Abstract
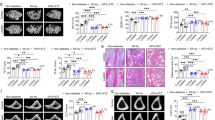
Type-1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) is a chronic condition characterized by long-term hyperglycemia that results in several complications such as painful peripheral neuropathy, bone deterioration, and increased risk of bone fractures. Lithium, a first-line therapy for bipolar disorder, has become an attractive agent for attenuating peripheral neuropathy and menopause-induced bone loss. Therefore, our aim was to determine the effect of chronic lithium treatment on mechanical hypersensitivity and trabecular bone loss induced by T1DM in mice. T1DM was induced in male C57BL/6J mice by intraperitoneal injection of streptozotocin (STZ, 50 mg/kg/day, for 5 consecutive days). 12 weeks after T1DM-induction, mice received a daily intraperitoneal injection of vehicle, 30 or 60 mg/kg lithium (as LiCl) for 6 weeks. Throughout the treatment period, blood glucose levels and mechanical sensitivity were evaluated every 2 weeks. After lithium treatment, the femur and L5 vertebra were harvested for microcomputed tomography (microCT) analysis. T1DM mice showed significant hyperglycemia, mechanical hypersensitivity, and significant trabecular bone loss as compared with the control group. Chronic lithium treatment did not revert the hindpaw mechanical hypersensitivity nor hyperglycemia associated to T1DM induced by STZ. In contrast, microCT analysis revealed that lithium reverted, in a dose-dependent manner, the loss of trabecular bone associated to T1DM induced by STZ at both the distal femur and L5 vertebra. Lithium treatment by itself did not affect any trabecular bone parameter in non-diabetic mice.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data supporting the findings of the article is available within the article.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Antika LD, Lee E-J, Kim Y-H, Kang M-K, Park S-H, Kim DY, Oh H, Choi Y-J, Kang Y-H (2017) Dietary phlorizin enhances osteoblastogenic bone formation through enhancing β-catenin activity via GSK-3β inhibition in a model of senile osteoporosis. J Nutr Biochem 49:42–52
Bai J, Xu Y, Dieo Y, Sun G (2019) Combined low-dose LiCl and LY294002 for the treatment of osteoporosis in ovariectomized rats. J Orthop Surg Res 14:177. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-019-1210-1
Banafshe HR, Mesdaghinia A, Arani MN, Ramezani MH, Heydari A, Hamidi GA (2012) Lithium attenuates pain-related behavior in a rat model of neuropathic pain: possible involvement of opioid system. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 100(3):425–430. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2011.10.004
Bernick J, Wang Y, Sigal IA, Alman BA, Whyne CM, Nam D (2014) Parameters for lithium treatment are critical in its enhancement of fracture-healing in rodents. J Bone Joint Surg Am 96(23):1990–1998. https://doi.org/10.2106/jbjs.n.00057
Bouxsein ML, Boyd SK, Christiansen BA, Guldberg RE, Jepsen KJ, Müller R (2010) Guidelines for assessment of bone microstructure in rodents using micro–computed tomography. J Bone Miner Res 25(7):1468–1486
Chaplan SR, Bach F, Pogrel J, Chung J, Yaksh T (1994) Quantitative assessment of tactile allodynia in the rat paw. J Neurosci Methods 53(1):55–63
Enríquez-Pérez IA, Galindo-Ordoñez KE, Pantoja-Ortíz CE, Martínez-Martínez A, Acosta-González RI, Muñoz-Islas E, Jiménez-Andrade JM (2017) Streptozocin-induced type-1 diabetes mellitus results in decreased density of CGRP sensory and TH sympathetic nerve fibers that are positively correlated with bone loss at the mouse femoral neck. Neurosci Lett 655:28–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2017.06.042
Esu KD, Bakare AO (2021) Effects of co-administration of vitamin E and lithium chloride on chronic constriction injury-induced neuropathy in male Wistar rats: focus on antioxidant and anti-inflammatory mechanisms. Pain Pract. https://doi.org/10.1111/papr.13064
Feldman EL, Callaghan BC, Pop-Busui R, Zochodne DW, Wright DE, Bennett DL, Bril V, Russell JW, Viswanathan V (2019) Diabetic neuropathy. Nat Rev Dis Primers 5(1):41. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41572-019-0092-1
Fowlkes JL, Nyman JS, Bunn RC, Jo C, Wahl EC, Liu L, Cockrell GE, Morris LM, Lumpkin CK Jr, Thrailkill KM (2013) Osteo-promoting effects of insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) in a mouse model of type 1 diabetes. Bone 57(1):36–40
Gill A, Kidd J, Vieira F, Thompson K, Perrin S (2009) No benefit from chronic lithium dosing in a sibling-matched, gender balanced, investigator-blinded trial using a standard mouse model of familial ALS. PLoS ONE 4(8):e6489
