Abstract
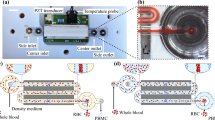
Density gradient centrifugation exploits density differences between different blood cells to accomplish separation of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from polymorphonuclear (PNM) cells, and erythrocytes or red blood cells (RBCs). While density gradient centrifugation offers a label-free alternative avoiding the use of harsh lysis buffers for blood cell isolation, it is a time-consuming and labor-intensive process during which blood cells are subject to high-levels of centrifugal force that can artifactually activate cells. To provide a low-stress alternative to this elegant method, we miniaturized and automated this process using microfluidics to ensure continuous PBMCs isolation from whole blood while avoiding the exposure to high-levels of centrifugal stress in a simple flow-through format. Within this device, a density gradient is established by exploiting laminar flow within microfluidic channels to layer a thin stream of blood over a larger stream of Ficoll. Using this approach we demonstrate successful isolation of PBMCs from whole blood with preservation of monocytes and different lymphocyte subpopulations similar to that seen with conventional density gradient centrifugation. Evaluation of activation status of PBMCs isolated using this technique shows that our approach achieves minimal isolation process induced activation of cells in comparison to conventional lysis or density gradient centrifugation. This simple, automated microfluidic density gradient centrifugation technique can potentially serve as tool for rapid and activation-free technique for isolation of PBMCs from whole blood for point-of-care applications.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Amasia, M. Madou, Large-volume centrifugal microfluidic device for blood plasma separation. Bioanalysis 2(10), 1701–1710 (2010)
M. Arras, W.D. Ito, D. Scholz, B. Winkler, J. Schaper, W. Schaper, Monocyte activation in angiogenesis and collateral growth in the rabbit hindlimb. J Clin Invest 101(1), 40–50 (1998)
F. Brosseron, K. Marcus, C. May, Isolating peripheral lymphocytes by density gradient centrifugation and magnetic cell sorting. Methods Mol Biol 1295, 33–42 (2015)
R. Burger, J. Ducree, Handling and analysis of cells and bioparticles on centrifugal microfluidic platforms. Expert Rev Mol Diagn 12(4), 407–421 (2012)
N.C. Dubois, A.M. Craft, P. Sharma, D.A. Elliott, E.G. Stanley, A.G. Elefanty, A. Gramolini, G. Keller, SIRPA is a specific cell-surface marker for isolating cardiomyocytes derived from human pluripotent stem cells. Nat Biotechnol 29(11), 1011–1018 (2011)
D. English, B.R. Andersen, Single-step separation of red blood cells. Granulocytes and mononuclear leukocytes on discontinuous density gradients of Ficoll-Hypaque. J Immunol Methods 5(3), 249–252 (1974)
Feezor, R. J., H. V. Baker, M. Mindrinos, D. Hayden, C. L. Tannahill, B. H. Brownstein, A. Fay, S. MacMillan, J. Laramie, W. Xiao, L. L. Moldawer, J. P. Cobb, K. Laudanski, C. L. Miller-Graziano, R. V. Maier, D. Schoenfeld, R. W. Davis, R. G. Tompkins, Inflammation and L.-S. C. R. P. Host Response to Injury (2004). "Whole blood and leukocyte RNA isolation for gene expression analyses." Physiol Genomics 19(3): 247-254.
R.S. Frank, Time-dependent alterations in the deformability of human neutrophils in response to chemotactic activation. Blood 76(12), 2606–2612 (1990)
A. Fritsche, H. Haring, M. Stumvoll, White blood cell count as a predictor of glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity. The role of inflammation in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Dtsch Med Wochenschr 129(6), 244–248 (2004)
S. Fukuda, T. Yasu, D.N. Predescu, G.W. Schmid-Schonbein, Mechanisms for regulation of fluid shear stress response in circulating leukocytes. Circ Res 86(1), E13–E18 (2000)
G. Gibson, The environmental contribution to gene expression profiles. Nat Rev Genet 9(8), 575–581 (2008)
J. He, D.S. Le, X. Xu, M. Scalise, A.W. Ferrante, J. Krakoff, Circulating white blood cell count and measures of adipose tissue inflammation predict higher 24-h energy expenditure. Eur J Endocrinol 162(2), 275–280 (2010)
C.C. Helms, M. Marvel, W. Zhao, M. Stahle, R. Vest, G.J. Kato, J.S. Lee, G. Christ, M.T. Gladwin, R.R. Hantgan, D.B. Kim-Shapiro, Mechanisms of hemolysis-associated platelet activation. J Thromb Haemost 11(12), 2148–2154 (2013)
E.M. Hersh, W.T. Butler, R.D. Rossen, R.O. Morgan, W. Suki, In vitro studies of the human response to organ allografts: appearance and detection of circulating activation lymphocytes. J Immunol 107(2), 571–578 (1971)
