Abstract
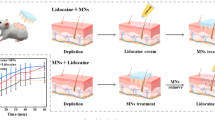
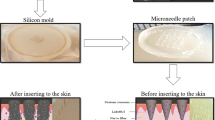
There is an urgent need for research into effective interventions for pain management to improve patients’ life quality. Traditional needle and syringe injection were used to administer the local anesthesia. However, it causes various discomforts, ranging from brief stings to trypanophobia and denial of medical operations. In this study, a dissolving microneedles (MNs) system made of composite matrix materials of polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP), polyvinyl alcohol (PVA), and sodium hyaluronate (HA) was successfully developed for the loading of lidocaine hydrochloride (LidH). The morphology, size and mechanical properties of the MNs were also investigated. After the insertion of MNs into the skin, the matrix at the tip of the MNs was swelled and dissolved by absorption of interstitial fluid, leading to a rapid release of loaded LidH from MNs’ tips. And the LidH in the back patching was diffused into deeper skin tissue through microchannels created by MNs insertion, forming a prolonged anesthesia effect. In addition, the back patching of MNs could be acted as a drug reservoir to form a prolonged local anesthesia effect. The results showed that LidH MNs provided a superior analgesia up to 8 h, exhibiting a rapid and long-lasting analgesic effects. Additionally, tissue sectioning and in vitro cytotoxicity tests indicated that the MNs patch we developed had a favorable biosafety profile.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data cannot be made publicly available upon publication because no suitable repository exists for hosting data in this field of study. The data that support the findings of this study are available upon reasonable request from the author.
References
S. Abdelghany, I.A. Tekko, L. Vora, E. Larraneta, A.D. Permana, R.F. Donnelly, Nanosuspension-based dissolving microneedle arrays for intradermal delivery of curcumin. Pharmaceutics. 11(7), 308 (2019)
H. Amani, M.A. Shahbazi, C. D’Amico, F. Fontana, S. Abbaszadeh, H.A. Santos, Microneedles for painless transdermal immunotherapeutic applications. J. Control Release. 330, 185–217 (2021)
S.H. Baek, J.H. Shin, Y.C. Kim, Drug-coated microneedles for rapid and painless local anesthesia. Biomed. Microdevices. 19(1), 2 (2017)
A.I. Basbaum, D.M. Bautista, G. Scherrer, D. Julius, Cellular and molecular mechanisms of pain. Cell 139, 267–284 (2009)
E. Caffarel-Salvador, S. Kim, V. Soares, R.Y. Tian, S.R. Stern, D. Minahan, R. Yona, X.Y. Lu, F.R. Zakaria, J. Collins, J. Wainer, J. Wong, R. McManus, S. Tamang, S. McDonnell, K. Ishida, A. Hayward, X.W. Liu, F. Hubalek, J. Fels, A. Vegge, M.R. Frederiksen, U. Rahbek, T. Yoshitake, J. Fujimoto, N. Roxhed, R. Langer, G. Traverso, A microneedle platform for buccal macromolecule delivery. Sci. Adv. 7(11), eabe2620 (2021)
S.R. Chaplan, F.W. Bach, J.W. Pogrel, J.M. Chung, T. L. Yaksh, Quantitative assessment of tactile allodynia in the rat paw. J. Neurosci. Meth. 53(1), 55–63 (1994)
M.J. Feng, G.H. Jiang, Y.F. Sun, U.E. Aharodnikau, K.E. Yunusov, T.Q. Liu, Z.Y. Zeng, Solomevich, Integration of metformin-loaded mesoporous bioactive glass nanoparticles and free metformin into polymer microneedles for transdermal delivery on diabetic rats. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 144, 109896 (2022)
