Abstract
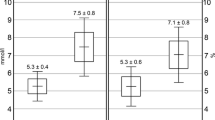
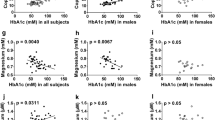
Previous researches have been conducted to study the associations of trace elements on Type 2 diabetes (T2D) risk. The present study focuses on the evaluation of potential associations between trace elements and Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) in patients with T2D, via the determination of their levels in human whole blood. 100 diabetes without complications, 75 prediabetes and 40 apparently healthy subjects were studied. The levels of eleven trace elements including lithium (Li), vanadium (V), chromium (Cr), manganese (Mn), iron (Fe), cobalt (Co), copper (Cu), zinc (Zn), selenium (Se), strontium (Sr) and molybdenum (Mo) were measured using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS). The levels of fasting glucose, HbA1c, Hemoglobin, lipid, liver function, kidney function, thyroid function and demographic data were obtained from the Laboratory Information System. Nonparametric correlation (Spearman) was used to analyze the relationship between trace elements and HbA1c. The contents of V, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Cu, Zn and Mo in diabetes increased comparing with the healthy subject while Li decreased. But the levels of Li, V, Cr, Mn, Co, Se and Mo negatively correlated with HbA1c in the diabetes subjects (r value: − 0.2189, − 0.2421, − 0.3260, − 0.2744, − 0.2812, − 0.2456, − 0.2240; 95% confidence interval − 0.4032 to − 0.0176, − 0.4235 to − 0.0420, − 0.4955 to − 0.1326, − 0.4515 to − 0.0765, − 0.4573 to − 0.0838, − 0.4266 to − 0.0458, − 0.4076 to − 0.0229; p < 0.05, p < 0.05, p < 0.001, p < 0.01, p < 0.01, p < 0.05, p < 0.05). Accordingly, the contents of V, Cr, Mn and Se showed lower in HbA1c ≥ 7.0% group in contrast to HbA1c < 7.0% group. No correlation of HbA1c (or FBG) and trace elements was found in the healthy subjects. Trace element levels and metabolic abnormalities of blood glucose may be mutually affected. The extra supplement of trace elements needs to be cautious.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and analyzed in this study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- T2D:
-
Type 2 diabetes
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- Fe:
-
Iron
- Cu:
-
Copper
- Zn:
-
Zinc
- Mn:
-
Manganese
- Se:
-
Selenium
- Sr:
-
Strontium
- Li:
-
Lithium
- V:
-
Vanadium
- Cr:
-
Chromium
- Mo:
-
Molybdenum
- Co:
-
Cobalt
- ICP-MS:
-
Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry
- FBG:
-
Fasting blood-glucose
- HbA1c:
-
Hemoglobin A1
References
American Diabetes Association (2020) 2. Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: standards of medical care in diabetes-2020. Diabetes Care 43(Suppl 1):S14–S31
Badran M, Morsy R, Soliman H, Elnimr T (2016) Assessment of trace elements levels in patients with type 2 diabetes using multivariate statistical analysis. J Trace Elem Med Biol 33:114–119
Calderón Guzmán D, Juárez Olguín H, Osnaya Brizuela N, Hernández Garcia E, Lindoro Silva M (2019) The use of trace and essential elements in common clinical disorders: roles in assessment of health and oxidative stress status. Nutr Cancer 71(1):13–20
Cannas D, Loi E, Serra M, Firinu D, Valera P, Zavattari P (2020) Relevance of essential trace elements in nutrition and drinking water for human health and autoimmune disease risk. Nutrients 12(7):2074
Chatterjee S, Khunti K, Davies MJ (2017) Type 2 diabetes. Lancet 389(10085):2239–2251
Chen S, Zhou L, Guo Q, Fang C, Wang M, Peng X, Yin J, Li S, Zhu Y, Yang W, Zhang Y, Shan Z, Chen X, Liu L (2020) Association of plasma chromium with metabolic syndrome among Chinese adults: a case-control study. Nutr J 19(1):107
Dubey P, Thakur V, Chattopadhyay M (2020) Role of minerals and trace elements in diabetes and insulin resistance. Nutrients 12(6):1864
Fukunaka A, Fujitani Y (2018) Role of zinc homeostasis in the pathogenesis of diabetes and obesity. Int J Mol Sci 19(2):476
Hanif S, Ilyas A, Shah MH (2018) Statistical evaluation of trace metals, TSH and T4 in blood serum of thyroid disease patients in comparison with controls. Biol Trace Elem Res 183(1):58–70
Joda BA, Ward NI (2021) Use of human teardrop fluid for the determination of trace elements in healthy individuals and diabetic patients. J Trace Elem Med Biol 65:126733
Jung SR, Park SY, Koh JH, Kim JY (2021) Lithium enhances exercise-induced glycogen breakdown and insulin-induced AKT activation to facilitate glucose uptake in rodent skeletal muscle. Pflugers Arch 473(4):673–682
