the p53 codon 72 Arg/Pro and the risk of HPV type 16/18-associated cervical and oral cancer in India. Mol Cell Biochem 252:117–124
Suspitsin EN, Buslov KG, Grigoriev MY, Ishutkina JG, Ulibina JM, Gorodinskaya VM, Pozharisski KM, Berstein LM, Hanson KP, Togo AV, Imyanitov EN (2003) Evidence against involvement of P53 polymorphism in breast cancer predisposition. Int J Cancer 103:431–433
Menzel HJ, Sarmanova J, Soucek P, Berberich R, Gru¨newald K, Haun M, Kraft HG (2004) Association of NQO1 polymorphism with spontaneous breast cancer in two independent populations. Br J Cancer 90:1989–1994
Noma C, Miyoshi Y, Taguchi T, Tamaki Y, Noguchi S (2004) Association of p53 genetic polymorphism (Arg72Pro) with estrogen receptor positive breast cancer risk in Japanese women. Cancer Lett 210:197–203
Mahasneh AA, Abdel-Hafiz SS (2004) Polymorphism of p53 gene in Jordanian population and possible associations with breast cancer and lung adenocarcinoma. Saudi Med J 25:1568–1573
Tommiska J, Eerola H, Heinonen M, Salonen L, Kaare M, Tallila J, Ristimäki A, von Smitten K, Aittomäki K, Heikkilä P, Blomqvist C, Nevanlinna H (2005) Breast cancer patients with p53 Pro72 homozygous genotype have a poorer survival. Clin Cancer Res 11:5098–5103
Kalemi TG, Lambropoulos AF, Gueorguiev M, Chrisafi S, Papazisis KT, Kotsis A (2005) The association of p53 mutations and p53 codon 72, Her 2 codon 655 and MTHFR C677T polymorphisms with breast cancer in Northern Greece. Cancer Lett 222:57–65
Siddique MM, Balram C, Fiszer-Maliszewska L, Aggarwal A, Tan A, Tan P, Soo KC, Sabapathy K (2005) Evidence for selective expression of the p53 codon 72 polymorphs: implications in cancer development. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 14:2245–2252
Ohayon T, Gershoni-Baruch R, Papa MZ, Distelman Menachem T, Eisenberg Barzilai S, Friedman E (2005) The R72P P53 mutation is associated with familial breast cancer in Jewish women. Br J Cancer 92:1144–1148
Damin AP, Frazzon AP, Damin DC, Roehe A, Hermes V, Zettler C, Alexandre CO (2006) Evidence for an association of TP53 codon 72 polymorphism with breast cancer risk. Cancer Detect Prev 30:523–529
Ma H, Hu Z, Zhai X, Wang S, Wang X, Qin J, Chen W, Jin G, Liu J, Gao J, Wang X, Wei Q, Shen H (2006) Joint effects of single nucleotide polymorphisms in P53BP1 and p53 on breast cancer risk in a Chinese population. Carcinogenesis 27:766–771
Baynes C, Healey CS, Pooley KA, Scollen S, Luben RN, Thompson DJ, Pharoah PD, Easton DF, Ponder BA, Dunning AM (2007) SEARCH breast cancer study: common variants in the ATM, BRCA1, BRCA2, CHEK2 and TP53 cancer susceptibility genes are unlikely to increase breast cancer risk. Breast Cancer Res 9(2):R27
Gochhait S, Bukhari SI, Bairwa N, Vadhera S, Darvishi K, Raish M, Gupta P, Husain SA, Bamezai RN (2007) Implication of BRCA2–26G>A 5′ untranslated region polymorphism in susceptibility to sporadic breast cancer and its modulation by p53 codon 72 Arg>Pro polymorphism. Breast Cancer Res 9:R71
Khadang B, Fattahi MJ, Talei A, Dehaghani AS, Ghaderi A (2007) Polymorphism of TP53 codon 72 showed no association with breast cancer in Iranian women. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 173:38–42
Schmidt MK, Reincke S, Broeks A, Braaf LM, Hogervorst FB, Tollenaar RA, Johnson N, Fletcher O, Peto J, Tommiska J, Blomqvist C, Nevanlinna HA, Healey CS, Dunning AM, Pharoah PD, Easton DF, Dörk T, Van’t Veer LJ (2007) Breast cancer association consortium: do MDM2 SNP309 and TP53 R72P interact in breast cancer susceptibility? A large pooled series from the breast cancer association consortium. Cancer Res 67:9584–9590
