Abstract
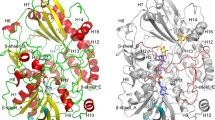
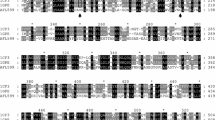
A FAD-dependent glucose dehydrogenase (FADGDH) mutant with narrow substrate specificity was constructed by site-directed mutagenesis. Several characteristics of FADGDH, such as high catalytic activity and high electron transfer ability, make this enzyme suitable for application to glucose sensors. However, for further applications, improvement of the broad substrate specificity is needed. In this paper, we mutated two residues, Asn475 and Ala472, which are located near the putative active site of the catalytic subunit of FADGDH and have been predicted from the alignment with the active site of glucose oxidase. Of the 38 mutants constructed, Ala472Phe and Asn475Asp were purified and their activities were analyzed. Both mutants showed a higher specificity toward glucose compared to the wild type enzyme.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Inose K, Fujikawa M, Yaniazaki T, Kojima K, Sode K (2003) Cloning and expression of the gene encoding catalytic subunit of thermostable glucose dehydrogenase from Burkholderia Cepacia in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta (Proteins and Proteomics) 1645:133–138
Janssen W, Harff G, Caers M, Schellekens A (1998) Positive interference of icodextrin metabolites in some enzymatic glucose methods. Clin Chem 44:2379–2380
Sode K, Tsugawa W, Yamazaki T, Watanabe M, Ogasawara N, Tanaka M (1996) A novel thermostable glucose dehydrogenase varying temperature properties by altering its quaternary structures. Enzyme Microbial Technol 19:82–85
Tsuya T, Ferri S, Fujikawa M, Yamaoka H, Sode K (2006) Cloning and functional expression of glucose dehydrogenase complex of Burkholderia Cepacia in Escherichia coli. J Biotechnol 123:127–136
Wohlfahrt G, Witt S, Hendle J, Schomburg D, Kalisz HM, Hecht HJ (1999) 1.8 and 1.9 a resolution structures of the Penicillium amagasakiense and Aspergillus niger glucose oxidases as a basis for modelling substrate complexes. Acta Cryst D55:969–977
Yamaoka H, Sode K (2007a) SPCE based glucose sensor employing novel thermostable glucose dehydrogenase, FADGDH: blood glucose measurement with 150 nL sample in one-second. J Diabetes Sci Technol 1:28–35
Yamaoka H, Sode K (2007b) A disposable electrochemical glucose sensor using catalytic subunit of novel thermostable glucose dehydrogenase. Open Biotechnol J 1:26–30
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yamaoka, H., Yamashita, Y., Ferri, S. et al. Site directed mutagenesis studies of FAD-dependent glucose dehydrogenase catalytic subunit of Burkholderia cepacia . Biotechnol Lett 30, 1967–1972 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-008-9777-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-008-9777-3