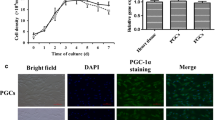
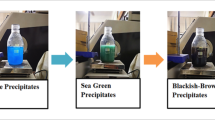
Abstract
Objectives
Granulosa cells are associated with steroidogenesis and ovarian function in females. Aims of the study are to understand the effects of gold nanoparticles (AuNP) on steroidogenesis and apoptotic pathway associated genes in buffalo granulosa cells.
Results
The AuNP were prepared chemically and thereby characterized by transmission electron microscope (TEM) imaging, absorbance and dynamic light scattering (DLS) measurements for hydrodynamic diameter and zeta potential. The cultured buffalo granulosa cells (BGC) were co-incubated with AuNP in two concentrations (2 × 109 and 2 × 1010 AuNP/ml) for 24 h. Treatment of BGC with AuNP significantly modulated the steroidogenesis associated genes (3β-Hsd and Cyp19A1) expression and progesterone accumulation in the culture fluid. AuNP affected the apoptotic pathway in BGC by affecting the gene expression of Caspase-3, Bad and Bax. The AuNP did not exert oxidative stress through anti-oxidant induction & lipid peroxidation in the buffalo GC.
Conclusions
AuNP may modulate the endocrine system by having impact on the steroidogenesis pathway and also have the potential to affect apoptotic pathway in a buffalo granulosa cell model.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data generated during this study and supporting this study are included in this article. The dataset analyzed during the current study is available from the corresponding author on a reasonable request.
References
Alkilany AM, Murphy CJ (2010) Toxicity and cellular uptake of gold nanoparticles: what we have learned so far? J Nanopart Res 12:2313–2333. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-010-9911-8
Brohi RD, Wang L, Talpur HS et al (2017) Toxicity of nanoparticles on the reproductive system in animal models: a review. Front Pharmacol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2017.00606
Caracciolo G, Farokhzad OC, Mahmoudi M (2017) Biological identity of nanoparticles in vivo: clinical implications of the protein corona. Trends Biotechnol 35:257–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2016.08.011
Chen Y-S, Hung Y-C, Liau I, Huang GS (2009) Assessment of the in vivo toxicity of gold nanoparticles. Nanoscale Res Lett 4:858–864. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11671-009-9334-6
Chomczynski P, Sacchi N (1987) Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem 162:156–159. https://doi.org/10.1006/abio.1987.9999
Das J, Choi Y-J, Song H, Kim J-H (2016) Potential toxicity of engineered nanoparticles in mammalian germ cells and developing embryos: treatment strategies and anticipated applications of nanoparticles in gene delivery. Hum Reprod Update 22:588–619. https://doi.org/10.1093/humupd/dmw020
Dawson KA, Salvati A, Lynch I (2009) Nanoparticles reconstruct lipids. Nat Nanotechnol 4:84–85. https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2008.426
Ema M, Hougaard KS, Kishimoto A, Honda K (2016) Reproductive and developmental toxicity of carbon-based nanomaterials: a literature review. Nanotoxicology 10:391–412. https://doi.org/10.3109/17435390.2015.1073811
Grandjean P (2016) Paracelsus revisited: the dose concept in a complex world. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 119:126–132. https://doi.org/10.1111/bcpt.12622
Hagens WI, Oomen AG, de Jong WH et al (2007) What do we (need to) know about the kinetic properties of nanoparticles in the body? Regulat Toxicol Pharmacol 49:217–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yrtph.2007.07.006
Hoet PH, Brüske-Hohlfeld I, Salata OV (2004) Nanoparticles – known and unknown health risks. J Nanobiotechnol 2:12. https://doi.org/10.1186/1477-3155-2-12
Hou C-C, Zhu J-Q (2017) Nanoparticles and female reproductive system: how do nanoparticles affect oogenesis and embryonic development. Oncotarget 8:109799–109817. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.19087
Iavicoli I, Fontana L, Leso V, Bergamaschi A (2013) The effects of nanomaterials as endocrine disruptors. Int J Mol Sci 14:16732–16801. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms140816732
Jain A, Ranjan S, Dasgupta N, Ramalingam C (2018) Nanomaterials in food and agriculture: an overview on their safety concerns and regulatory issues. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 58:297–317. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2016.1160363
Larson JK, Carvan MJ, Teeguarden JG et al (2014) Low-dose gold nanoparticles exert subtle endocrine-modulating effects on the ovarian steroidogenic pathway ex vivo independent of oxidative stress. Nanotoxicology 8:856–866. https://doi.org/10.3109/17435390.2013.837208
Lesniak A, Fenaroli F, Monopoli MP et al (2012) Effects of the presence or absence of a protein corona on silica nanoparticle uptake and impact on cells. ACS Nano 6:5845–5857. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn300223w
