Abstract
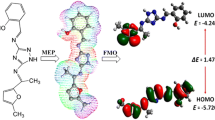
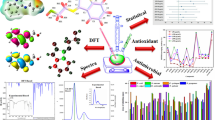
The scientific interest in developing new complexes as inhibitors of bacterial biofilm related infections is constantly rising. The present work describes the chemical synthesis, structural and biological scrutiny of a triazole Schiff base ligand and its corresponding complexes. Triazole Schiff base, (2-methoxy-4-[(1H-1,2,4-triazol-3-ylimino)methyl]phenol) was synthesized from the condensation reaction of 3-amino-1,2,4-triazole and 4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzaldehyde in an equimolar ratio. The triazole ligand (H2L) was characterized by physical (solubility, color, melting point), spectroscopic [UV–visible (UV–Vis), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), proton nuclear magnetic resonance (1H-NMR) and mass spectra (MS)] and micro analysis to evaluate their elemental composition. The bidentate ligand was complexed with transition metal [VO(IV), Fe(II), Co(II), Ni(II), Cu(II) and Zn(II)] in 1:2 molar ratio. The complexes were characterized by physical (color, solubility, decomposition temperature, conductance and magnetic moment), FT-IR, UV–Vis and elemental analysis. Thermal stability and fluorescence properties of the compounds were also determined. Density functional theory based theoretical calculations were accomplished to gain more insight into spectroscopic properties. The frontier molecular orbital analysis revealed that the ligand was less reactive with reduced electron donating capability and more kinetic stability than complexes. The as-synthesized compounds were scrutinized for anti-bacterial and anti-fungal activity against selected strains. Cobalt complex exhibited highest antibacterial activity against Escherichia coli and nickel complex has shown highest antifungal activity against Aspergillus niger. All the compounds also showed good antioxidant activity. The theoretical results reflect consistency with the experimental findings signifying that such compounds could be the promising chemical scaffolds in the near future against microbial infectious.
Graphic abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abu-Dief AM, Abdel-Rahman LH, Abdel-Mawgoud AAH (2020) A robust in vitro anticancer, antioxidant and antimicrobial agents based on new metal-azomethine chelates incorporating Ag(I), Pd(II) and VO(II) cations: probing the aspects of DNA interaction. Appl Organomet Chem 34(2):1–20. https://doi.org/10.1002/aoc.5373
Akin S, Demir EA, Colak A, Kolcuoglu Y, Yildirim N, Bekircan O (2019) Synthesis, biological activities and molecular docking studies of some novel 2,4,5-trisubstituted-1,2,4-triazole-3-one derivatives as potent tyrosinase inhibitors. J Mol Struct 1175:280–286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2018.07.065
Ali A, Al-Hassani R, Hussain D, Jabir M, Meteab H (2020) Anti-proliferative activity and tubulin targeting of novel micro and nanoparticles complexes of 4-amino-3-thion-1,2,4-triazole derivatives. Nano Biomed Eng 12(1):75–89. https://doi.org/10.5101/nbe.v12i1.p75-89
Alphonsa AT, Loganathan C, Anand, SAA, Kabilan S (2016) Molecular structure, NMR, UV-visible, vibrational spectroscopic and HOMO, LUMO analysis of (E)-1-(2,6-bis(4-methoxyphenyl)-3,3-dimethylpiperidine-4-ylidene)-2-(3-(3,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)pyrazin-2-yl)hydrazine by DFT method. J Mol Struct 1106:277–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2015.11.005
Aly HM, Moustafa ME, Nassar MY, Abdelrahman EA (2015) Synthesis and characterization of novel Cu(II) complexes with 3-substituted-4-amino-5-mercapto-1,2,4-triazole Schiff bases: a new route to CuO nanoparticles. J Mol Struct 1086:223–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2015.01.017
Badea M, Calu L, Chifiriuc MC, Bleotu C, Marin A, Ion S, Ioniţă G, Stanică N, Măruţescu L, Lazăr V (2014) Thermal behaviour of some novel antimicrobials based on complexes with a Schiff base bearing 1,2,4-triazole pharmacophore. J Therm Anal Calorim 118(2):1145–1157. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-014-3821-4