Hie M, Shimono M, Fujii K, Tsukamoto I (2007) Increased cathepsin K and tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase expression in bone of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Bone 41(6):1045–1050. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bone.2007.08.030
Hoeppner LH, Secreto FJ, Westendorf JJ (2009) Wnt signaling as a therapeutic target for bone diseases. Expert Opin Ther Targets 13(4):485–496. https://doi.org/10.1517/14728220902841961
Hu X, Wang Z, Shi J, Guo X, Wang L, Ping Z, Tao Y, Yang H, Zhou J, Xu Y, Geng D (2017) Lithium chloride inhibits titanium particle-induced osteoclastogenesis by inhibiting the NF-κB pathway. Oncotarget 8(48):83949–83961. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.20000
IDF (2021) Diabetes atlas, 10th edn. International Diabetes Federation, Brussels
Iyer S, Han L, Ambrogini E, Yavropoulou M, Fowlkes J, Manolagas SC, Almeida M (2017) Deletion of FoxO1, 3, and 4 in Osteoblast Progenitors Attenuates the Loss of Cancellous Bone Mass in a Mouse Model of Type 1 Diabetes. J Bone Miner Res 32(1):60–69. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbmr.2934
Jin Y, Xu L, Hu X, Liao S, Pathak JL, Liu J (2017) Lithium chloride enhances bone regeneration and implant osseointegration in osteoporotic conditions. J Bone Miner Metab 35(5):497–503. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-016-0783-6
Klontzas M, Kenanidis I, MacFarlane EJ, Michail R, Potoupnis TE, Heliotis M, Mantalaris M, Tsiridis E (2016) Investigational drugs for fracture healing: preclinical & clinical data. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 25(5):585–596
Kurgan N, Bott KN, Helmeczi WE, Roy BD, Brindle ID, Klentrou P, Fajardo VA (2019) Low dose lithium supplementation activates Wnt/β-catenin signalling and increases bone OPG/RANKL ratio in mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 511(2):394–397
Lewicki M, Paez H, Mandalunis PM (2006) Effect of lithium carbonate on subchondral bone in sexually mature Wistar rats. Exp Toxicol Pathol 58(2–3):197–201
Li L, Peng X, Qin Y, Wang R, Tang J, Cui X, Wang T, Liu W, Pan H, Li B (2017) Acceleration of bone regeneration by activating Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway via lithium released from lithium chloride/calcium phosphate cement in osteoporosis. Sci Rep 7(1):1–12
Liu B, Wu Q (2019) Lithium use and risk of fracture: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Osteoporos Int 30:257–266. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-018-4745-9
Malhi GS, Tanious M, Das P, Coulston CM, Berk M (2013) Potential mechanisms of action of lithium in bipolar disorder. CNS Drugs 27(2):135–153
Martínez-Martínez A, Muñoz-Islas E, Ramírez-Rosas MB, Acosta-González RI, Torres-Rodríguez HF, Jiménez-Andrade JM (2020) Blockade of the colony-stimulating factor-1 receptor reverses bone loss in osteoporosis mouse models. Pharmacol Rep 72(6):1614–1626. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43440-020-00091-5
Mauricio D, Alonso N, Gratacòs M (2020) Chronic Diabetes Complications: The Need to Move beyond Classical Concepts. Trends Endocrinol Metab 31(4):287–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tem.2020.01.007
Maycas M, McAndrews KA, Sato AY, Pellegrini GG, Brown DM, Allen MR, Plotkin LI, Gortazar AR, Esbrit P, Bellido T (2017) PTHrP-Derived Peptides Restore Bone Mass and Strength in Diabetic Mice: Additive Effect of Mechanical Loading. J Bone Miner Res 32(3):486–497. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbmr.3007
Motyl KJ, McCauley LK, McCabe LR (2012) Amelioration of type I diabetes-induced osteoporosis by parathyroid hormone is associated with improved osteoblast survival. J Cell Physiol 227(4):1326–1334
National Research Council (2011) Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, 8th edn. The National Academies Press, Washington, DC
NOM (1999) NOM-062-ZOO-1999 Especificaciones ténicas para la producción, cuidado y uso de los animales de laboratorio. Diario Oficial de la Federación México
Patterson CC, Karuranga S, Salpea P, Saeedi P, Dahlquist G, Soltesz G, Ogle GD (2019) Worldwide estimates of incidence, prevalence and mortality of type 1 diabetes in children and adolescents: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 157:107842
Peng J, Hui K, Hao C, Peng Z, Gao QX, Jin Q, Lei G, Min J, Qi Z, Bo C, Dong QN, Bing ZH, Jia XY, Fu DL (2016) Low bone turnover and reduced angiogenesis in streptozotocin-induced osteoporotic mice. Connect Tissue Res 57(4):277–289. https://doi.org/10.3109/03008207.2016.1171858
