Abstract
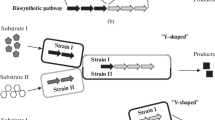
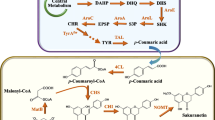
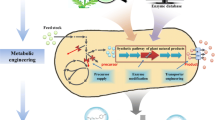
Heterologous biosynthesis has been long pursued as a viable approach for high efficiency production of natural products with various industrial values. Conventional methods for heterologous biosynthesis use the mono-culture of an engineered microbe for accommodating the whole target biosynthetic pathway to produce the desired product. The emergence of modular co-culture engineering, which divides the pathway between multiple co-culture strains, presents a new perspective to conduct heterologous biosynthesis and improve the bioproduction performance of natural products. This review highlights recent advances in utilizing the modular co-culture engineering approaches to address the challenges of plant and fungal natural product biosynthesis. Potential directions for future research in this promising field are also discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmadi MK, Pfeifer BA (2016) Recent progress in therapeutic natural product biosynthesis using Escherichia coli. Curr Opin Biotechnol 42:7–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2016.02.010
Ahmadi MK, Fang L, Moscatello N, Pfeifer BA (2016) E coli metabolic engineering for gram scale production of a plant-based anti-inflammatory agent. Metab Eng 38:382–388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2016.10.001
Becker J, Wittmann C (2016) Systems metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for the heterologous production of high value molecules-a veteran at new shores. Curr Opin Biotechnol 42:178–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2016.05.004
Camacho-Zaragoza JM, Hernandez-Chavez G, Moreno-Avitia F, Ramirez-Iniguez R, Martinez A, Bolivar F, Gosset G (2016) Engineering of a microbial coculture of Escherichia coli strains for the biosynthesis of resveratrol. Microb Cell Fact 15:163. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-016-0562-z
Chen Z, Sun X, Li Y, Yan Y, Yuan Q (2017) Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for microbial synthesis of monolignols. Metab Eng 39:102–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2016.10.021
Cragg GM, Newman DJ (2013) Natural products: a continuing source of novel drug leads. Biochem Biophys Acta 1830:3670–3695. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagen.2013.02.008
Ganesan V, Li Z, Wang X, Zhang H (2017) Heterologous biosynthesis of natural product naringenin by co-culture engineering. Synth Syst Biotechnol 2:236–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.synbio.2017.08.003
Gupta SS (1994) Prospects and perspectives of natural products in medicine. Indian J Pharmacol 26:1–12
Hoffmeister D, Keller NP (2007) Natural products of filamentous fungi: enzymes, genes, and their regulation. Nat Prod Rep 24:393–416. https://doi.org/10.1039/b603084j
Jones JA, Wang X (2017) Use of bacterial co-cultures for the efficient production of chemicals. Curr Opin Biotechnol 53:33–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2017.11.012
Jones JA et al (2016) Experimental and computational optimization of an Escherichia coli co-culture for the efficient production of flavonoids. Metab Eng 35:55–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2016.01.006
Jones JA et al (2017) Complete biosynthesis of anthocyanins using E. coli polycultures. MBio. https://doi.org/10.1128/mbio.00621-17
Kovacic P, Somanathan R (2010) Multifaceted approach to resveratrol bioactivity: focus on antioxidant action, cell signaling and safety. Oxid Med Cell Long 3:86–100. https://doi.org/10.4161/oxim.3.2.3
Lee K-H (2004) Current developments in the discovery and design of new drug candidates from plant natural product leads. J Nat Prod 67:273–283. https://doi.org/10.1021/np030373o
Li S, Li Y, Smolke CD (2018a) Strategies for microbial synthesis of high-value phytochemicals. Nat Chem 10:395–404. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41557-018-0013-z
Li T, Zhou W, Bi H, Zhuang Y, Zhang T, Liu T (2018b) Production of caffeoylmalic acid from glucose in engineered Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Lett 40:1057–1065. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-018-2580-x
Liu X et al (2018a) Convergent engineering of syntrophic Escherichia coli coculture for efficient production of glycosides. Metab Eng 47:243–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2018.03.016
Liu Y et al (2018b) Engineered monoculture and co-culture of methylotrophic yeast for de novo production of monacolin J and lovastatin from methanol. Metab Eng 45:189–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2017.12.009
Luo Y et al (2015) Engineered biosynthesis of natural products in heterologous hosts. Chem Soc Rev 44:5265–5290. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5cs00025d
Marmann A, Aly AH, Lin W, Wang B, Proksch P (2014) Co-cultivation: a powerful emerging tool for enhancing the chemical diversity of microorganisms. Mar Drugs 12:1043–1065. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12021043
Niu FX, He X, Wu YQ, Liu JZ (2018) Enhancing production of pinene in Escherichia coli by using a combination of tolerance, evolution, and modular co-culture engineering. Front Microbiol 9:1623. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.01623
Schueffler A, Anke T (2014) Fungal natural products in research and development. Nat Prod Rep 31:1425–1448. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4np00060a
Sgobba E et al (2018) Synthetic Escherichia coli-Corynebacterium glutamicum consortia for l-lysine production from starch and sucrose. Bioresour Technol 260:302–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.03.113
Thuan NH, Chaudhary AK, Van Cuong D, Cuong NX (2018a) Engineering co-culture system for production of apigetrin in Escherichia coli. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 45:175–185. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-018-2012-x
Thuan NH, Trung NT, Cuong NX, Van Cuong D, Van Quyen D, Malla S (2018b) Escherichia coli modular coculture system for resveratrol glucosides production. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 34:75. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-018-2458-z
Wang J et al (2018) A novel process for cadaverine bio-production using a consortium of two engineered Escherichia coli. Front Microbiol 9:1312. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.01312
Zhang H, Wang X (2016) Modular co-culture engineering, a new approach for metabolic engineering. Metab Eng 37:114–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2016.05.007
Zhang H, Wang Y, Pfeifer BA (2008) Bacterial hosts for natural product production. Mol Pharm 5:212–225. https://doi.org/10.1021/mp7001329
Zhang H, Boghigian BA, Armando J, Pfeifer BA (2011) Methods and options for the heterologous production of complex natural products. Nat Prod Rep 28:125–151. https://doi.org/10.1039/c0np00037j
Zhang H, Pereira B, Li Z, Stephanopoulos G (2015) Engineering Escherichia coli coculture systems for the production of biochemical products. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112:8266–8271. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1506781112
Zhang S, Wang S, Zhan J (2016) Engineered biosynthesis of medicinally important plant natural products in microorganisms. Curr Top Med Chem 16:1740–1754
Zhang W et al (2017) Production of naringenin from d-xylose with co-culture of E. coli and S. cerevisiae. Eng Life Sci 17:1021–1029. https://doi.org/10.1002/elsc.201700039
Zhou K, Qiao K, Edgar S, Stephanopoulos G (2015) Distributing a metabolic pathway among a microbial consortium enhances production of natural products. Nat Biotechnol 33:377. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.3095
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by startup research funds provided by Rutgers, The State University of New Jersey. Tingting Chen is a recipient of CSC PhD fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, T., Zhou, Y., Lu, Y. et al. Advances in heterologous biosynthesis of plant and fungal natural products by modular co-culture engineering. Biotechnol Lett 41, 27–34 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-018-2619-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-018-2619-z