Bheemarasetti M, Palakuri K, Raj S, Saudagar P, Gandamalla D, Yellu NR, Kotha LR (2018) Novel Schiff base metal complexes: synthesis, characterization, DNA binding, DNA cleavage and molecular docking studies. J Iran Chem Soc 15(6):1377–1389. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-018-1338-7
Bouhidel Z, Cherouana A, Durand P, Doudouh A, Morini F, Guillot B, Dahaoui S (2018) Synthesis, spectroscopic characterization, crystal structure, Hirshfeld surface analysis and antimicrobial activities of two triazole Schiff bases and their silver complexes. Inorg Chim Acta 482:34–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ica.2018.05.028
Bulut N, Kocyigit UM, Gecibesler IH, Dastan T, Karci H, Taslimi P, Dastan SD, Gulcin I, Cetin A (2018) Synthesis of some novel pyridine compounds containing bis-1,2,4-triazole/thiosemicarbazide moiety and investigation of their antioxidant properties, carbonic anhydrase, and acetylcholinesterase enzymes inhibition profiles. J Biochem Mol Toxic 32(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbt.22006
Chaurasia M, Tomar D, Chandra S (2019) Synthesis, spectral characterization, and DNA binding studies of Co(II), Ni(II), Cu(II) and Zn(II) complexes of Schiff base 2-((1H–1, 2, 4-triazol-3-ylimino)methyl)-5-methoxyphenol. J Mol Struct 1179:431–442. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2018.11.027
Chohan ZH, Hanif M (2013) Antibacterial and antifungal metal based triazole Schiff bases. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 28(5):944–953. https://doi.org/10.3109/14756366.2012.696246
Emam SM, Tolan DA, El-Nahas AM (2020) Synthesis, structural, spectroscopic, and thermal studies of some transition-metal complexes of a ligand containing the amino mercapto triazole moiety. Appl Organomet Chem 34(5):1–26. https://doi.org/10.1002/aoc.5591
Eze FI, Ajali U, Ukoha PO (2014) Synthesis, physicochemical properties, and antimicrobial studies of Iron(III) complexes of ciprofloxacin, cloxacillin, and amoxicillin. Int J Med Chem 2014:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/735602
Frisch E, Hratchian HP, Dennington II RD, Keith TA, Millam J, Nielsen B, Holder AJ Hiscocks J (2009) GaussView Version 5.0.8. Gaussian, Inc. Wallinford
Gaber M, El-Ghamry HA, Fathalla SK, Mansour MA (2018) Synthesis, spectroscopic, thermal and molecular modeling studies of Zn2+, Cd2+ and UO22+ complexes of Schiff bases containing triazole moiety. Antimicrobial, anticancer, antioxidant and DNA binding studies. Mater Sci Eng C 83:78–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2017.11.004
Ghanaat J, Khalilzadeh MA, Zareyee D (2020) Molecular docking studies, biological evaluation and synthesis of novel 3-mercapto-1,2,4-triazole derivatives. Mol Divers 25:223–232. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1068162020010069
Hanif M, Chohan ZH (2013a) Design, spectral characterization and biological studies of transition metal(II) complexes with triazole Schiff bases. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 104:468–476. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2012.11.077
Hanif M, Chohan ZH (2013b) Synthesis, spectral characterization and biological studies of transition metal(II) complexes with triazole Schiff bases. Appl Organomet Chem 27(1):36–44. https://doi.org/10.1002/aoc.2936
Hassan AU, Sumrra SH, Zafar MN, Nazar MF, Mughal EU, Zafar MN, Iqbal M (2021) New organosulfur metallic compounds as potent drugs: synthesis, molecular modeling, spectral, antimicrobial, drug likeness and DFT analysis. Mol Divers. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11030-020-10157-4
Jamil W, Kumari D, Taha M, Khan MN, Baharudin MS, Ali M, Kanwal M, Lashari MS, Khan KM (2018) Synthesis, β-glucuronidase inhibition, and molecular docking studies of 1,2,4-triazole hydrazones. J Iran Chem Soc 15(11):2441–2454. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-018-1433-9
