Summary
Alterations in the mechanisms of apoptosis are responsible not only for the progression of breast cancer, but for different responses to treatment as well. Among the genes regulators of apoptosis, the tumor suppressor gene p53 and the bcl-2 gene have raised interest for their possible role as predictors of response to therapy and markers of prognosis. The purpose of our study was to prospectively analyze the prognostic value of the expression of p53 and bcl-2 genes in a series of 235 consecutive patients operated on for breast cancer at the Department of General Surgery and Surgical Oncology of the University of Siena, Italy.
p53 and bcl-2 expression were evaluated by immunohistochemistry, their association with conventional clinicopathological factors was analyzed by univariate analysis and their prognostic impact was evaluated by multivariate analysis.
p53 and bcl-2 were detected respectively in 15.7 and 75.7% of cases, and resulted significantly related to presence of estrogen receptors for p53 over-expression and presence of peritumor lymphovascular invasion (LVI) for bcl-2 expression.
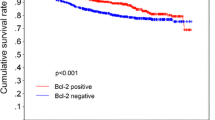
With a median follow-up of 79 months, an independent negative prognostic impact on disease free and overall survival was observed for presence of LVI, absence of bcl-2 expression and number of involved axillary lymphnodes. The expression of bcl-2 improved the prognosis of LVI positive tumors up to values similar to LVI negative cases, while its absence associated to presence of LVI resulted in a poor outcome with only 28% of patients alive at 8 years.
These data may indicate that expression of bcl-2 is a marker of breast cancers with reduced capability of distant colonization, even in presence of LVI, and may be particularly useful in the clinical setting, allowing to identify a subset of patients with an high risk of relapse.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cianfrocca M, Goldstein LJ:Prognostic and predictive factors in early breast cancer. Oncologist9:606–616, 2004
Frassoldati A, Maur M, Guarneri V, Nicolini M, Conte PF:Predictive value of biologic parameters for primary chemotherapy in operable breast cancer. Clin Breast Cancer6:315–324, 2005
Meterissian SH:Apoptosis: its role in the progression of and chemotherapy for carcinoma. J Am Coll Surg184:658–666, 1997
Krajewski S, Krajewska M, Turner BC, Pratt C, Howard B, Zapata JM, Frenkel V, Robertson S, Ionov Y, Yamamoto H, Perucho M, Takayama S, Reed JC:Prognostic significance of apoptosis regulators in breast cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer6:29–40, 1999
Miller LD, Smeds J, George J, Vega VB, Vergara L, Ploner A, Pawitan Y, Hall P, Klaar S, ET Liu, Bergh J:An expression signature for p53 status in human breast cancer predicts mutation status, transcriptional effects, and patient survival. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA102:13,550–13,555, 2005
Silvestrini R, Daidone MG, Benini E, Faranda A, Tomasic G, Boracchi P, Salvatori B, Veronesi U:Validation of p53 accumulation as a predictor of distant metastases at 10 years of follow-up in 1400 node negative breast cancers. Clin Cancer Res2:2007–2013, 1996
Elledge RM, Allred DC:Prognostic and predictive value of p53 and p21 in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat52:79–98, 1998
Pharoah PD, Day NE, Caldas C:Somatic mutations in the p53 gene and prognosis in breast cancer: a meta-analysis. Brit J Cancer80:1968–1973, 1999
Yamashita H, Nishio M, Toyama T, Sugiura H, Zhang Z, Kobayashi S, Iwase H:Coexistence of HER2 over-expression and p53 protein accumulation is a strong prognostic molecular marker in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res6:24–30, 2004
Korsmeyer SJ:Bcl-2 initiates a new category of oncogenes: regulators of cell death. Blood80: 879–886, 1992
Hockenbery DM, Zutter M, Hickey W, Nahm M, Korsmeyer SJ:BCL2 protein is topographically restricted in tissues characterized by apoptotic cell death. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA88: 6961–6965, 1991
Silvestrini R, Veneronis S, Daidone MG, Benini E, Boracchi P, Mezzetti M, Di Fronzo G, Rilke F, Veronesi U:The bcl-2 protein: a prognostic indicator strongly related to p53 protein in lymph node-negative breast cancer patients. J Natl Cancer Inst86:499, 1994
Berardo MD, Elledge RM, de Moor C, Clark GM, Osborne CK, Allred DC:Bcl-2 and apoptosis in lymphnode positive breast carcinoma. Cancer82:1296–1302, 1998