B.B. Gao, M.Z. Guo, K. Lyu, T.S. Chu, B. F. He, Intelligent silk fibroin based microneedle dressing (i-SMD). Adv. Funct. Mater. 31(3), 2006839 (2021)
G. Goodwin, S.B. McMahon, The physiological function of different voltage-gated sodium channels in pain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 22(5), 263–274 (2021)
D.H. Gwon, S.I. Kim, S.H. Lee, C. Noh, Y. Kim, S. Yun, W.H. Lee, J.Y. Oh, D.W. Kim, J. Hong, S.Y. Lee, NFAT5 deficiency alleviates formalin-induced inflammatory Pain through mTOR. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22(5), 2587 (2021)
H. Hermanns, M.W. Hollmann, M.F. Stevens, P. Lirk, T. Brandenburger, T. Piegeler, R. Werdehausen, Molecular mechanisms of action of systemic lidocaine in acute and chronic pain: a narrative review. Brit J. Anaesth. 123(3), 335–349 (2019)
Y. Ito, J. Ohta, K. Imada, S. Akamatsu, N. Tsuchida, G. Inoue, N. Inoue, K. Takada, Dissolving microneedles to obtain rapid local anesthetic effect of lidocaine at skin tissue, J. Drug Target. 21(8), 770 – 775 (2013)
D. Jang, J. Tang, S.P. Schwendeman, M.R. Prausnitz, Effect of surface interactions on microsphere loading in dissolving microneedle patches. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 14, 29577–29587 (2022)
S. Khan, A. Hasan, F. Attar, M.M.N. Babadaei, H.A. Zeinabad, M. Salehi, M. Alizadeh, M. Hassan, H. Derakhshankhah, M.R. Hamblin, Q. Bai, M. Sharifi, M. Falahati, L. M. Ten Hagen, Diagnostic and drug release systems based on microneedle arrays in breast cancer therapy. J. Control Release. 338, 341–357 (2021)
J.Y. Kim, M.R. Han, Y.H. Kim, S.W. Shin, S.Y. Nam, J. H. Park, Tip-loaded dissolving microneedles for transdermal delivery of donepezil hydrochloride for treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 105, 148–155 (2016)
J. W. Lee, J.H. Park, M. R. Prausnitz, Dissolving microneedles for transdermal drug delivery. Biomaterials 29(13), 2113–2124 (2008)
B.M. Lee, C. Lee, S.F. Lahiji, U.W. Jung, G. Chung, H. Jung, Dissolving microneedles for rapid and painless local anesthesia. Pharmaceutics 12(4), 366 (2020)
H. Lee, H.S. Min, M. Jang, G. Kang, S. Gong, C. Lee, Y.W. Song, U.W. Jung, S. Lee, H.Y. Ryu, H. Yang, H. Y.G. Jung, Lidocaine-loaded dissolving microneedle for safe local anesthesia on oral mucosa for dental procedure, Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 20(6), 851–861 (2023)
X.J. Li, W.T. Shan, Y. Yang, D. Joralmon, Y.Z. Zhu, Y.Y. Chen, Y. Yuan, H. Xu, J.H. Rong, R. Dai, Q. Nian, Y. Chai, Y. Chen, Limpet tooth-inspired painless microneedles fabricated by magnetic field-assisted 3D printing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 31(5), 2003725 (2021)
D.P. Liu, B. Yu, G.H. Jiang, W.J. Yu, Y. Zhang, B. Xu, Fabrication of composite microneedles integrated with insulin-loaded CaCO3 microparticles and PVP for transdermal delivery in diabetic rats. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 90, 180–188 (2018)
T.Q. Liu, G.H. Jiang, G. Song, J.Y. Zhu, Y.H. Yang, Fabrication of separable microneedles with phase change coating for NIR-triggered transdermal delivery of metformin on diabetic rats. Biomed. Microdevices. 22(1), 11 (2020)