Liu J, Lu Y (2006) Preparation of aptamer-linked gold nanoparticle purple aggregates for colorimetric sensing of analytes. Nat Protoc 1:246–252. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2006.38
Liu X, Qin D, Cui Y et al (2010) The effect of calcium phosphate nanoparticles on hormone production and apoptosis in human granulosa cells. Reproduct Biol Endocrinol 8:32. https://doi.org/10.1186/1477-7827-8-32
Lohse SE, Murphy CJ (2012) Applications of colloidal inorganic nanoparticles: from medicine to energy. J Am Chem Soc 134:15607–15620. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja307589n
Lombi E, Donner E, Dusinska M, Wickson F (2019) A One Health approach to managing the applications and implications of nanotechnologies in agriculture. Nat Nanotechnol 14:523–531. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-019-0460-8
Mu Q, Jiang G, Chen L et al (2014) Chemical basis of interactions between engineered nanoparticles and biological systems. Chem Rev 114:7740–7781. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr400295a
Nayan V, Onteru SK, Singh D (2018) Mangifera indica flower extract mediated biogenic green gold nanoparticles: efficient nanocatalyst for reduction of 4-nitrophenol. Environ Prog Sustain Energy 37:283–294. https://doi.org/10.1002/ep.12669
Nel A, Xia T, Mädler L, Li N (2006) Toxic potential of materials at the nanolevel. Science 311:622–627. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1114397
Nel AE, Mädler L, Velegol D et al (2009) Understanding biophysicochemical interactions at the nano–bio interface. Nat Mater 8:543–557. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat2442
Ranjan S, Dasgupta N, Chakraborty AR et al (2014) Nanoscience and nanotechnologies in food industries: opportunities and research trends. J Nanopart Res 16:2464. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-014-2464-5
Shukla R, Bansal V, Chaudhary M et al (2005) Biocompatibility of gold nanoparticles and their endocytotic fate inside the cellular compartment: a microscopic overview. Langmuir 21:10644–10654. https://doi.org/10.1021/la0513712
Stelzer R, Hutz RJ (2009) Gold nanoparticles enter rat ovarian granulosa cells and subcellular organelles, and alter in-vitro estrogen accumulation. J Reprod Dev 55:685–690. https://doi.org/10.1262/jrd.20241
Tenzer S, Docter D, Kuharev J et al (2013) Rapid formation of plasma protein corona critically affects nanoparticle pathophysiology. Nat Nanotech 8:772–781. https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2013.181
Turkevich J, Stevenson PC, Hillier J (1951) A study of the nucleation and growth processes in the synthesis of colloidal gold. Discuss Faraday Soc 11:55–75. https://doi.org/10.1039/DF9511100055
Wang F, Yu L, Monopoli MP et al (2013) The biomolecular corona is retained during nanoparticle uptake and protects the cells from the damage induced by cationic nanoparticles until degraded in the lysosomes. Nanomedicine 9:1159–1168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nano.2013.04.010
Yang O, Kim HL, Weon J-I, Seo YR (2015) Endocrine-disrupting chemicals: review of toxicological mechanisms using molecular pathway analysis. J Cancer Prev 20:12–24. https://doi.org/10.15430/JCP.2015.20.1.12
Zhang M, Jin J, Chang Y-N et al (2014) Toxicological properties of nanomaterials. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 14:717–729. https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2014.9198
Acknowledgements
The authors are very grateful to Director ICAR-CIRB (Hisar), ICAR-NDRI (Karnal) and ICAR-NRCE (Hisar) for providing the necessary facilities for this study. We acknowledge the NIPER, Mohali for accessing their facilities for EM imaging and EDX.
Funding
This work was supported by the [ICAR-Central institute for Research on Buffaloes, Hisar] under Grant [Project Code: IXX12688]. Facilities under [BMGF Project] under Grant [Project Code: OXX04350]; and [CABin Project] under Grant [Project Code: OXX04610] were also availed.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
VN, ELL, AB, PS, SKO, DS conceived and designed the experiments; ELL, VN, MV, SK, TB, JD, SP performed the experiments or assisted in the experiments; ELL, VN, MV analyzed the data; VN, AB, SKO, PS and DS contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools; ELL and VN wrote the paper. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All the methods were performed in accordance with the relevant guidelines and regulations of the ICAR-Central Institute for Research on Buffaloes.
Informed consent
We give our consent to participate under the ‘Ethics, consent and permissions’ heading.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lyngdoh, E.L., Nayan, V., Vashisht, M. et al. Gold nanoparticles modulate the steroidogenic and apoptotic pathway in a buffalo granulosa cell model. Biotechnol Lett 42, 1383–1395 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-020-02896-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-020-02896-z