Abstract
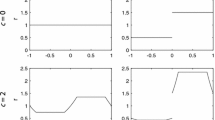
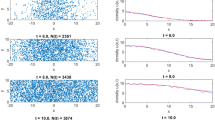
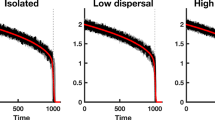
A few spatiotemporal models of population dynamics are considered in relation to biological invasion and biological control. The patterns of spread in one and two spatial dimensions are studied by means of extensive numerical simulations. We show that, in the case that population multiplication is damped by the strong Allee effect (when the population growth rate becomes negative for small population density), in a certain parameter range the spread can take place not via the intuitively expected circular expanding population front but via motion and interaction of separate patches. Alternatively, the patchy spread can take place in a system without Allee effect as a result of strong environmental noise. We then show that the phenomenon of deterministic patchy invasion takes place ‘at the edge of extinction’ so that a small change of controlling parameters either brings the species to extinction or restores the travelling population fronts. Moreover, we show that the regime of patchy invasion in two spatial dimensions actually takes place when the species go extinct in the corresponding 1-D system.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G Abramson V Kenkre T Yates R Parmenter (2003) ArticleTitleTraveling waves of infection in the Hantavirus epidemics Bulletin of Mathematical Biology 65 519–534 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0092-8240(03)00013-2 Occurrence Handle12749537
Allen L (2003) An Introduction to Stochastic Processes with Applications to Biology. Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River, NJ, 424 pp
Anishenko V, Astakov V, Neiman A, Vadivasova T and Schimansky-Geier L (2003) Nonlinear Dynamics of Chaotic and Stochastic Systems. Tutorial and Modern Developments. Springer Series in Synergetics. Springer, Berlin, 530 pp
E Beltrami TO Carroll (1994) ArticleTitleModeling the role of viral disease in recurrent phytoplankton blooms Journal of Mathematical Biology 32 857–863 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00168802
J Chattopadhyay S Pal (2002) ArticleTitleViral infection on phytoplankton–zooplankton system – a mathematical model Ecological Modelling 151 15–28 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0304-3800(01)00415-X
J Chattopadhyay R Sarkar S Pal (2003) ArticleTitleDynamics of nutrient–phytoplankton interaction in the presence of viral infection BioSystems 68 5–17 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0303-2647(02)00055-2 Occurrence Handle12543518
F Courchamp G Sugihara (1999) ArticleTitleBiological control of alien predator populations to protect native island prey species from extinction Ecological Applications 9 112–123
Diekmann O and Heesterbeek JAP (2000) Mathematical Epidemiology of Infectious Diseases: Model Building, Analysis and Interpretation.Wiley, Chichester, 388 pp
K Dietz D Schenzle (1985) ArticleTitleProportionate mixing models for age-dependent infection transmission Journal of Mathematical Biology 22 117–120 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00276550 Occurrence Handle3926925 Occurrence HandleMR802739
Drake JA, Mooney HA, di Castri F, Groves RH, Kruger FJ, Rejmanek M and Williamson M (eds) (1989) Biological Invasions: Global Perspective. John Wiley, New York, 656 pp
WF Fagan JG Bishop (2000) ArticleTitleTrophic interactions during primary succession: herbivores slow a plant reinvasion at Mount St. Helens American Naturalist 155 238–251 Occurrence Handle10.1086/303320 Occurrence Handle10686163
BM Fitzgerald CR Veitch (1985) ArticleTitleThe cats of Herecopare Island, New Zealand: their hystory, ecology and effects on birdlife New Zealand Journal of Zoology 12 319–330
J Fuhrman (1999) ArticleTitleMarine viruses and their biogeochemical and ecological effects Nature 399 541–548 Occurrence Handle10.1038/21119 Occurrence Handle10376593
MD Gastrich JA Leigh-Bell CJ Gobler OR Anderson SW Wilhelm M Bryan (2004) ArticleTitleViruses as potential regulators of regional brown tide blooms caused by the alga, Aureococcus anophagefferens Estuaries 27 112–119
B Grenfell O Bjørnstad J Kappey (2001) ArticleTitleTravelling waves and spatial hierarchies in measles epidemics Nature 414 716–723 Occurrence Handle10.1038/414716a Occurrence Handle11742391
