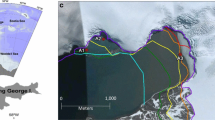
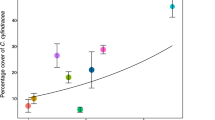
Abstract
Posidonia oceanica seagrass meadows are one of most resistant Mediterranean habitats to invasion by the green alga Caulerpa cylindracea. We evaluated the hypothesis that light reduction caused by the seagrass canopy can limit algal photosynthesis and growth and hence potentially explain this resistance. To this end, we analysed light regimes and C. cylindracea biomass and photoacclimative variables measured outside and within P. oceanica meadows at different sites and during contrasting times. The success of photoacclimatory responses was assessed using an ecophysiological, carbon balance approach. C. cylindracea abundance significantly varied depending on the sampling site and time, but its biomass was always 10- to 50-fold higher outside the meadow. Outside the canopy, C. cylindracea showed characteristic morphological and photosynthetic plasticity closely related to the spatio-temporal variation in light regimes, which varied as expected with depth and season. Under these conditions, the alga was able to perform successful photoacclimation, although some degree of light limitation was observed at the deepest sites and in winter conditions, as indicated by near-zero carbon balance and lower algal abundances. Within the P. oceanica canopy, light was reduced by 60–89 % relative to that outside and was at its lowest levels recorded (1–7 % of the sub-surface irradiance), close to the minimum light requirements for growth. Light limitation was evident inside the canopy in the winter sampling, when the photosynthetic plasticity of the alga appears to be exceeded and when carbon balances were clearly negative. Therefore, light appears to play a key role in the apparent incapacity of C. cylindracea to penetrate within P. oceanica meadow edges.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arenas F, Sánchez I, Hawkins SJ, Jenkins SR (2006) The invasibility of marine algal assamblages: role of functional diversity and identity. Ecology 87:2851–2861
Argyrou M, Demetropoulos A, Hadjichristophorou M (1999) Expansion of the macroalga Caulerpa racemosa and changes in soft bottom macrofaunal assemblages in Moni Bay, Cyprus. Oceanol Acta 22:517–528
Balata D, Piazzi L, Cinelli F (2004) A comparison among assemblages in areas invaded by Caulerpa taxifolia and Caulerpa racemosa on a subtidal Mediterranean rocky bottom. Mar Ecol 25:1–13
Balestri E, Cinelli F, Lardicci C (2003) Spatial variation in Posidonia oceanica structural, morphological and dynamic features in a northwestern Mediterranean coastal area: a multi-scale analysis. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 250:51–60
Baly ECC (1935) The kinetics of photosynthesis. Proc R Soc Lond Ser B Biol Sci 117:218–239
Bernardeau-Esteller J, Marín-Guirao L, Sandoval-Gil JM, Ruiz JM (2011) Photosynthesis and daily metabolic carbon balance of the invasive Caulerpa racemosa var. cylindracea (Chlorophyta: Caulerpales) along a depth gradient. Sci Mar 75:803–810
Boudouresque CF, Meisnez A (1982) Découverte de l’herbier de Posidonie. Parc National de Port-Cros, Parc Naturel Regional de la Corse, Cahier n. 4, p. 79
Britton-Simmons KH (2006) Functional group diversity, resource pre-emption and the genesis of invasion resistance in a community of marine algae. Oikos 113:395–401
Buia MC, Zupo V, Mazella L (1992) Primary production and growth dynamics in Posidonia oceanic. Mar Ecol 13:2–16
Buia MC, Gambi MC, Terlizzi A, Mazzella L (2001). Colonization of Caulerpa racemosa along the southern Italian coasts: distribution, phenological variability and ecological role. In: Gravez V, Ruitton S, Boudouresque CF, Le Diréac’h L, Meinesz A, Scabbia G, Verlaque M (eds) Proceedings of fourth international workshop on Caulerpa taxifolia, pp 350–360
