Abstract
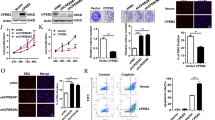
The ribose nucleic acid (RNA)-binding motif protein 24 (RBM24) has been recognized as a critical regulatory protein in various types of tumors. However, its specific role in glioblastoma (GBM) has not been thoroughly investigated. The objective of this study is to uncover the role of RBM24 in GBM and understand the underlying mechanism. The expression of RBM24 in GBM was initially analyzed using the Gene Expression Profiling Interactive Analysis (GEPIA). Subsequently, the RBM24 expression levels in clinical samples of GBM were examined, and the survival curves of GBM patients were plotted based on high- and low-expression levels of RBM24 using Kaplan–Meier (KM) plotter. In addition, RBM24 knockdown cell lines and overexpression vectors were created to assess the effects on proliferation, apoptosis, and invasion abilities. Finally, the binding level of RBM24 protein to LATS1 messenger RNA (mRNA) was determined by RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) assay, and the expression levels of RBM24 and LATS1 were measured through quantitative reverse-transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) and Western blot (WB). Our data revealed a significant decrease in RBM24 mRNA and protein levels in GBM patients, indicating that those with low RBM24 expression had a worse prognosis. Overexpression of RBM24 led to inhibited cell proliferation, reduced invasion, and increased apoptosis in LN229 and U87 cells. In addition, knocking down LATS1 partially reversed the effects of RBM24 on cell proliferation, invasion, and apoptosis in GBM cells. In vivo xenograft model further demonstrated that RBM24 overexpression reduced the growth of subcutaneous tumors in nude mice, accompanied by a decrease in Ki-67 expression and an increase in apoptotic events in tumor tissues. There was also correlation between RBM24 and LATS1 protein expression in the xenograft tumors. RBM24 functions to stabilize LATS1 mRNA, thereby inhibiting the proliferation, suppressing invasion, and promoting apoptosis in GBM cells.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author via email request.
References
Cappoli N, Jenkinson MD, Dello Russo C, Dickens D (2022) LAT1, a novel pharmacological target for the treatment of glioblastoma. Biochem Pharmacol 201:115103
Casati G, Giunti L, Iorio AL, Marturano A, Galli L, Sardi I (2021) Hippo pathway in regulating drug resistance of glioblastoma. Int J Mol Sci 22(24):13431
Chen Z, Wu H, Yang H, Fan Y, Zhao S, Zhang M (2021) Identification and validation of RNA-binding protein-related gene signature revealed potential associations with immunosuppression and drug sensitivity in glioma. Cancer Med 10(20):7418–7439
Chen Y, Li J, Ma J, Bao Y (2023) ZNF143 facilitates the growth and migration of glioma cells by regulating KPNA2-mediated Hippo signalling. Sci Rep 13(1):11097
Choi JH et al (2021) TPRG1-AS1 induces RBM24 expression and inhibits liver cancer progression by sponging miR-4691-5p and miR-3659. Liver Int 41(11):2788–2800
Fabro F, Lamfers MLM, Leenstra S (2022) Advancements, challenges, and future directions in tackling glioblastoma resistance to small kinase inhibitors. Cancers (Basel) 14(3):600
Filippova N, Yang X, Wang Y, Gillespie GY, Langford C, King PH, Wheeler C, Nabors LB (2011) The RNA-binding protein HuR promotes glioma growth and treatment resistance. Mol Cancer Res 9(5):648–659
Grifone R et al (2021) Rbm24 displays dynamic functions required for myogenic differentiation during muscle regeneration. Sci Rep 11(1):9423
Hamad A et al (2023) Recent developments in glioblastoma therapy: oncolytic viruses and emerging future strategies. Viruses 15(2):547
Han W, Xin Z, Zhao Z, Bao W, Lin X, Yin B, Zhao J, Yuan J, Qiang B, Peng X (2013) RNA-binding protein PCBP2 modulates glioma growth by regulating FHL3. J Clin Investig 123(5):2103–2118
He B et al (2021) miR-383 increases the cisplatin sensitivity of lung adenocarcinoma cells through inhibition of the RBM24-mediated NF-κB signaling pathway. Int J Oncol 59(5):87
Hua WF et al (2016) RBM24 suppresses cancer progression by upregulating miR-25 to target MALAT1 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cell Death Dis 7(9):e2352
Huang QR, Li JW, Pan XB (2021) A novel risk signature with 6 RNA binding proteins for prognosis prediction in patients with glioblastoma. Medicine (Baltimore) 100(48):e28065
Ji T, Liu D, Shao W, Yang W, Wu H, Bian X (2012) Decreased expression of LATS1 is correlated with the progression and prognosis of glioma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 31(1):67
Lah TT, Novak M, Breznik B (2020) Brain malignancies: glioblastoma and brain metastases. Semin Cancer Biol 60:262–273
Le Rhun E et al (2019) Molecular targeted therapy of GBM. Cancer Treat Rev 80:101896
Li X, Wu C, Chen N, Gu H, Yen A, Cao L, Wang E, Wang L (2016) PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway and targeted therapy for glioblastoma. Oncotarget 7(22):33440–33450