Jin R, Wang Y, Guo H, Long X, Li J, Yue S, Zhang S, Zhang G, Meng Q, Wang C, Yan H, Tang Y, Zhou S (2020) Design, synthesis, biological activity, crystal structure and theoretical calculations of novel 1,2,4-triazole derivatives. J Mol Struct 1202:127234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2019.127234
Joshi R, Kumari A, Singh K, Mishra H, Pokharia S (2019) New diorganotin(IV) complexes of Schiff base derived from 4-amino-3-hydrazino-5-mercapto-4H-1,2,4-triazole: synthesis, structural characterization, density functional theory studies, atoms-in-molecules analysis and antifungal activity. Appl Organomet Chem 33(5):1–22. https://doi.org/10.1002/aoc.4894
Kaproń B, Łuszczki JJ, Płazińska A, Siwek A, Karcz T, Gryboś A, Nowak G, Kocka AM, Walczak KK, Langner E, Szalast K, Marciniak S, Paczkowska M, Cielecka-Piontek J, Ciesla LM, Plech T (2019) Development of the 1,2,4-triazole-based anticonvulsant drug candidates acting on the voltage-gated sodium channels. Insights from in-vivo, in-vitro, and in-silico studies. Eur J Pharm Sci 129:42–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejps.2018.12.018
Kaushal R, Thakur S (2013) Synthesis and biological screening of Schiff base of titanium(IV). Chem Eng Trans 32:1801–1806. https://doi.org/10.3303/CET1332301
Khan B, Naiyer A, Athar F, Ali S, Thakur SC (2021) Synthesis, characterization and anti-inflammatory activity evaluation of 1,2,4-triazole and its derivatives as a potential scaffold for the synthesis of drugs against prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase. J Biomol Struct Dyn 39(2):457–475. https://doi.org/10.1080/07391102.2019.1711193
Machado PM, Cassaro RAA, de Assis VM, Machado SDP, Horn A Jr, Lachter ER (2019) Synthesis, characterization and DFT studies of a new unsymmetrical dinuclear vanadium(IV) complex with a bipodal N2O-donor ligand. J Mol Struct 1193:110–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2019.04.098
Maharramov AM, Mahmudov KT, Kopylovich MN, Pombeiro AJL (2016) Non-covalent interactions in the synthesis and design of new compounds. Wiley, London
Matshwele JT, Nareetsile F, Mapolelo D, Matshamek P, Leteane M, Nkwe DO, Odisitse S (2020) Synthesis of mixed ligand ruthenium(II/III) complexes and their antibacterial evaluation on drug-resistant bacterial organisms. J Chem 2020:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/2150419
Munawar K, Ali S, Tahir M, Khalid N, Abbas Q, Qureshi I, Shahzadi S (2015) Investigation of derivatized Schiff base ligands of 1,2,4-triazole amine and their oxovanadium(IV) complexes: synthesis, structure, DNA binding, alkaline phosphatase inhibition, biological screening, and insulin mimetic properties. Russ J Gen Chem 85(9):2183–2197. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1070363215090248
Naik S, Naik PP, Krishnamurthy G, Venugopal N, Naik N, Naik TR (2020) Synthesis, characterization, DFT studies and biological activity of Ru(III), La(III) and Ce(III) triphenylphosphine complexes containing 2-aminothiazole and 2-aminotriazole. J Inorg Organomet Polym 30:3332–3356. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-020-01492-y
Nasli-Esfahani E, Mohammadi-Khanaposhtani M, Rezaei S, Sarrafi Y, Sharafi Z, Samadi N, Faramarzi MA, Bandarian F, Hamedifar H, Larijani B (2019) A new series of Schiff base derivatives bearing 1,2,3-triazole: design, synthesis, molecular docking, and α-glucosidase inhibition. Arch Pharm 352(8):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1002/ardp.201900034
Nastasa C, Vodnar D, Ionut I, Stana A, Benedec D, Tamaian R, Oniga O, Tiperciuc B (2018) Antibacterial evaluation and virtual screening of new thiazolyl-triazole Schiff bases as potential DNA-gyrase inhibitors. Int J Mol Sci 19(1):222–240. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19010222