Barbareschi M, Caffo O, Veronese E, Leek RD, Fina P, Fox S, Bolzanini M, Girlando S, Morelli L, Eccher C, Pezzella F, Doglioni C, Della Palma C, Harris A:Bcl-2 and p53 expression in node-negative breast carcinoma: a study with long-term follow-up. Hum Pathol27:1149–1155, 1996
Linjawi A, Kontogiannea M, Halwani F, Edwardes M, Meterissian S:Prognostic significance of p53, bcl-2, and Bax expression in early breast cancer. J Am Coll Surg198:83–90, 2004
Takayama S, Sato T, Krajewski S, Kochel K, Irie S, Millan JA, Reed JC:Cloning and functional analysis of BAG-1: a novel bcl-2 binding protein with anti-cell death activity. Cell80: 2279–2284, 1995
Oltvai ZN, Milliman CL, Korsmeyer SJ:Bcl-2 heterodimerizes in vivo with a conserved homolog, Bax, that accelerates programmed cell death. Cell74: 609–619, 1993
Yang E, Zha J, Jockel J, Boise LH, Thompson CB, Korsmeyer SJ:Bad, a heterodimeric partner for bcl-xL and bcl-2, displaces Bax and promotes cell death. Cell 80: 285–291,1995
Sobin LH, Wittekind C: TNM classification of malignant tumors. 6th edn. John Wiley & Sons (ed), New York, 2002
Elston CW, Ellis IO:Pathological prognostic factors in breast cancer. I. The value of histological grade in breast cancer: experience from a large study with long-term follow-up. Histopathology19: 403–410, 1991
Ellis PA, Smith IE, Detre S, Burton SA, Salter J, A’Hern R, Walsh G, Johnston SR, Dowsett M:Reduced apoptosis and proliferation and increased bcl-2 in residual breast cancer following preoperative chemotherapy. Breast Cancer Res Treat48:107–116, 1998
Norberg T, Jansson T, Sjogren S, Martensson C, Andreasson I, Fjallskog ML, Lindman H, Nordgren H, Lindgren A, Holmberg L, Bergh J:Overview on human breast cancer with focus on prognostic and predictive factors with special attention on the tumor suppressor gene p53. Acta Oncol35:96–102, 1996
Jager JJ, Janse LH, Arends JW:Clinical relevance of apoptotic markers in breast cancer not yet clear. Apoptosis7:361–365, 2002
Rozan S, Vincent-Salomon A, Zafrani B, Validire P, De Cremoux P, Bernoux A, Nieruchalski M, Fourquet A, Clough K, Dieras V, Pouillart P, Sastre-Garau X:No significant predictive value of c-erbB-2 or p53 expression regarding sensitivity to primary chemotherapy or radiotherapy in breast cancer. Int J Cancer79:27–33, 1998
Archer SG, Eliopoulos A, Spandidos D, Barnes D, Ellis IO, Blamey RW, Nicholson RI, Robertson JF:Expression of ras p21, p53 and c-erbB-2 in advanced breast cancer and response to first line hormonal therapy. Br J Cancer72:1259–1266 1995
Korkolis DP, Tsoli E, Fouskakis D, Yiotis J, Koullias GJ, Giannopoulos D, Papalambros E, Nikiteas NI, Patsouris E, Asimacopoulos P, Gorgoulis VG:Tumor histology and stage but not p53, Her2-neu or cathepsin-D expression are independent prognostic factors in breast cancer patients. Anticancer Res24:2061–2068, 2004
Hartmann A, Blaszyk H, McGovern RM, Schroeder JJ, Cunningham J, De Vries EM, Kovach JS, Sommer SS:p53 gene mutations inside and outside of exons 5–8: the pattern differs in breast and other cancers. Oncogene10:681–688, 1995
Bull SB, Ozcelik H, Pinnaduwage D, Blackstein ME, Sutherland DA, Pritchard KI, Tzontcheva AT, Sidlofsky S, Hanna WM, Qizilbash AH, Tweeddale ME, Fine S, Mc Ready DR, Andrulis IR:The combination of p53 mutation and neu/erbB-2 amplification is associated with poor survival in node-negative breast cancer. J Clin Oncol22:86–96, 2004
Kymionis GD, Dimitrikakis CE, Konstadoulakis MM, Arzimanoglou I, Leandros E, Chalkiadakis G, Keramopoulos A, Michalas S:Can expression of apoptosis genes, bcl-2 and bax, predict survival and responsiveness to chemotherapy in node negative breast cancer patients?. J Surg Res99:161–168, 2001
Yang Q, Sakurai T, Yoshimura G, Suzuma T, Umemura T, Nakamura M, Mori I, Kaduko K:Prognostic value of bcl-2 in invasive breast cancer receiving chemotherapy and endocrine therapy. Oncol Rep10:121–125, 2003
Knowlton K, Mancini M, Creason S, Morales C, Hockenbery D, Anderson BO:Bcl-2 slows in vitro breast cancer growth despite its anti-apoptotis effect. J Surg Res81:387–392, 1998
Woo CS, Silberman H, Nakamura SK, Ye W, Sposto R, Colburn W, Waisman JR, Silverstein MJ:Lymph node status combined with lymphovascular invasion creates a more powerful tool for predicting outcome in patients with invasive breast cancer. Am J Surg184:337–340, 2002
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Neri, A., Marrelli, D., Roviello, F. et al. Bcl-2 expression correlates with lymphovascular invasion and long-term prognosis in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 99, 77–83 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-006-9183-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-006-9183-2