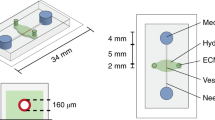
Abstract
Existing microfluidic devices, e.g. parallel plate flow chambers, do not accurately depict the geometry of microvascular networks in vivo. We have developed a synthetic microvascular network (SMN) on a polydimethalsiloxane (PDMS) chip that can serve as an in vitro model of the bifurcations, tortuosities, and cross-sectional changes found in microvascular networks in vivo. Microvascular networks from a cremaster muscle were mapped using a modified Geographical Information System, and then used to manufacture the SMNs on a PDMS chip. The networks were cultured with bovine aortic endothelial cells (BAEC), which reached confluency 3–4 days after seeding. Propidium iodide staining indicated viable and healthy cells showing normal behavior in these networks. Anti-ICAM-1 conjugated 2-μm microspheres adhered to BAEC cells activated with TNF-α in significantly larger numbers compared to control IgG conjugated microspheres. This preferential adhesion suggests that cultured cells retain an intact cytokine response in the SMN. This microfluidic system can provide novel insight into characterization of drug delivery particles and dynamic flow conditions in microvascular networks.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.P. Camp, T. Stokol, M.L. Shuler, Biomed. Microdevices 10, 2 (2007)
K.E. Caputo, D. Lee, M.R. King, D.A. Hammer, Biophys. J 92, 3 (2007). doi:10.1529/biophysj.106.082321
G.R. Cokelet, R. Soave, G. Pugh, L. Rathbun, Microvasc. Res. 46, 3 (1993). doi:10.1006/mvre.1993.1062
P. Decuzzi, M. Ferrari, Biomaterials 29, 3 (2008). doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2007.09.025
J. El Ali, P.K. Sorger, K.F. Jensen, Nature 442, 7101 (2006). doi:10.1038/nature05063
C. Fidkowski, M.R. Kaazempur-Mofrad, J. Borenstein, J.P. Vacanti, R. Langer, Y. Wang, Tissue Eng 11, 1–2 (2005). doi:10.1089/ten.2005.11.302
C. Fiehn, F. Kratz, G. Sass, U. Muller-Ladner, E. Neumann, Ann. Rheum. Dis 67, 8 (2008). doi:10.1136/ard.2007.086843
M.D. Frame, I.H. Sarelius, Microcirculation 2, 4 (1995). doi:10.3109/10739689509148282
P. Gaehtgens, Int. J. Microcirc. Clin. Exp 11, 2 (1992)
K.J. Kelly, R.M. Sandoval, K.W. Dunn, B.A. Molitoris, P.C. Dagher, Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol 284, 2 (2003)
M.F. Kiani, H. Yuan, X. Chen, L. Smith, M.W. Gaber, D.J. Goetz, Pharm. Res 19, 9 (2002). doi:10.1023/A:1020350708672
M.J. Levesque, R.M. Nerem, J. Biomech. Eng 107, 4 (1985)
R.E. Mott, B.P. Helmke, Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol 293, 5 (2007). doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00457.2006
M.S. Mulligan, A.A. Vaporciyan, M. Miyasaka, T. Tamatani, P.A. Ward, Am. J. Pathol 142, 6 (1993)
C.B. Pattillo, F. Sari-Sarraf, R. Nallamothu, B.M. Moore, G.C. Wood, M.F. Kiani, Pharm. Res 22, 7 (2005). doi:10.1007/s11095-005-5646-0
B. Prabhakarpandian, D.J. Goetz, R.A. Swerlick, X. Chen, M.F. Kiani, Microcirculation 8, 5 (2001). doi:10.1038/sj.mn.7800105
B. Prabhakarpandian, K. Pant, R.C. Scott, C.B. Patillo, D. Irimia, M.F. Kiani, S. Sundaram, Biomed. Microdevices 10, 4 (2008). doi:10.1007/s10544-008-9170-y
N.M. Roth, M.F. Kiani, Ann. Biomed. Eng 27, 1 (1999). doi:10.1114/1.204
H.S. Sakhalkar, M.K. Dalal, A.K. Salem, R. Ansari, J. Fu, M.F. Kiani, D.T. Kurjiaka, J. Hanes, K.M. Shakesheff, D.J. Goetz, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100, 26 (2003). doi:10.1073/pnas.2631433100
H.S. Sakhalkar, J. Hanes, J. Fu, U. Benavides, R. Malgor, C.L. Borruso, L.D. Kohn, D.T. Kurjiaka, D.J. Goetz, FASEB J 19, 7 (2005)
U.Y. Schaff, M.M. Xing, K.K. Lin, N. Pan, N.L. Jeon, S.I. Simon, Lab Chip 7, 4 (2007). doi:10.1039/b617915k
R.C. Scott, B. Wang, R. Nallamothu, C.B. Pattillo, G. Perez-Liz, A. Issekutz, L.D. Valle, G.C. Wood, M.F. Kiani, Biotechnol. Bioeng 96, 4 (2007). doi:10.1002/bit.21233
M. Shin, K. Matsuda, O. Ishii, H. Terai, M. Kaazempur-Mofrad, J. Borenstein, M. Detmar, J.P. Vacanti, Biomed. Microdevices 6, 4 (2004). doi:10.1023/B:BMMD.0000048559.29932.27
S.K. Sia, G.M. Whitesides, Electrophoresis 24, 21 (2003). doi:10.1002/elps.200305584
L.A. Smith, H. Aranda-Espinoza, J.B. Haun, D.A. Hammer, Biophys. J 92, 2 (2007)
T.A. Springer, Cell 76, 2 (1994). doi:10.1016/0092-8674(94)90337-9
A. Werner, C.U. Kloss, J. Walter, G.W. Kreutzberg, G. Raivich, J. Neurocytol 27, 4 (1998). doi:10.1023/A:1006928830251
G.M. Whitesides, Nature 442, 7101 (2006). doi:10.1038/nature05058
B. Wilson, M.K. Samanta, K. Santhi, K.P. Kumar, N. Paramakrishnan, B. Suresh, T. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm 70, 1 (2008). doi:10.1016/j.ejpb.2008.03.009
H. Yuan, D.J. Goetz, M.W. Gaber, A.C. Issekutz, T.E. Merchant, M.F. Kiani, Radiat. Res 163, 5 (2005). doi:10.1667/RR3361
X. Zhang, S.J. Haswell, Ernst. Schering. Found. Symp. Proc. 3 (2006)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by NIH (2R44HL076034-02), the Pennsylvania Department of Health and the Nanotechnology Institute.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rosano, J.M., Tousi, N., Scott, R.C. et al. A physiologically realistic in vitro model of microvascular networks. Biomed Microdevices 11, 1051 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-009-9322-8
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-009-9322-8