Y. Liu, M. Cheng, J. Zhao, X. Zhang, Z. Huang, Y. Zang, Y. Ding, J. Zhang, Z. Ding, Transdermal delivery of lidocaine-loaded elastic nano-liposomes with microneedle array pretreatment. Biomedicines 9(6), 592 (2021)
T.Q. Liu, Y.F. Sun, G.H. Jiang, W.J. Zhang, R. Wang, L. Nie, A. Shavandi, K.E. Yunusov, U.E. Aharodnikau, S. O. Solomevich, Porcupine-inspired microneedles coupled with an adhesive back patching as dressing for accelerating diabetic wound healing. Acta Biomater. 160, 32–44 (2023)
G. J. Ma, W. Wu, Microneedle, bio-microneedle and bio-inspired microneedle: a review. J. Control Release. 251, 11–23 (2017)
J. E. McKenna, R. Melzack, Dissociable effects of lidocaine injection into medial versus lateral thalamus in tail-flick and formalin pain tests. Mol. Pathophysiology 1(3), 205–214 (1994)
C.R. McNamara, J. Mandel-Brehm, D.M. Bautista, J. Siemens, K.L. Deranian, M. Zhao, N.J. Hayward, J.A. Chong, D. Julius, M.M. Moran, C. M. Fanger, TRPA1 mediates formalin-induced pain. PNAS. 104(33), 13525–13530 (2007)
S. Pain, Painful progress. Nature 535(7611), 518 – 19 (2016)
D. Ramadon, L.F.P. Sutrisna, Y. Harahap, K.S.S. Putri, F. Ulayya, P. Hartrianti, Q.K. Anjani, R. F. Donnelly, Enhancing intradermal delivery of lidocaine by dissolving microneedles: comparison between hyaluronic acid and poly(vinyl pyrrolidone) backbone polymers. Pharmaceutics 15(1), 289 (2023)
S. Ray, D.M. Wirth, O.A. Ortega-Rivera, N.F. Steinmetz, J. K. Pokorski, Dissolving microneedle delivery of a prophylactic HPV vaccine. Biomacromolecules 23(3), 903–912 (2022)
L.M. Ruan, G. Song, X.Y. Zhang, T.Q. Liu, Y.F. Sun, J.L. Zhu, Z.Y. Zeng, G.H. Jiang, Transdermal delivery of multifunctional CaO2@Mn-PDA nanoformulations by microneedles for NIR-induced synergistic therapy against skin melanoma. Biomater. Sci. 9(20), 6830–6841 (2021)
R.Z. Seeni, M.J. Zheng, D.C.S. Lio, C. Wiraja, M.F.B. Yusoff, W.T.Y. Koh, Y.C. Liu, B.T. Goh, C. J. Xu, Targeted delivery of anesthetic agents to bone tissues using conductive microneedles enhanced iontophoresis for painless dental anesthesia. Adv. Funct. Mater. 31(47), 2105686 (2021)
G. Song, G.H. Jiang, T.Q. Liu, X.Y. Zhang, Z.Y. Zeng, R.F. Wang, P.F. Li, Y. H. Yang, Separable microneedles for synergistic chemo-photothermal therapy against superficial skin tumors. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 6(7), 4116–4125 (2020)
G. Song, Y.F. Sun, T.Q. Liu, X.Y. Zhang, Z.Y. Zeng, R.F. Wang, P.F. Li, C.H. Li, G. H. Jiang, Transdermal delivery of Cu-doped polydopamine using microneedles for photothermal and chemodynamic synergistic therapy against skin melanoma. Chem. Eng. J. 426, 130790 (2021)
A.A. van de Loosdrecht, E. Nennie, G.J. Ossenkoppele, R.H. Beelen, M.M. Langenhuijsen, Cell mediated cytotoxicity against U 937 cells by human monocytes and macrophages in a modified colorimetric MTT assay. J. Immunol. Methods. 141(1), 15–22 (1991)
E.R. Viscusi, L. Reynolds, S. Tait, T. Melson, L. E. Atkinson, An iontophoretic fentanyl patient-activated analgesic delivery system for postoperative pain: a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Anesth. Analg. 102(1), 188–194 (2006)
M. Voute, V. Morel, G. Pickering, Topical lidocaine for chronic pain treatment. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 15, 4091–4103 (2021)
