Abstract
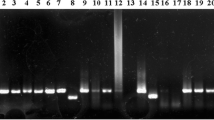
A new method, termed metagenomic gene specific multi-primer PCR (MGSM-PCR), is presented that uses multiple gene specific primers derived from an isolated gene from a constructed metagenomic library rather than degenerate primers designed based on a known enzyme family. The utility of MGSM-PCR was shown by applying it to search for homologues of the glycoside hydrolase family 9 cellulase in metagenomic DNA. The success of the multiplex PCR was verified by visualizing products on an agarose gel following gel electrophoresis. A total of 127 homologous genes were amplified with combinatorial multi-primer reactions from 34 soil DNA samples. Multiple alignments revealed extensive sequence diversity among these captured sequences with sequence identity varying from 26 to 99.7%. These results indicated that significantly diverse homologous genes were indeed readily accessible when using multiple metagenomic gene specific primers.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bell PJL, Sunna A, Gibbs MD, Curach NC, Nevalainen H et al (2002) Prospecting for novel lipase genes using PCR. Microbiology 148:2283–2291
Boubakri H, Beuf M, Simonet P, Vogel TM (2006) Development of metagenomic DNA shuffling for the construction of a xenobiotic gene. Gene 375:87–94
Contreras-Moreira B, Sachman-Ruiz B, Figueroa-Palacios I, Vinuesa P (2009) Primers4clades: a web server that uses phylogenetic trees to design lineage-specific PCR primers for metagenomic and diversity studies. Nucleic Acids Res 37:W95–W100
Cowan D, Meyer Q, Stafford W, Muyanga S, Cameron R et al (2005) Metagenomic gene discovery: past, present and future. Trends Biotechnol 23:321–329
Crooks GE, Hon G, Chandonia JM, Brenner SE (2004) WebLogo: a sequence logo generator. Genome Res 14:1188–1190
Daniel R (2005) The metagenomics of soil. Nat Rev Microbiol 3:470–478
Eschenfeldt WH, Stols L, Rosenbaum H, Khambatta ZS, Quaite-Randall E et al (2001) DNA from uncultured organisms as a source of 2,5-diketo-d-gluconic acid reductases. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:4206–4214
Khademi S, Guarino LA, Watanabe H, Tokuda G, Meyer EF (2002) Structure of an endoglucanase from termite, Nasutitermes takasagoensis. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 58:653–659
Kim B, Kim S, Park J, Park W, Hwang K et al (2007) Sequence-based screening for self-sufficient P450 monooxygenase from a metagenome library. J Appl Microbiol 102:1392–1400
Kotik M (2009) Novel genes retrieved from environmental DNA by polymerase chain reaction: current genome-walking techniques for future metagenome applications. J Biotechnol 144:75–82
Labes A, Karlsson EN, Fridjonsson OH, Turner P, Hreggvidson GO et al (2008) Novel members of glycoside hydrolase family 13 derived from environmental DNA. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:1914–1921
Liebeton K, Eck J (2004) Identification and expression in E. coli of novel nitrile hydratases from the metagenome. Eng Life Sci 4:557–562
Rose TM, Schultz ER, Henikoff JG, Pietrokovski S, McCallum CM et al (1998) Consensus-degenerate hybrid oligonucleotide primers for amplification of distantly related sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 26:1628–1635
Rose TM, Henikoff JG, Henikoff S (2003) CODEHOP (COnsensus-DEgenerate Hybrid Oligonucleotide Primer) PCR primer design. Nucleic Acids Res 31:3763–3766
Streit WR, Schmitz RA (2004) Metagenomics—the key to the uncultured microbes. Curr Opin Microbiol 7:492–498
Teather RM, Wood PJ (1982) Use of Congo red-polysaccharide interactions in enumeration and characterization of cellulolytic bacteria from the bovine rumen. Appl Environ Microbiol 43:777–780
Tuffin M, Anderson D, Heath C, Cowan DA (2009) Metagenomic gene discovery: How far have we moved into novel sequence space? Biotechnol J 4:1671–1683
Wang Q, Wu H, Wang A, Du P, Pei X et al (2010) Prospecting metagenomic enzyme subfamily genes for DNA family shuffling by a novel PCR-based approach. J Biol Chem 285:41509–41516
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (30900253, 20906016 and 21006018), the Technology Research and Development Program of Hangzhou (20101131N03) and the Normal Science Project of Zhejiang Province (2009C31086).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiong, X., Yin, X., Pei, X. et al. Retrieval of glycoside hydrolase family 9 cellulase genes from environmental DNA by metagenomic gene specific multi-primer PCR. Biotechnol Lett 34, 875–882 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-012-0855-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-012-0855-1