HW Hethcote (2000) ArticleTitleThe mathematics of infectious diseases SIAM Review 42 599–653
D Higham (2001) ArticleTitleAn algorithmic introduction to numerical simulation of stochastic differential equations SIAM Review 43 525–546
EE Holmes MA Lewis JE Banks RR Veit (1994) ArticleTitlePartial differential equations in ecology: spatial interactions and population dynamics Ecology 75 17–29
S Jacquet M Heldal D Iglesias-Rodriguez A Larsen W Wilson G Bratbak (2002) ArticleTitleFlow cytometric analysis of an Emiliana huxleyi bloom terminated by viral infection Aquatic Microbial Ecology 27 111–124
S Jiang J Paul (1998) ArticleTitleSignificance of lysogeny in the marine environment: studies with isolates and a model of lysogenic phage production Microbial Ecology 35 235–243 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s002489900079 Occurrence Handle9569281
TH Keitt MA Lewis RD Holt (2001) ArticleTitleAllee effects, invasion pinning, and species borders American Naturalist 157 203–216 Occurrence Handle10.1086/318633
Kloeden P and Platen E (1992) Numerical Solution of Stochastic Differential Equations. Applications of Mathematics. Volume 23, Springer, Berlin, 512 pp
R Lande (1998) ArticleTitleDemographic stochastisity and Allee effect on a scale with isotropic noise Oikos 83 353–358
MA Lewis (2000) ArticleTitleSpread rate for a nonlinear stochastic invasion Journal of Mathematical Biology 41 430–454 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s002850000022 Occurrence Handle11151707
Lewis MA and Kareiva P (1993) Allee dynamics and the spread of invading organisms. Theoretical Population Biology 42: 141–158
MA Lewis S Pacala (2000) ArticleTitleModeling and analysis of stochastic invasion processes Journal of Mathematical Biology 41 387–429 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s002850000050 Occurrence Handle11151706
J Lin V Andreasen R Casagrandi S Levin (2003) ArticleTitleTraveling waves in a model of influenza A drift Journal of Theoretical Biology 222 437–445 Occurrence Handle12781742 Occurrence HandleMR2068368
H Malchow SV Petrovskii (2002) ArticleTitleDynamical stabilization of an unstable equilibrium in chemical and biological systems Mathematical and Computer Modelling 36 307–319 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0895-7177(02)00127-9
H Malchow SV Petrovskii AB Medvinsky (2002) ArticleTitleNumerical study of plankton-fish dynamics in a spatially structured and noisy environment Ecological Modelling 149 247–255 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0304-3800(01)00467-7
H Malchow F Hilker SV Petrovskii K Brauer (2004) ArticleTitleOscillations and waves in a virally infected plankton system, I. The lysogenic stage Ecological Complexity 1 211–223 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.ecocom.2004.03.002
H McCallum N Barlow J Hone (2001) ArticleTitleHow should pathogen transmission be modelled? Trends in Ecology and Evolution 16 295–300 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0169-5347(01)02144-9 Occurrence Handle11369107
AB Medvinsky SV Petrovskii IA Tikhonova H Malchow BL Li (2002) ArticleTitleSpatiotemporal complexity of plankton and fish dynamics SIAM Review 44 311–370
AY Morozov SV Petrovskii BL Li (2004) ArticleTitleBifurcations and chaos in a predator–prey system with the Allee effect Proceedings of Royal Society of London B 271 1407–1414 Occurrence Handle10.1098/rspb.2004.2733
Murray JD (1989) Mathematical Biology. Springer, Berlin. 849 pp
Nisbet RM and Gurney WSC (1982) Modelling Fluctuating Populations. Wiley & Sons, Chichester, 398 pp
A Nold (1980) ArticleTitleHeterogeneity in disease-transmission modeling Mathematical Biosciences 52 227–240 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0025-5564(80)90069-3
A Ortmann J Lawrence C Suttle (2002) ArticleTitleLysogeny and lytic viral production during a bloom of the cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp Microbial Ecology 43 225–231 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s00248-001-1058-9 Occurrence Handle12023729
Owen M and Lewis MA (2001) How predation can slow, stop or reverse a prey invasion. Bulletin of Mathematical Biology 63: 655–684