L.J. Hofland, P.M. van Koetsveld, T.M. Verleun, S.W. Lamberts, Heterogeneity of pituitary adenoma cell subpopulations from acromegalic patients obtained by Percoll density gradient centrifugation. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 121(2), 270–278 (1989)
B. Jude, B. Agraou, E.P. McFadden, S. Susen, C. Bauters, P. Lepelley, C. Vanhaesbroucke, P. Devos, A. Cosson, P. Asseman, Evidence for time-dependent activation of monocytes in the systemic circulation in unstable angina but not in acute myocardial infarction or in stable angina. Circulation 90(4), 1662–1668 (1994)
D.J. Kinahan, S.M. Kearney, N.A. Kilcawley, P.L. Early, M.T. Glynn, J. Ducree, Density-Gradient Mediated Band Extraction of Leukocytes from Whole Blood Using Centrifugo-Pneumatic Siphon Valving on Centrifugal Microfluidic Discs. PLoS One 11(5), e0155545 (2016)
J. Krutmann, R. Kirnbauer, A. Kock, T. Schwarz, E. Schopf, L.T. May, P.B. Sehgal, T.A. Luger, Cross-linking Fc receptors on monocytes triggers IL-6 production. Role in anti-CD3-induced T cell activation. J Immunol 145(5), 1337–1342 (1990)
S.H. Li, X. Liao, T.E. Zhou, L.L. Xiao, Y.W. Chen, F. Wu, J.R. Wang, B. Cheng, J.X. Song, H.W. Liu, Evaluation of 2 Purification Methods for Isolation of Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Based on Red Blood Cell Lysis With Ammonium Chloride and Hypotonic Sodium Chloride Solution. Ann Plast Surg 78(1), 83–90 (2017)
J.R. Mellembakken, P. Aukrust, M.K. Olafsen, T. Ueland, K. Hestdal, V. Videm, Activation of leukocytes during the uteroplacental passage in preeclampsia. Hypertension 39(1), 155–160 (2002)
S.T. Moen, C.L. Hatcher, A.K. Singh, A Centrifugal Microfluidic Platform That Separates Whole Blood Samples into Multiple Removable Fractions Due to Several Discrete but Continuous Density Gradient Sections. PLoS One 11(4), e0153137 (2016)
V. Naranbhai, P. Bartman, D. Ndlovu, P. Ramkalawon, T. Ndung'u, D. Wilson, M. Altfeld, W.H. Carr, Impact of blood processing variations on natural killer cell frequency, activation, chemokine receptor expression and function. J Immunol Methods 366(1-2), 28–35 (2011)
R.A. Newton, M. Thiel, N. Hogg, Signaling mechanisms and the activation of leukocyte integrins. J Leukoc Biol 61(4), 422–426 (1997)
J.C. Nieto, E. Canto, C. Zamora, M.A. Ortiz, C. Juarez, S. Vidal, Selective loss of chemokine receptor expression on leukocytes after cell isolation. PLoS One 7(3), e31297 (2012)
V. Parichehreh, P. Sethu, Inertial lift enhanced phase partitioning for continuous microfluidic surface energy based sorting of particles. Lab Chip 12(7), 1296–1301 (2012)
V. Parichehreh, R. Estrada, S.S. Kumar, K.K. Bhavanam, V. Raj, A. Raj, P. Sethu, Exploiting osmosis for blood cell sorting. Biomed Microdevices 13(3), 453–462 (2011)
V. Parichehreh, K. Medepallai, K. Babbarwal, P. Sethu, Microfluidic inertia enhanced phase partitioning for enriching nucleated cell populations in blood. Lab Chip 13(5), 892–900 (2013)
P. Sethu, M. Anahtar, L.L. Moldawer, R.G. Tompkins, M. Toner, Continuous flow microfluidic device for rapid erythrocyte lysis. Anal Chem 76(21), 6247–6253 (2004)
P. Sethu, L.L. Moldawer, M.N. Mindrinos, P.O. Scumpia, C.L. Tannahill, J. Wilhelmy, P.A. Efron, B.H. Brownstein, R.G. Tompkins, M. Toner, Microfluidic isolation of leukocytes from whole blood for phenotype and gene expression analysis. Anal Chem 78(15), 5453–5461 (2006)
Y. Sun, P. Sethu, Microfluidic Adaptation of Density-Gradient Centrifugation for Isolation of Particles and Cells. Bioengineering (Basel) 4(3) (2017)
A. von Bonin, J. Huhn, B. Fleischer, Dipeptidyl-peptidase IV/CD26 on T cells: analysis of an alternative T-cell activation pathway. Immunol Rev 161, 43–53 (1998)
C. Weber, W. Erl, P.C. Weber, Enhancement of monocyte adhesion to endothelial cells by oxidatively modified low-density lipoprotein is mediated by activation of CD11b. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 206(2), 621–628 (1995)
Acknowledgements
YS was supported by an Alabama EPSCoR Graduate Research Scholars Program. This work was supported by the NSF CAREER Award # 1149059 to PS and the Comprehensive Cardiovascular Center and the Division of Cardiovascular Disease at the University of Alabama at Birmingham.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, Y., Sethu, P. Low-stress Microfluidic Density-gradient Centrifugation for Blood Cell Sorting. Biomed Microdevices 20, 77 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-018-0323-3
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-018-0323-3