R. Wang, G.H. Jiang, U.E. Aharodnikau, K. Yunusov, Y.F. Sun, T.Q. Liu, S.O. Solomevich, Recent advances in polymer microneedles for drug transdermal delivery: design strategies and applications. Macromol. Rapid Comm. 43(8), 2200037 (2022)
R. Wang, H. Wang, G. Jiang, Y. Sun, T. Liu, L. Nie, A. Shavandi, K.E. Yunusov, U.E. Aharodnikau, S.O. Solomevich, Transdermal delivery of allopurinol to acute hyperuricemic mice via polymer microneedles for the regulation of serum uric acid levels. Biomater. Sci. 11(5), 1704–1713 (2023)
H. Yang, G. Kang, M. Jang, D.J. Um, J. Shin, H. Kim, J. Hong, H. Jung, H. Ahn, S. Gong, C. Lee, U.W. Jung, H. Jung, Development of lidocaine-loaded dissolving microneedle for rapid and efficient local anesthesia. Pharmaceutics 12(11), 1067 (2020)
Z.Y. Zeng, G.H. Jiang, T.Q. Liu, G. Song, Y.F. Sun, X.Y. Zhang, Y.T. Jing, M.J. Feng, Y.F. Shi, Fabrication of gelatin methacryloyl hydrogel microneedles for transdermal delivery of metformin in diabetic rats. Bio-Des Manuf. 4(4), 902–911 (2021)
H.H. Zhan, F.S. Ma, Y.C. Huang, J. Zhang, X.Y. Jiang, Y.C. Qian, Application of composite dissolving microneedles with high drug loading ratio for rapid local anesthesia. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 121, 330–337 (2018)
Y. Zhang, G. Jiang, W. Yu, D. Liu, B. Xu, Microneedles fabricated from alginate and maltose for transdermal delivery of insulin on diabetic rats. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 85, 18–26 (2018)
X.Y. Zhang, G.H. Jiang, G. Song, T.Q. Liu, Y.F. Sun, Z.Y. Zeng, Fabrication of h-MnO2@PDA composite nanocarriers for enhancement of anticancer cell performance by photo-chemical synergetic therapies. Front. Mater. Sci. 15(2), 291–298 (2021)
Z.Q. Zhao, B.Z. Chen, X.P. Zhang, H. Zheng, X.D. Guo, An update on the routes for the delivery of donepezil. Mol. Pharmaceut. 18(7), 2482–2494 (2021)
T.T. Zhu, X.X. Yu, X. Yi, X.L. Guo, L.H. Li, Y.P. Hao, W.C. Wang, Lidocaine-Loaded hyaluronic acid adhesive microneedle patch for oral mucosal topical anesthesia. Pharmaceut. 14(4), 686 (2022)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Huadong Medicine Joint Funds of the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (LHDMZ23H300003), National Natural Science Foundation of China (51873194), and Science and Technology Planning Project of Hangzhou Health Commission (20220919Y011), the General Program Foundation from the Science and Technology Bureau of Hangzhou City (20171226Y17), and the General Program Foundation from the Hangzhou City Health Bureau (A20210250).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Y. M. and C. Z.: prepared MNs and operated experiments. Y. M. and G. J.: analyzed results and wrote the manuscript. G. J. and Y. S.: designed the project and guided the work and founded the research. Z. S. and X. Z.: designed the animal experiment and discussed the results of animal experiment. L. N., A. S. and K. E. Y.: supported the suggestion and observed and reviewed on the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mao, Y., Zhang, X., Sun, Y. et al. Fabrication of lidocaine-loaded polymer dissolving microneedles for rapid and prolonged local anesthesia. Biomed Microdevices 26, 9 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-024-00695-1
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-024-00695-1