Lucchesi C, Zhang J, Chen X (2016) Modulation of the p53 family network by RNA-binding proteins. Transl Cancer Res 5(6):676–684
Masliantsev K, Karayan-Tapon L, Guichet PO (2021) Hippo signaling pathway in gliomas. Cells 10(1):184
Moon SU, Kim JH, Woo HG (2021) Tumor suppressor RBM24 inhibits nuclear translocation of CTNNB1 and TP63 expression in liver cancer cells. Oncol Lett 22(3):674
Noch EK, Ramakrishna R, Magge R (2018) Challenges in the treatment of glioblastoma: multisystem mechanisms of therapeutic resistance. World Neurosurg 116:505–517
Ostrom QT et al (2018) CBTRUS statistical report: primary brain and other central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2011–2015. Neuro-Oncology 20(suppl_4):iv1–iv86
Shergalis A, Bankhead A 3rd, Luesakul U, Muangsin N, Neamati N (2018) Current challenges and opportunities in treating glioblastoma. Pharmacol Rev 70(3):412–445
Shi DL (2022) RBM24 in the post-transcriptional regulation of cancer progression: anti-tumor or pro-tumor activity? Cancers (Basel) 14(7):1843
Treps L, Perret R, Edmond S, Ricard D, Gavard J (2017) Glioblastoma stem-like cells secrete the pro-angiogenic VEGF-A factor in extracellular vesicles. J Extracell Vesicles 6(1):1359479
Wang Z, Tang W, Yuan J, Qiang B, Han W, Peng X (2020) Integrated analysis of RNA-binding proteins in glioma. Cancers (Basel) 12(4):892
Wei P et al (2020) lncRNA HAND2-AS1 regulates prostate cancer cell growth through targeting the miR-106a-5p/RBM24 axis. OncoTargets Ther 13:4523–4531
Xia RM et al (2021) RNA-binding protein RBM24 represses colorectal tumourigenesis by stabilising PTEN mRNA. Clin Transl Med 11(10):e383
Xu H, Zong H, Ma C, Ming X, Shang M, Li K, He X, Du H, Cao L (2017) Epidermal growth factor receptor in glioblastoma. Oncol Lett 14(1):512–516
Yabuta N et al (2013) N-terminal truncation of Lats1 causes abnormal cell growth control and chromosomal instability. J Cell Sci 126(Pt 2):508–520
Yan T, Tan Y, Deng G, Sun Z, Liu B, Wang Y, Yuan F, Sun Q, Hu P, Gao L, Tian D, Chen Q (2022) TGF-β induces GBM mesenchymal transition through upregulation of CLDN4 and nuclear translocation to activate TNF-α/NF-κB signal pathway. Cell Death Dis 13(4):339
Yang Y et al (2021) TRIM56 suppresses the malignant development of hepatocellular carcinoma via targeting RBM24 and inactivating the Wnt signaling. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 25(2):722–730
Yu T, Bachman J, Lai ZC (2013) Evidence for a tumor suppressor role for the large tumor suppressor genes LATS1 and LATS2 in human cancer. Genetics 195(3):1193–1196
Yu T, Bachman J, Lai ZC (2015) Mutation analysis of large tumor suppressor genes LATS1 and LATS2 supports a tumor suppressor role in human cancer. Protein Cell 6(1):6–11
Zhang D et al (2020a) Circular RNA SMARCA5 suppressed non-small cell lung cancer progression by regulating miR-670-5p/RBM24 axis. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai) 52(10):1071–1080
Zhang M et al (2020b) Rbm24 modulates adult skeletal muscle regeneration via regulation of alternative splicing. Theranostics 10(24):11159–11177
Zhang P, Zhang Y, Ji N (2022) Challenges in the treatment of glioblastoma by chimeric antigen receptor T-cell immunotherapy and possible solutions. Front Immunol 13:927132
Zhao N, Wang F, Ahmed S, Liu K, Zhang C, Cathcart SJ, DiMaio DJ, Punsoni M, Guan B, Zhou P, Wang S, Batra SK, Bronich T, Hei TK, Lin C, Zhang C (2021) Androgen receptor, although not a specific marker for, is a novel target to suppress glioma stem cells as a therapeutic strategy for glioblastoma. Front Oncol 11:616625
Zuccarini M, Giuliani P, Ziberi S, Carluccio M, Iorio PD, Caciagli F, Ciccarelli R (2018) The role of Wnt signal in glioblastoma development and progression: a possible new pharmacological target for the therapy of this tumor. Genes (Basel) 9(2):105
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
The authors received no financial support for the research authorship and/or publication of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Hao Ye and Xuewen Lu mainly participated in literature search, study design, writing and critical revision, prepared Figs. 1, 2, and 3. Xuewen Lu, Yong Xie, Guolin Ding and Wei Sun mainly participated in data collection, data analysis and data interpretation, prepared Figs. 4 and 5. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval and Consent to Participate
The study was approved by the Ethical Committee of the First People’s Hospital of Qujing. Patients provided a signed informed consent form for the sample collection. The protocols for all animal studies were observed and approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of the First People’s Hospital of Qujing.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, X., Xie, Y., Ding, G. et al. RBM24 Suppresses the Tumorigenesis of Glioblastoma by Stabilizing LATS1 mRNA. Biochem Genet (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-024-10715-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-024-10715-7