Kohler LN, Foote J, Kelley CP, Florea A, Shelly C, Chow HS, Hsu P, Batai K, Ellis N, Saboda K, Lance P, Jacobs ET (2018) Selenium and type 2 diabetes. Syst Rev Nutr 10(12):1924
Laakso M (2019) Biomarkers for type 2 diabetes. Mol Metab 27S(Suppl):S139–S146
Laur N, Kinscherf R, Pomytkin K, Kaiser L, Knes O, Deigner HP (2020) ICP-MS trace element analysis in serum and whole blood. PLoS ONE 15(5):e0233357
Lian S, Zhang T, Yu Y, Zhang B (2021) Relationship of circulating copper level with gestational diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis and systemic review. Biol Trace Elem Res 199(12):4396–4409
Luan F, Liu B, Sun S, Chen Y, Xu Y, Jiang X, Guo X, Cheng S, Wang Y (2022) Analysis of eight nutrient elements in whole blood of children and adolescents using inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry. Biol Trace Elem Res 200(7):3078–3087
Ma J, He H, Yang X, Chen D, Tan C, Zhong L, Du Q, Wu X, Gao Y, Liu G, Wang C, Ran X (2021) A new approach for investigating the relative contribution of basal glucose and postprandial glucose to HbA1C. Nutr Diabetes 11(1):14
Nordberg M, Nordberg GF (2016) Trace element research-historical and future aspects. J Trace Elem Med Biol 38:46–52
Shan Z, Chen S, Sun T, Luo C, Guo Y, Yu X, Yang W, Hu FB, Liu L (2016) U-shaped association between plasma manganese levels and type 2 diabetes. Environ Health Perspect 124(12):1876–1881
Siddiqi SM, Sun C, Wu X, Shah I, Mehmood A (2020) The Correlation between dietary selenium intake and type 2 diabetes: a cross-sectional population-based study on North Chinese adults. Biomed Res Int 2020:8058463
Sun C, Wu QJ, Gao SY, Ma ZM, Liu YS, Zhang JY, Zhao YH (2020) Association between the ferritin level and risk of gestational diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis of observational studies. J Diabetes Investig 11(3):707–718
Wang XL, Yang TB, Wei J, Lei GH, Zeng C (2016) Association between serum selenium level and type 2 diabetes mellitus: a non-linear dose-response meta-analysis of observational studies. Nutr J 15(1):48
Weihrauch-Blüher S, Richter M, Staege MS (2018) Body weight regulation, socioeconomic status and epigenetic alterations. Metabolism 85:109–115
Wu Q, Sun X, Chen Q, Zhang X, Zhu Y (2021) Genetically predicted selenium is negatively associated with serum TC, LDL-C and positively associated with HbA1C levels. J Trace Elem Med Biol 67:126785
Yary T, Virtanen JK, Ruusunen A, Tuomainen TP, Voutilainen S (2016) Serum zinc and risk of type 2 diabetes incidence in men: the Kuopio Ischaemic Heart Disease Risk Factor Study. J Trace Elem Med Biol 33:120–124
Yin J, Wang X, Li S, Zhu Y, Chen S, Li P, Luo C, Huang Y, Li X, Hu X, Yang W, Bao W, Shan Z, Liu L (2019) Interactions between plasma copper concentrations and SOD1 gene polymorphism for impaired glucose regulation and type 2 diabetes. Redox Biol 24:101172
Zemrani B, Bines JE (2020) Recent insights into trace element deficiencies: causes, recognition and correction. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 36(2):110–117
Zhang H, Yan C, Yang Z, Zhang W, Niu Y, Li X, Qin L, Su Q (2017) Alterations of serum trace elements in patients with type 2 diabetes. J Trace Elem Med Biol 40:91–96
Zhao T, Huang Q, Su Y, Sun W, Huang Q, Wei W (2019) Zinc and its regulators in pancreas. Inflammopharmacology 27(3):453–464
Acknowledgements
Authors thank all those who participated in this study.
Funding
This work was financially supported by grants from the Key Development Program of Shandong Province (Grant No.:2018GSF118116), the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (Grant No.: ZR2020MH307) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81101484).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
FL and YW conceived and designed study. YC, YX, and XJ contributed to acquisition of data. FL, BL and YW analyzed the data and wrote the paper. All authors assisted in revising the text and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of Shandong First Medical University in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki (ethical approval number is NSFC: No. 2021-112).
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Participants were provided a study overview and verbal consent was attained.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luan, F., Chen, Y., Xu, Y. et al. Associations between whole blood trace elements concentrations and HbA1c levels in patients with type 2 diabetes. Biometals 35, 1011–1022 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-022-00419-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-022-00419-z