Nayak SG, Poojary B (2020) Design, synthesis, in silico docking studies, and antibacterial activity of some thiadiazines and 1,2,4-triazole-3-thiones bearing pyrazole moiety. Russ J Bioorg Chem 46(1):97–106. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1068162020010069
Ngo TC, Dao DQ, Nguyen MT, Nam PC (2017) A DFT analysis on the radical scavenging activity of oxygenated terpenoids present in the extract of the buds of Cleistocalyx operculatus. RSC Adv 7(63):39686–39698. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7RA04798C
Ommenya F, Nyawade E, Andala D, Kinyua J (2020) Synthesis, characte rization and antibacterial activity of Schiff base, 4-chloro-2-{(E)-[(4-fluorophenyl)imino]methyl}phenol metal(II) complexes. J Chem 2020:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/1745236
Patil SA, Unki SN, Kulkarni AD, Naik VH, Badami PS (2011) Co (II), Ni (II) and Cu (II) complexes with coumarin-8-yl Schiff-bases: spectroscopic, in vitro antimicrobial, DNA cleavage and fluorescence studies. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 79:1128–1136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2011.04.032
Qin J, Lei N, Zhu HL (2014) Synthesis, structural characterization, molecular docking, and urease inhibition studies of dinuclear cobalt(II) complexes derived from 3,5-bis(pyridin-2-yl)-4-amino-1,2,4-triazole. Coord Chem 67(7):1279–1289. https://doi.org/10.1080/00958972.2014.909591
Rambabu A, Ganji N, Daravath S, Venkateswarlu K, Rangan K (2020) Mononuclear Co(II), Ni(II) and Cu(II) complexes of the Schiff base, 2-(((4-trifluoromethoxy) phenylimino)methyl)-6-tert-butylphenol: synthesis, spectroscopic characterization, X-ray study and biological evaluation. J Mol Struct 1199:127006. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2019.127006
Sert Y, Doğan OE, Gökce H, Ağar T, Ucun F, Dege N (2020) Synthesis, crystal structure, Hirshfeld surface analysis, spectral characterization, and quantum computational evaluation of (E)-2-(((4-bromophenyl)imino)methyl)-6-methylphenol. J Phys Chem Solids 144:109478. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2020.109478
Shafi S, Alam MM, Mulakayala N, Mulakayala C, Vanaja G, Kalle AM, Pallu R, Alam MS (2012) Synthesis of novel 2-mercapto benzothiazole and 1,2,3-triazole based bisheterocycles: their anti-inflammatory and anti-nociceptive activities. Eur J Med Chem 49:324–333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2012.01.032
Shen QK, Gong GH, Li G, Jin M, Cao LH, Quan ZS (2020) Discovery and evaluation of novel synthetic 5-alkyl-4-oxo-4,5-dihydro-[1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a]quinoxaline-1-carbox-amide derivatives as anti-inflammatory agents. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 35(1):85–95. https://doi.org/10.1080/14756366.2019.1680658
Subashchandrabose S, Krishnan AR, Saleem H, Parameswari R, Sundaraganesan N, Thanikachalam V, Manikandan G (2010) Vibrational spectroscopic study and NBO analysis on bis (4-amino-5-mercapto-1,2, 4-triazol-3-yl) methane using DFT method. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 77(4):877–884. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2010.08.023
Sumrra SH, Chohan ZH (2012) Metal based new triazoles: their synthesis, characterization and antibacterial/antifungal activities. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 98:53–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2012.08.026
Sumrra SH, Chohan ZH (2013) Antibacterial and antifungal oxovanadium(IV) complexes of triazole-derived Schiff bases. Med Chem Res 22(8):3934–3942. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-012-0388-0
Sumrra SH, Hanif M, Chohan ZH (2015) Design, synthesis and in vitro bactericidal/fungicidal screening of some vanadyl(IV) complexes with mono-and di-substituted ONS donor triazoles. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 30(5):800–888. https://doi.org/10.3109/14756366.2014.976565