IM Parker D Simberloff WM Londsdale K Goodell M Wonham PM Kareiva MH Williamson B Von Holle PB Moyle JE Byers L Goldwasser (1999) Impact: toward a framework for understanding the ecological effects of invaders. Biological Invasions 1 3–19
M Pascual (1993) ArticleTitleDiffusion-induced chaos in a spatial predator–prey system Proceedings of Royal Society of London B 251 1–7
SV Petrovskii H Malchow (2000) ArticleTitleCritical phenomena in plankton communities: KISS model revisited Nonlinear Analysis: Real World Applications 1 37–51 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0362-546X(99)00392-2 Occurrence HandleMR1794937
Petrovskii SV and Venturino E (2004) Patterns of patchy spatial spread in models of epidemiology and population dynamics. University of Torino, preprint #20/2004 (available online: http://www.dm.unito.it/quadernidipartimento/quaderni.php)
SV Petrovskii AY Morozov E Venturino (2002a) ArticleTitleAllee effect makes possible patchy invasion in a predator–prey system Ecology Letters 5 345–352 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1461-0248.2002.00324.x
SV Petrovskii ME Vinogradov AY Morozov (2002b) ArticleTitleSpatio-temporal horizontal plankton patterns caused by biological invasion in a two-species model of plankton dynamics allowing for the Allee effect Oceanology 42 384–393
Petrovskii SV, Malchow H and Li BL (2005a) An exact solution of a diffusive predator–prey system. Proceedings of Royal Society of London A 461: 1029–1053
Petrovskii SV, Morozov AY and Li BL (2005b) Regimes of biological invasion in a predator–prey system with the Allee effect. Bulletin of Mathematical Biology 67: 637–661
Pimentel D (2002) Biological Invasions: Economic and Environmental Costs of Alien Plant, Animal and Microbe Species. CRC Press, New York, 524 pp
M Scheffer (1991) ArticleTitleFish and nutrients interplay determines algal biomass: a minimal model Oikos 62 271–282
JA Sherratt (2001) ArticleTitlePeriodic travelling waves in cyclic predator–prey systems Ecology Letters 4 30–37 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1461-0248.2001.00193.x
JA Sherratt MA Lewis AC Fowler (1995) ArticleTitleEcological chaos in the wake of invasion Proceedings of US National Academy of Science 92 2524–2528
Shigesada N and Kawasaki K (1997) Biological Invasions: Theory and Practice. Oxford University Press, Oxford, 205 pp
C Suttle (2000) Ecological, evolutionary, and geochemical consequences of viral infection of cyanobacteria and eukaryotic algae C Hurst (Eds) Viral Ecology Academic Press San Diego 247–296
K Tarutani K Nagasaki M Yamaguchi (2000) ArticleTitleViral impachts on total abundance and clonal composition of the harmful bloom-forming phytoplankton Heterosigma akashiwo Applied and Environmental Microbiology 66 IssueID11 4916–4920 Occurrence Handle10.1128/AEM.66.11.4916-4920.2000 Occurrence Handle11055943
Thomas J (1995) Numerical partial differential equations: Finite difference methods. Texts in Applied Mathematics. Volume 22. Springer, New York, 477 pp
AI Volpert VA Volpert VA Volpert (1994) Travelling Wave Solutions of Parabolic Systems American Mathematical Society Providence 455
ME Vinogradov EA Shushkina EI Musaeva PY Sorokin (1989) ArticleTitleA new invader to the Black Sea – ctenophore Mnemiopsis leidyi (A. Agassiz) (Ctenophora Lobata) Oceanology 29 293–299
ME Vinogradov EA Shushkina LL Anochina SV Vostokov NV Kucheruk TA Lukashova (2000) ArticleTitleMass development of ctenophore Beroe ovata Eschscholtz off the north-eastern coast of the Black Sea Oceanology 40 52–55
K Wommack R Colwell (2000) ArticleTitleVirioplankton: viruses in aquatic ecosystems Microbial Molecular Biology Review 64 IssueID1 69–114 Occurrence Handle10.1128/MMBR.64.1.69-114.2000
V Zhdanov (2003) ArticleTitlePropagation of infection and the prey–predator interplay Journal of Theoretical Biology 225 489–492 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0022-5193(03)00291-1 Occurrence Handle14615207 Occurrence HandleMR2079302
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Petrovskii, S., Malchow, H., Hilker, F. et al. Patterns of Patchy Spread in Deterministic and Stochastic Models of Biological Invasion and Biological Control. Biol Invasions 7, 771–793 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10530-005-5217-7
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10530-005-5217-7