Bulleri F, Benedetti-Cecchi L (2008) Facilitation of the introduced green alga Caulerpa racemosa by resident algal turfs: experimental evaluation of underlying mechanisms. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 364:77–86
Bulleri F, Balata D, Bertocci I, Tamburello L, Benedetti-Cecchi L (2010) The seaweed Caulerpa racemosa on Mediterranean rocky reefs: from passenger to driver of ecological change. Ecology 91:2205–2212
Calvert HE (1976) Culture studies on some Florida species of Caulerpa: morphological responses to reduced illumination. Br Phycol J 11:203–214
Calvín-Calvo JC, Franco I, Marín A, Martínez A, Belmonte A, Ruiz JM (1998) El litoral sumergido de la región de Murcia, Cartografía bionómica y valores ambientales. Dirección General del Medio Natural, Comunidad Autónoma de la Región de Murcia, Murcia Region, Spain
Canhan CD, Denslow IS, Platt WI, Runkle JR, Spies TA, White PS (1990) Light regimes beneath closed canopies and tree-fall gaps in temperate and tropical forest. Can J For Res 20:620–631
Capiomont A, Breugnot E, den Hann M, Meinesz A (2005) Phenology of a deep-water population of Caulerpa racemosa var. cylindracea in the northwestern Mediterranean Sea. Bot Mar 48:80–83
Cebrian E, Ballesteros E (2009) Temporal and spatial variability in shallow- and deep-water populations of the invasive Caulerpa racemosa var. cylindracea in the Western Mediterranean. Estuar Coast Shelf Scib 83:469–474
Ceccherelli G, Campo D (2002) Different effects of Caulerpa racemosa on two co-occurring seagrasses in the Mediterranean. Bot Mar 45:71–76
Ceccherelli G, Piazzi L, Cinelli F (2000) Response of non-indigenous Caulerpa racemosa (Forsskål) J. Agardh to the native seagrass Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile: effect of density of shoots and orientation of edges of meadows. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 243:227–240
Chisholm JRM, Jaubert JM (1997) Photoautotrophic metabolism of Caulerpa taxifolia (Chlorophyta) in the NW Mediterranean. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 153:113–123
Clark RP, Edwards MS, Foster MS (2004) Effects of shade from multiple kelp canopies on an understory algal assemblage. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 267:107–119
Collado-Vides L, Robledo D (1999) Morphology and photosynthesis of Caulerpa (Chlorophyta) in relation to growth form. J Phycol 35:325–330
Collier CJ, Lavery PS, Ralph PJ, Masini RJ (2008) Physiological characteristics of the seagrass Posidonia sinuosa along a depth-related gradient of light availability. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 353:69–75
Dalla Via J, Strumbauer C, Schönweger G, Sötz E, Mathekowitsch S, Stifter M, Rieger R (1998) Light gradients and meadow structure in Posidonia oceanica: ecomorphological and functional correlates. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 163:267–278
De Senerpont Domis LN, Fama P, Bartlett AJ, Van Reine WFP, Espinosa CA, Trono GC (2003) Defining taxon boundaries in members if the morphologically and genetically plastic genus Caulerpa (Caulerpales, Chlorophyta). J Phycol 39:1019–1037
Dennison WC (1990) Chlorophyll content. In: Phillips RC, McRoy CP (eds) Seagrass research methods. UNESCO, Paris, pp 83–86
Dennison WC, Alberte RS (1982) Photosynthetic responses of Zostera marina L. (eelgrass) to in situ manipulations of light intensity. Oecologia 55:137–144
Dennison WC, Alberte RS (1985) Role of daily light period in the depth distribution of Zostera marina (eelgrass). Mar Ecol Prog Ser 25:51–61