Sumrra SH, Hanif M, Chohan ZH, Akram MS, Akhtar J, Al-Shehri SM (2016) Metal based drugs: design, synthesis and in-vitro antimicrobial screening of Co(II), Ni(II), Cu(II) and Zn(II) complexes with some new carboxamide derived compounds: crystal structures of N-[ethyl (propan-2-yl) carbamothioyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide and its copper(II) complex. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 31(4):590–598. https://doi.org/10.3109/14756366.2015.1050011
Tadavi SK, Rajput JD, Bagul SD, Hosamani AA, Sangshetti JN, Bendre RS (2017) Synthesis, crystal structures, biological screening and electrochemical analysis of some salen-based transition metal complexes. Res Chem Intermed 43(8):4863–4879. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-017-2917-4
Tarawneh AH, Leon F, Jain SK, Gadetskaya AV, Abu-Orabi ST, Tekwani BL, Cutler SJ (2018) Evaluation of triazole and isoxazole derivatives as potential anti-infective agents. Med Chem Res 27(4):1269–1275. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-018-2146-4
Utthra PP, Raman N (2018) Probing the potency of triazole tethered Schiff base complexes and the effect of substituents on their biological attributes. Int J Biol Macromol 116:194–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.05.009
Vinusha H, Kollur SP, Revanasiddappa H, Ramu R, Shirahatti PS, Prasad MN, Chandrashekar S, Begum M (2019) Preparation, spectral characterization and biological applications of Schiff base ligand and its transition metal complexes. Results Chem 1:100012. https://doi.org/10.33263/LIANBS93.13721388
Wang X, Ling N, Zhang Y, Zeng D, Yang H (2019) Synthesis, crystal structure and biological properties of two Cu(II) complexes based on 1-(benzotriazole-1-methyl)-1-(2-ethylimidazole). J Mol Struct 1193:348–356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2019.05.036
Xavier RJ, Gobinath E (2012) FT-IR, FT-Raman, ab initio and DFT studies, HOMO–LUMO and NBO analysis of 3-amino-5-mercapto-1,2,4-triazole. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 86:242–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2011.10.031
Yakan H, Bakır TK, Çavuş MS, Muğlu H (2020) New β-isatin aldehyde-N,N′-thiocarbohydrazones: preparation, spectroscopic studies and DFT approach to antioxidant characteristics. Res Chem Intermed 46(12):5417–5440. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-020-04270-0
Yasmeen S, Sumrra SH, Akram MS, Chohan ZH (2017) Antimicrobial metal-based thiophene derived compounds. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 32(1):106–112. https://doi.org/10.1080/14756366.2016.1238363
Yousef TA, El-Reash GA, AL-Zahab MA, Safaan MAA (2019) Physicochemical investigations, biological studies of the Cr(III), Mn(II), Fe(III), Co(II), Ni(II), Cu(II), Zn(II), Cd(II), Hg(II) and UO2(VI) complexes of picolinic acid hydrazide derivative: a combined experimental and computational approach. J Mol Struct 1197:564–575. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2019.07.088
Zafar W, Sumrra SH, Chohan ZH (2021) A review: Pharmacological aspects of metal based 1,2,4-triazole derived Schiff bases. Eur J Med Chem 222:113602. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2021.113602
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to the Higher Education Commission (HEC) of Pakistan for providing financial support through the NRPU Project # 7800. The authors also express their appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Khalid University Saudi Arabia for funding through research groups program under Grant Number R.G.P. 2/3/42.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest:
The authors report no declarations of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sumrra, S.H., Zafar, W., Javed, H. et al. Facile synthesis, spectroscopic evaluation and antimicrobial screening of metal endowed triazole compounds. Biometals 34, 1329–1351 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-021-00345-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-021-00345-6