Sprague BL, Trentham-Dietz A, Garcia-Closas M, Newcomb PA, Titus-Ernstoff L, Hampton JM, Chanock SJ, Haines JL, Egan KM (2007) Genetic variation in TP53 and risk of breast cancer in a population-based case control study. Carcinogenesis 28:1680–1686
Zhang W, Jin MJ, Chen K (2007) Association of p53 polymorphisms and its haplotypes with susceptibility of breast cancer. Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban 36:561–566
Rajkumar T, Samson M, Rama R, Sridevi V, Mahji U, Swaminathan R, Nancy N (2008) TGFb1 (Leu10Pro), p53 (Arg72Pro) can predict for increased risk for breast cancer in south Indian women and TGFb1 Pro (Leu10Pro) allele predicts response to neo-adjuvant chemo-radiotherapy. Breast Cancer Res Treat 112:81–87
Cox DG, Deer D, Guo Q, Tworoger SS, Hankinson SE, Hunter DJ, De Vivo I (2007) The p53 Arg72Pro and MDM2-309 polymorphisms and risk of breast cancer in the nurses’ health studies. Cancer Causes Control 18:621–625
Gaudet MM, Gammon MD, Bensen JT, Sagiv SK, Shantakumar S, Teitelbaum SL, Eng SM, Neugut AI, Santella RM (2008) Genetic variation of TP53, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbonrelated exposures, and breast cancer risk among women on Long Island, New York. Breast Cancer Res Treat 108:93–99
Garcia-Closas M, Kristensen V, Langerod A, Qi Y, Yeager M, Burdett L, Welch R, Lissowska J, Peplonska B, Brinton L, Gerhard DS, Gram IT, Perou CM, Borresen-Dale AL, Chanock S (2007) Common genetic variation in TP53 and its flanking genes, WDR79 and ATP1B2, and susceptibility to breast cancer. Int J Cancer 121:2532–2538
Johnson N, Fletcher O, Palles C, Rudd M, Webb E, Sellick G, dos Santos Silva I, McCormack V, Gibson L, Fraser A, Leonard A, Gilham C, Tavtigian SV, Ashworth A, Houlston R, Peto J (2007) Counting potentially functional variants in BRCA1, BRCA2 and ATM predicts breast cancer susceptibility. Hum Mol Genet 16:1051–1057
Franeková M, Zúbor P, Stanclová A, Dussan CA, Bohusová T, Galo S, Dobrota D, Kajo K, Péc M, Racay P (2007) Association of p53 polymorphisms with breast cancer: a case–control study in Slovak population. Neoplasma 54:155–161
Pharoah PD, Tyrer J, Dunning AM, Easton DF, Ponder BA, SEARCH Investigators (2007) Association between common variation in 120 candidate genes and breast cancer risk. PloS Genet 3:e42
Samson M, Swaminathan R, Rama R, Sridevi V, Nancy KN, Rajkumar T (2007) Role of GSTM1 (Null/Present), GSTP1 (Ile105Val) and P53 (Arg72Pro) genetic polymorphisms and the risk of breast cancer: a case control study from South India. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 8:253–257
Akkiprik M, Sonmez O, Gulluoglu BM, Caglar HB, Kaya H, Demirkalem P, Abacioglu U, Sengoz M, Sav A, Ozer A (2009) Analysis of p53 gene polymorphisms and protein over-expression in patients with breast cancer. Pathol Oncol Res 15:359–368
Singh V, Rastogi N, Mathur N, Singh K, Singh MP (2008) Association of polymorphism in MDM-2 and p53 genes with breast cancer risk in Indian women. Ann Epidemiol 18:48–57
Lum SS, Chua HW, Li H, Li WF, Rao N, Wei J, Shao Z, Sabapathy K (2008) MDM2 SNP309 G allele increases risk but the Tallele is associated with earlier onset age of sporadic breast cancers in the Chinese population. Carcinogenesis 29:754–761
Cavallone L, Arcand SL, Maugard C, Ghadirian P, Mes-Masson AM, Provencher D, Tonin PN (2008) Haplotype analysis of TP53 polymorphisms, Arg72Pro and Ins16, in BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutation carriers of French Canadian descent. BMC Cancer 8:96
Costa S, Pinto D, Pereira D, Rodrigues H, Cameselle-Teijeiro J, Medeiros R, Schmitt F (2008) Importance of TP53 codon 72 and intron 3 duplication 16 bp polymorphisms in prediction of susceptibility on breast cancer. BMC Cancer 8:32