Duarte C, Fourqurean JW, Krause-Jensen D, Olesen B (2006) Dynamics of seagrass stability and change. In: Larkum AWD, Orth RJ, Duarte CM (eds) Seagrass: biology, ecology and conservation. Springer, The Netherlands, pp 271–294
Dumay O, Fernández C, Pergent G (2002) Primary productivity and vegetative cycle in Posidonia oceanica when in competition with the green algae Caulerpa taxifolia and Caulerpa racemosa. J Mar Biol Assoc of the UK 82:379–387
Dunton KH, Shell DM (1986) Seasonal carbon budget and growth of Laminaria solidungula in the Alaskan high Artic. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 31:57–66
Enríquez S, Pantoja-Reyes NI (2005) From-function analysis of the effect of canopy morphology on leaf self-shading in the seagrass Thalassia testudinum. Oecologia 145:235–243
Enriquez S, Agusti S, Duarte CM (1992) Light Absorption by seagrass Posidonia oceanica leaves. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 86:201–204
Enríquez S, Marbà N, Cebrián J, Duarte CM (2004) Annual variation in leaf photosynthesis and leaf nutrient content of four Mediterranean seagrasses. Bot Mar 47:295–306
Falkowski PG, Raven JA (2007) Aquatic photosynthesis. Blackwell Scientific Publishers, Oxford
Flagella MM, Lorenti M, Buia MC (2008) Temperature response in a shallow-water Mediterranean population of Caulerpa racemosa var. cylindracea (Caulerpales, Chlorophyta), and a possible strategy of season anticipation. Bot Mar 51:277–278
Gagne JA, Mann KH, Chapman ARO (1982) Seasonal patterns of growth and storage in Laminaria longicruris in relation to differing patterns of availability of nitrogen in the water. Mar Biol 69:91–101
Gatusso JP, Jaubert J (1985) Photosynthesis and respiration of Caulerpa racemosa (Chlorophyceae, Caulerpales) grown in aquaria: effects of light and temperature. Bot Mar 28:327–332
Giaccone G, Di Martino V (1995) La vegetazione a Caulerpa racemosa (Forsskål) J. Agardh nella Baia di S. Panagia (Sicilia Sud-Orientale). Boll Accad Gioenia Sci Nat Catania 28:59–73
Gómez I, Wiencke C (1998) Seasonal changes in C, N and major organic compounds and their significance to morpho-functional processes in the endemic Antarctic brown alga Ascoseira mirabilis. Polar Biol 19:115–124
Gómez I, Weykam G, Klöser H, Wiencke C (1997) Photosynthetic light requirements, metabolic carbon balance and zonation of sublitoral macroalgae from King George Island (Antarctica). Mar Ecol Prog Ser 148:281–293
Holmer M, Marbà N, Lamote M, Duarte CM (2009) Deterioration of sediment quality in seagrass meadows (Posidonia oceanica) invaded by macroalgae (Caulerpa sp). Estuar Coasts 32:456–466
Infantes E, Terrados J, Orfila A (2011) Assesment of substratum effect on the distribution of two invasive Caulerpa (Chlorophyta) species. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 91:434–441
Katsanevakis S, Issaris Y, Poursanidis D, Thessalou-Legaki M (2010) Vulnerability of marine habitats to the invasive green alga Caulerpa racemosa var cylindracea within a marine protected area. Mar Environ Res 70:210–218
Kirk JTO (1994) Light and photosynthesis in aquatic ecosystems, 2nd edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Klein J, Verlaque M (2008) The Caulerpa racemosa invasion: a critical review. Mar Pollut Bull 56:205–225
Klein J, Verlaque M (2009) Macroalgal assemblages of disturbed coastal detritic bottoms subject to invasive species. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 82:461–468
Koch EW (2001) Beyond light: physical, geological and geochemical parameters as possible submerged aquatic vegetation habitat requirements. Estuaries 24:1–17