Petersmann A, Müller-Wieland D, Müller UA, Landgraf R, Nauck M, Freckmann G, Heinemann L, Schleicher E (2019) Definition, classification and diagnosis of diabetes mellitus. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 127:01. https://doi.org/10.1055/a-1018-9078
Pourmohammadi N, Alimoradi H, Mehr SE, Hassanzadeh G, Hadian MR, Sharifzadeh M, Bakhtiarian A, Dehpour AR (2012) Lithium attenuates peripheral neuropathy induced by paclitaxel in rats. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 110(3):231–237. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-7843.2011.00795.x
Romero-Díaz C, Duarte-Montero D, Gutiérrez-Romero SA, Mendivil CO (2021) Diabetes and bone fragility. Diabetes Ther 12(1):71–86. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13300-020-00964-1
Shah VN, Shah CS, Snell-Bergeon JK (2015) Type 1 diabetes and risk of fracture: meta-analysis and review of the literature. Diabet Med 32(9):1134–1142. https://doi.org/10.1111/dme.12734
Shimizu T, Shibata M, Wakisaka S, Inoue T, Mashimo T, Yoshiya I (2000) Intrathecal lithium reduces neuropathic pain responses in a rat model of peripheral neuropathy. Pain 85(1–2):59–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0304-3959(99)00249-3
Singh R, Kishore L, Kaur N (2014) Diabetic peripheral neuropathy: current perspective and future directions. Pharmacol Res 80:21–35
Thangavelu T, Silverman E, Akhter MP, Lyden E, Recker RR, Graeff-Armas LA (2020) Trabecular bone score and transilial bone trabecular histomorphometry in type 1 diabetes and healthy controls. Bone 137:115451. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bone.2020.115451
Vachhani K, Whyne C, Wang Y, Burns DM (2018) Low-dose lithium regimen enhances endochondral fracture healing in osteoporotic rodent bone. J Orthop Res 36:1783–1789. https://doi.org/10.1002/jor.23799
Vestergaard P (2007) Discrepancies in bone mineral density and fracture risk in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes—a meta-analysis. Osteoporos Int 18(4):427–444. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-006-0253-4
Volkmann C, Bschor T, Köhler S (2020) Lithium treatment over the lifespan in bipolar disorders. Front Psychiatry 11:377. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2020.00377
Wang F-S, Ko J-Y, Weng L-H, Yeh D-W, Ke H-J, Wu S-L (2009) Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3β attenuates glucocorticoid-induced bone loss. Life Sci 85(19–20):685–692
Wang X, Zhu S, Jiang X, Li Y, Song D, Hu J (2015) Systemic administration of lithium improves distracted bone regeneration in rats. Calcif Tissue Int 96(6):534–540
Weinsanto I, Mouheiche J, Laux-Biehlmann A, Aouad M, Maduna T, Petit-Demouliere N, Chavant V, Poisbeau P, Darbon P, Charlet A (2018) Lithium reverses mechanical allodynia through a mu opioid-dependent mechanism. Mol Pain 14:1744806917754142
Wong SK, Chin KY, Ima-Nirwana S (2020) The Skeletal-Protecting Action and Mechanisms of Action for Mood-Stabilizing Drug Lithium Chloride: Current Evidence and Future Potential Research Areas. Front Pharmacol 11:430. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.00430
Yang J, Chen S, Zong Z, Yang L, Liu D, Bao Q, Du W (2020) The increase in bone resorption in early-stage type I diabetic mice is induced by RANKL secreted by increased bone marrow adipocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 525(2):433–439. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.02.079
Zamani A, Omrani GR, Nasab MM (2009) Lithium’s effect on bone mineral density. Bone 44(2):331–334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bone.2008.10.001
Funding
This work was supported by the Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología (CONACYT) project CB 2017–2018/A1-S-27869 (EMI) and project No. 316211 (RIAG).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JMJA conceived the project. MAGA, HFTR, REMM, and VMVM performed the experiments. JMJA, RIAG and EMI analyzed and interpreted the data. JMJA, MAGA, HFTR, REMM, RIAG, GCC and EMI wrote and edited the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Protocol was obtained by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of the Facultad de Medicina, Universidad Autónoma del Estado de Morelos (FM/20/110).
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Graniel-Amador, M.A., Torres-Rodríguez, H.F., Martínez-Mendoza, R.E. et al. Effect of chronic lithium on mechanical sensitivity and trabecular bone loss induced by type-1 diabetes mellitus in mice. Biometals 35, 1033–1042 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-022-00421-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-022-00421-5