Abstract
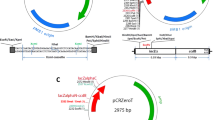
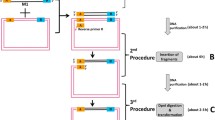
As gene cloning from difficult templates with regionalized high GC content is a long recognized problem, we have developed a novel and reliable method to clone such genes. Firstly, the high GC content region of the target cDNA was synthesized directly after codon optimization and the remaining cDNA fragment without high GC content was generated by routine RT-PCR. Then the entire redesigned coding sequence of the target gene was obtained by fusing the above available two cDNA fragments with SOE-PCR (splicing by overlapping extension-PCR). We have cloned the human RANK gene (ten exons; CDS 1851 bp) using this strategy. The redesigned cDNA was transfected into an eukaryotic expression system (A459 cells) to verify its expression. RT-PCR and western blotting confirmed this. To validate our method, we also successfully cloned human TIMP2 gene (five exons; CDS 660 bp) also having a regionalized high GC content. Our strategy for combining codon optimization and SOE-PCR to clone difficult genes is thus feasible and potentially universally applicable.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abhishek DG (2009) Efficient in silico designing of oligonucleotides for artificial gene synthesis. Protoc Exch. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2009.15
Bustin SA, Benes V, Nolan T, Pfaffl MW (2005) Quantitative real-time RT-PCR—a perspective. J Mol Endocrinol 34(3):597–601
Gustafsson C, Govindarajan S, Minshull J (2004) Codon bias and heterologous protein expression. Trends Biotechnol 22(7):346–353
Hanada R, Hanada T, Penninger JM (2010) Physiology and pathophysiology of the RANKL/RANK system. Biol Chem 391(12):1365–1370
Hoover DM, Lubkowski J (2002) DNAWorks: an automated method for designing oligonucleotides for PCR-based gene synthesis. Nucleic Acids Res 30(10):e43
Horton RM, Cai ZL, Ho SN, Pease LR (1990) Gene splicing by overlap extension: tailor-made genes using the polymerase chain reaction. Biotechniques 8(5):528–535
Kozak M (1989) The scanning model for translation: an update. J Cell Biol 108(2):229–241
Lu Q (2005) Seamless cloning and gene fusion. Trends Biotechnol 23(4):199–207
Musso M, Bocciardi R, Parodi S, Ravazzolo R, Ceccherini I (2006) Betaine, dimethyl sulfoxide, and 7-deaza-dGTP, a powerful mixture for amplification of GC-rich DNA sequences. J Mol Diagn 8(5):544–550
Sahdev S, Saini S, Tiwari P, Saxena S, Singh Saini K (2007) Amplification of GC-rich genes by following a combination strategy of primer design, enhancers and modified PCR cycle conditions. Mol Cell Probes 21(4):303–307
Zhang Z, Huang K, Zhang Y, Liu N, Yang K (1994) Interference by complex structures of target DNA with specific PCR amplification. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 44(1):15–20
Zhang YJ, Pan HY, Gao SJ (2001) Reverse transcription slippage over the mRNA secondary structure of the LIP1 gene. Biotechniques 31(6):1286, 1288, 1290, passim
Acknowledgment
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81000834), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 20070420769), and the Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing (CSTC2007BB5077).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Gang Huang, Qianjun Wen, and Qiangguo Gao contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, G., Wen, Q., Gao, Q. et al. An efficient and rapid method for cDNA cloning from difficult templates using codon optimization and SOE-PCR: with human RANK and TIMP2 gene as examples. Biotechnol Lett 33, 1939–1947 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-011-0656-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-011-0656-y