Lenzi M, Franchi E, Giovani A, Micarelli P, Perra G, Roffilli R,Solari D, Focardi S (2007) Change in the phytobenthos settlement along the Santa Liberata coast (Southern Toscany, Italy). In: United Nations Environment Programme (ed) Proceedings of the 3rd Mediterranean symposium on marine vegetation. Tunis, Tunisia pp 88–95
Lichtenthaler HK, Wellburn AR (1983) Determination of total carotenoids and chlorophyll a and b of leaf extracts in different solvents. Biochem Soc T 603:591–592
Littler MM, Littler DS, Blair SM, Norris JN (1986) Deep-water plant communities from an unchartered seamount of San Salvador Island, Bahamas: distribution, abundance and primary productivity. Deep Sea Res 33:881–892
Lobban CS, Harrison PJ (1997) Seaweed ecology and physiology. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Londsale WM (1999) Global patterns of plants invasions and the concept of invasibility. Ecology 80:1522–1536
Lüning K (1990) Seaweeds: their environment, biogeography and ecophysiology. Wiley, New York
Markager S, Sand-Jensen K (1994) The physiology and ecology of light-growth relationships in macroalgae. In: Round FE, Chapman DJ (eds) Progress in Phycological Research, 10. Biopress, Bristol, pp 209–298
Matta JL, Chapman DJ (1991) Photosynthetic responses and daily carbon balance of Colpomenia peregrina: seasonal variations and differences between intertidal and subtidal populations. Mar Biol 108:303–313
Montefalcone M, Morri C, Peirano A, Albertelli G, Bianchi CN (2007) Substitution and phase shift within Posidonia oceanica seagrass meadows of NW Mediterranean Sea. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 75:63–71
NISC. The National Invasive Species Council. 2006. Invasive species definition clarification and guidance white paper. Invasive Species Advisory Committee. http://www.invasivespecies.gov. Accesed 15 Sept 2011
Nizamuddin M (1991) The green marine algae of Lybia. Elga, Bern
Occhipinti-Ambrogi A, Savini D (2003) Biological invasions as a component of global change in stressed marine ecosystems. Mar Pollut Bull 46:542–551
Ohba H, Enomoto S (1987) Culture studies on Caulerpa (Caulerpales, Chlorophyceae) II. Morphological variation of C. racemosa var. laetevirens under various culture conditions. Jpn J Phycol 25:178–188
Olesen B, Enríquez S, Duarte CM, Sand-Jensen K (2002) Depth-acclimation of photosynthesis, morphology and demography of Posidonia oceanica and Cymodocea nodosa in the Spanish Mediterranean Sea. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 236:89–97
Pérez-Lloréns JL, Vergara JJ, Pino RR, Hernández I, Peralta G, Niell FX (1996) The effect of photacclimatation on the photosynthetic physiology of Ulva curvata and Ulva rotundata (Ulvales, Chlorophyta). Eur J Phycol 31:349–359
Pergent G, Pergent-Martini C, Boudouresque CF (1995) Utilisation de l’herbier a Posidonia oceanica comme indicateur biologique de la qualité du milieu litoral en Mediterranée: etat des connaissances. Mésogée 54:3–27
Pergent G, Bazairi H, Bianchi CN, Boudouresque CF, Buia MC, Clabaut P, Harmelin M, Mateo MA, Montefalcone M, Morri C, Orfanidis S, Pergent-Martini C, Semroud R, Serrano O, Verlaque M (2012) Mediterranean seagrass meadows: resilience and contribution to climate change mitigation, A short summary. IUCN publ. Gland, Málaga. pp 1–40
Piazzi L, Balata D (2008) The spread of Caulerpa racemosa var. cylindracea in the Mediterranean Sea: an example of how biological invasions can influence beta diversity. Mar Environ Res 65:50–61
Piazzi L, Cinelli F (1999) Development and seasonal dynamics of a population of the tropical alga Caulerpa racemosa (Forsskål) J Agardh in the Mediterranean. Cryptogam Algol 20:295–300