De Vecchi G, Verderio P, Pizzamiglio S, Manoukian S, Bernard L, Pensotti V, Volorio S, Ravagnani F, Radice P, Peterlongo P (2008) The p53 Arg72Pro and Ins16 bp polymorphisms and their haplotypes are not associated with breast cancer risk in BRCA-mutation negative familial cases. Cancer Detect Prev 32:140–143
Nordgard SH, Alnaes GI, Hihn B et al (2008) Pathway based analysis of SNPs with relevance to 5-FU therapy: relation to intratumoral mRNA expression and survival. Int J Cancer 123:577–585
Henrırquez-Hernandez LA, Murias-Rosales A, Herna′ndez GA, Cabrera DLA, Dı′az-Chico BN, Mori DSM, Ferna′ndez PL (2009) Gene polymorphisms in TYMS, MTHFR, p53 and MDR1 as risk factors for breast cancer: a case–control study. Oncol Rep 22:1425–1433
Kazemi M, Salehi Z, Chakosari RJ (2009) TP53 codon 72 polymorphism and breast cancer in northern Iran. Oncol Res 18(1):25–30
Denisov EV, Cherdyntseva NV, Litvyakov NV, Slonimskaya EM (2009) TP53 mutations and Arg72Pro polymorphism in breast cancers. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 192:93–95
Aoki MN, da Silva AHAC, Amarante MK, do Val Carneiro JL, Fungaro MH, Watanabe MA (2009) CCR5 and p53 codon 72 gene polymorphisms: implications in breast cancer development. Int J Mol Med 23:429–435
Song F, Zheng H, Liu B, Wei S, Dai H, Zhang L, Calin GA, Hao X, Wei Q, Zhang W, Chen K (2009) An miR-502-binding site single-nucleotide polymorphism in the 3′-untranslated region of the SET8 gene is associated with early age of breast cancer onset. Clin Cancer Res 15(19):6292–6300
Lång A, Palmebäck Wegman P, Wingren S (2009) The significance of MDM2 SNP309 and p53 Arg72Pro in young women with breast cancer. Oncol Rep 22:575–579
Hrstka R, Beranek M, Klocova K, Nenutil R, Vojtesek B (2009) Intronic polymorphisms in TP53 indicate lymph node metastasis in breast cancer. Oncol Rep 22:1205–1211
Kara N, Karakus N, Ulusoy AN, Ozaslan C, Gungor B, Bagci H (2010) P53 codon 72 and HER2 codon 655 polymorphisms in Turkish breast cancer patients. DNA Cell Biol 29:7
Ebner F, Schremmer-Danninger E, Rehbock J (2010) The role of TP53 and p21 gene polymorphisms in breast cancer biology in a well specified and characterized German cohort. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 136:1369–1375
Bisof V, Salihović MP, Narancić NS, Skarić-Jurić T, Jakić-Razumović J, Janićijević B, Turek S, Rudan P (2010) TP53 gene polymorphisms and breast cancer in Croatian women: a pilot study. Eur J Gynaecol Oncol 31(5):539–544
Mantel N, Haenszel W (1959) Statistical aspects of the analysis of data from retrospective studies of disease. J Natl Cancer Inst 22:719–748
DerSimonian R, Laird N (1986) Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials 7:177–188
Thompson SG, Higgins JPT (2002) How meta-regression analyses be undertaken and ihterpreted? Statist Med 21:1559–1573
Begg CB, Mazumdar M (1994) Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias. Biometrics 50(4):1088–1101
Egger M, Smith DG, Schneider M (1997) Minder C Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 315:629–634
Buyru N, Altinisik J, Demokan S, Dalay N (2007) p53 genotypes 153 and haplotypes associated with risk of breast cancer. Cancer Detect Prev 31:207–213
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, XF., Su, J., Zhang, Y. et al. Association between the p53 polymorphisms and breast cancer risk: meta-analysis based on case–control study. Breast Cancer Res Treat 130, 517–529 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-011-1583-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-011-1583-2