Piazzi L, Acunto S, Magri M, Rindi F, Balestri E (1997a) Preliminary observations on the spread of Caulerpa racemosa (Forsskål) J. Agardh in Meloria Shoals (Livorno, Italy). Biol Mar Medit 4:426–428
Piazzi L, Balestri E, Magri M, Cinelli F (1997b) Expansion de l’algue tropicale Caulerpa racemosa (Forsskål) J. Agardh (Bryopsidophyceae, Chlorophyta) le long de la côte toscane (Italie). Cryptogam Algol 18:343–350
Piazzi L, Cecherelli G, Cinelli F (2001) Threat to macroalgal diversity: effects of the introduced green alga Caulerpa racemosa in the Mediterranean. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 210:149–159
Piazzi L, Meinesz A, Verlaque M, Akçali B, Antolic B, Argyrou M, Balata D, Ballesteros E, Calvo S, Cinelli F, Cirik S, Cossu A, D’archino R, Djellouli AS, Javel F, Lanfranco E, Mifsud C, Pala D, Panayotidis P, Peirano A, Pergent G, Petrocelli A, Ruitton S, Zuljevic A, Ceccherelli G (2005) Invasion of Caulerpa racemosa var. cylindracea (Caulerpales, Chlorophyta) in the Mediterranean Sea: an assessment of the spread. Cryptogam Algol 26:189–202
Procaccini G, Buia MC, Gambi MC, Pérez M, Pergent G, Pergent-Martini C, Romero J (2003) The Seagrasses of the Western Mediterranean. In: Green EP, Short FT (eds) World of atlas seagrasses. University of California press, Berkeley, pp 43–58
Quinn G, Keough M (2002) Experimental design and data analysis for biologists. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Ralph PJ, Durako MJ, Enríquez S, Collier CJ, Doblin MA (2007) Impact of light limitation on seagrasses. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 350:176–193
Raniello R, Lorenti M, Brunet C, Buia MC (2004) Photosynthetic plasticity of an invasive variety of Caulerpa racemosa in a coastal Mediterranean area: light harvesting capacity and seasonal acclimation. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 271:113–120
Raniello R, Lorenti M, Brunet C, Buia MC (2006) Photoacclimation of the invasive alga Caulerpa racemosa var. cylindracea to depth and daylight patterns and putative new role for siphonaxanthin. Mar Ecol 27:20–30
Raniello R, Mollo E, Lorenti M, Gavagnin M, Buia MC (2007) Phytotoxic activity of Caulerpenyne from the Mediterranean invasive variety of Caulerpa racemosa: a potential allelochemical. Biol Invasions 9:361–368
Robledo D, Freile-Pelegrín Y (2005) Seasonal variations in photosynthesis and biochemical composition of Caulerpa spp (Bryopsidales, Chlorophyta) from the Gulf of Mexico. Phycologia 44:312–319
Romero J (1989) Primary production of Posidonia oceanica beds in the Medas Islands (Girona, NE Spain). In: Boudouresque CF, Meinesz A, Fresi E, Gravez V (eds) International workshop on Posidonia oceanica beds 2. GIS Posidonie Publ, Marseille, pp 85–91
Rosemberg C, Ramus J (1982) Ecological growth strategies in the seaweed Gracilaria foliifera (Rodophyceae) and Ulva sp (Chlorophyceae) soluble nitrogen and reverve carbohydrates. Mar Biol 66:247–251
Ruitton S, Verlaque M, Boudouresque CF (2005) Seasonal changes of the introduced Caulerpa racemosa var. cylindracea (Caulerpales, Chlorophyta) at the northwest limit of its Mediterranean range. Aquat Bot 82:55–70
Ruiz JM, Barberá C, Marín-Guirao L, García R, Bernardeau J, Sandoval JM (2010a). Las praderas de Posidonia en Murcia. Red de seguimiento y voluntariado ambiental. IEO Institutional Digital Repository. http://hdl.handle.net/10508/495. Accessed 28 Feb 2012
Ruiz JM, Marco-Méndez C, Sánchez-Lizaso JL (2010b) Remote influence of off-shore fish farm waste on Mediterranean seagrass (Posidonia oceanica) meadows. Mar Environ Res 69:118–126
Ruiz JM, Marín-Guirao L, Bernardeau-Esteller J, Ramos-Segura A, García-Muñoz R, Sandoval-Gil JM (2011) Spread of the invasive alga Caulerpa racemosa var. cylindracea (Caulerpales, Chlorophyta) along the Mediterranean coast of the Murcia region (SE Spain). Anim Biodivers Conserv 34:73–82
Scurlock JMO, Asner GP, Gower ST (2001) Global leaf area index from field measurements, 1932-2000 Oak Ridge National Laboratory Distributed Active Archive Center, Oak Ridge, Tennessee, USA. http://daac.ornl.gov/VEGETATION/guides/LAI_guide.html. Accessed 4 Feb 2015
Streftaris N, Zenetos A (2006) Alien marine species in the Mediterranean—the 100 ‘worst invasives’ and their impact. Mediterr Mar Sci 7:87–118
Templado J, Ballesteros E, Garcia-Raso JE, San Martín G, Lopez-Garcia E, Salas C, Luque AA, Sanchez-Lizaso JL, Moreno D (2004) La comunidad posidonícola. In: Luque AA, Templado J (eds) Praderas y bosques marinos de Andalucía. Consejería de Medio ambiente, Junta de Andalucía, Sevilla, pp 89–116
Ter Braack CJF, Šmilauer P (2002) CANOCO reference manual and CanoDraw for Windows user´s guide: Software for canonical community ordination (version 4.5). Microcomputer Power, Ithaca
Terrados J, Ros JD (1992) The influence of temperature on seasonal variation of Caulerpa prolifera (Forsskal) lamouroux photosynthesis and respiration. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 162:199–212
Underwood AJ (1997) Experiments in ecology. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Vargas-Yáñez M, García-Martínez MC, Moya Ruiz F, Tel E, Parilla G, Lavín A, García MJ, Fraile-Nuez E et al. (2010) Cambio climático en el Mediterráneo español. Temas de Oceanografía 3, Instituto Español de Oceanografía, Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación, Spain
Vázquez-Luis M, Sánchez-Jerez P, Bayle-Sempere JT (2008) Changes in amphipod (Crustacea) assemblages associated with shallow-water algal habitats invaded by Caulerpa racemosa var. cylindracea in the western Mediterranean Sea. Mar Environ Res 65:416–426
Zimmerman RC (2006) Light and photosynthesis in seagrass meadows. In: Larkum AWD, Orth RJ, Duarte CM (eds) Seagrasses: biology, ecology and conservation. Springer, The Netherlands, pp 303–321
Acknowledgments
This research was funded by the Servicio de Pesca y Acuicultura (Dirección General de Ganadería y Pesca of the Regional Government of Murcia (Comunidad Autónoma de Murcia), the European Fisheries Fund and a research grant awarded to J. B.-E. and J.M. S.-G. by the University of Alicante. The authors sincerely appreciate the enthusiastic efforts and expertise of the technicians Rocio García-Muñoz and Aranzazu Ramos-Segura and Tamara Huete-Staufer, during the field and analytical parts of the work. We really appreciate all constructive suggestions provided by the anonymous reviewers, and in particular we are grateful to the associate editor of the journal Erik Ladd Jonhson for his invaluable help and assistance for a proper statistical data analyses. We also thank the Dirección General (D.G.) de Recursos Pesqueros y Acuicultura of the Spanish Ministry of the Environment (Ministerio de Agricultura, Alimentación y Medio Ambiente) and the D.G. de Medio Ambiente and D.G. de Ganadería y Pesca of the regional government for their support in field sampling performed in the Cabo Palos-Islas Hormigas Marine Reserve and in the declared Zone of Special Bird Proteccion Isla Grosa (ZEPA ES0000200) of the Natura 2000 Network.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marín-Guirao, L., Bernardeau-Esteller, J., Ruiz, J.M. et al. Resistance of Posidonia oceanica seagrass meadows to the spread of the introduced green alga Caulerpa cylindracea: assessment of the role of light. Biol Invasions 17, 1989–2009 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10530-015-0852-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10530-015-0852-0