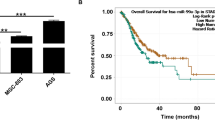
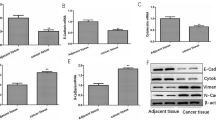
Abstract
Lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) is a common malignancy. Many studies have shown that LUAD is resistant to gemcitabine chemotherapy, resulting in poor treatment outcomes in patients. We designed this study to reveal influences of hsa-miR-195-5p/E2F7/CEP55 axis on gemcitabine resistance and autophagy of LUAD cells. The expression data of LUAD-related mRNAs were downloaded from TCGA-LUAD database for differential expression analysis. The bioinformatics databases (hTFtarget, starBase and TargetScan) were used to predict the upstream and downstream regulatory molecules of E2F7. Then the binding relationships between E2F7 and regulatory molecules were verified by ChIP and dual-luciferase reporter assay. qRT-PCR and western blot were used to detect the mRNA and protein levels of has-miR-195-5p, E2F7, and CEP55. CCK-8 assay was used to analyze the half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) and cell proliferation ability of LUAD cells after gemcitabine treatment. Apoptosis was detected by flow cytometry. Apoptosis/autophagy markers and LC3 aggregation were detected by western blot and immunofluorescence, respectively. Finally, the mouse transplantation model was constructed to verify the regulation mechanism in vivo. In LUAD cells and tissues, E2F7 and CEP55 were highly expressed, while has-miR-195-5p was relatively less expressed. The ChIP or dual-luciferase assays demonstrated the binding relationships of E2F7 to the CEP55 promoter region and has-miR-195-5p to the 3’-UTR of E2F7. Cell experiments demonstrated that overexpression of hsa-miR-195-5p stimulated LUAD cell apoptosis and inhibited autophagy and gemcitabine resistance, while further overexpression E2F7/CEP55 could reverse the impact by hsa-miR-195-5p overexpression. In vivo experiments identified that hsa-miR-195-5p/E2F7/CEP55 axis constrained the growth of LUAD tumor. Hsa-miR-195-5p promoted apoptosis, repressed proliferation, and autophagy via E2F7/CEP55 and reduced gemcitabine resistance in LUAD, indicating that hsa-miR-195-5p/E2F7/CEP55 may be a novel target for LUAD.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated and analyzed during the current study are not publicly available, but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
An Q, Zhou L, Xu N (2018) Long noncoding RNA FOXD2-AS1 accelerates the gemcitabine-resistance of bladder cancer by sponging miR-143. Biomed Pharmacother 103:415–420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.03.138
Booth LA, Roberts JL, Dent P (2020) The role of cell signaling in the crosstalk between autophagy and apoptosis in the regulation of tumor cell survival in response to sorafenib and neratinib. Semin Cancer Biol 66:129–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2019.10.013
Bu L, Tian Y, Wen H, Jia W, Yang S (2021) miR-195-5p exerts tumor-suppressive functions in human lung cancer cells through targeting TrxR2. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin 53:189–200. https://doi.org/10.1093/abbs/gmaa159
Chen W et al (2021) Downregulation of lncRNA ZFAS1 inhibits the hallmarks of thyroid carcinoma via the regulation of miR3023p on cyclin D1. Mol Med Rep. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2020.11640
Chiu HW et al (2016) Combination of the novel histone deacetylase inhibitor YCW1 and radiation induces autophagic cell death through the downregulation of BNIP3 in triple-negative breast cancer cells in vitro and in an orthotopic mouse model. Mol Cancer 15:46. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-016-0531-5
DeGregori J, Johnson DG (2006) Distinct and overlapping roles for E2F family members in transcription. Prolif Apoptosis Curr Mol Med 6:739–748. https://doi.org/10.2174/1566524010606070739
Duan L et al (2022) Immune-related miRNA-195–5p inhibits the progression of lung adenocarcinoma by targeting polypyrimidine tract-binding protein 1. Front Oncol 12:862564. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2022.862564
Endo-Munoz L et al (2009) E2F7 can regulate proliferation, differentiation, and apoptotic responses in human keratinocytes: implications for cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma formation. Cancer Res 69:1800–1808. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-2725
Fabbro M et al (2005) Cdk1/Erk2- and Plk1-dependent phosphorylation of a centrosome protein, Cep55, is required for its recruitment to midbody and cytokinesis. Dev Cell 9:477–488. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2005.09.003
Guo H, Zhang L (2019) MicroRNA-30a suppresses papillary thyroid cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion by directly targeting E2F7. Exp Ther Med 18:209–215. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2019.7532
Guo X, Liu L, Zhang Q, Yang W, Zhang Y (2020) E2F7 transcriptionally inhibits MicroRNA-199b expression to promote USP47, thereby enhancing colon cancer tumor stem cell activity and promoting the occurrence of colon cancer. Front Oncol 10:565449. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2020.565449
He J et al (2015) Downregulation of ATG14 by EGR1-MIR152 sensitizes ovarian cancer cells to cisplatin-induced apoptosis by inhibiting cyto-protective autophagy. Autophagy 11:373–384. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2015.1009781
Huang L et al (2018) MicroRNA-29c increases the chemosensitivity of pancreatic cancer cells by inhibiting USP22 mediated autophagy. Cell Physiol Biochem 47:747–758. https://doi.org/10.1159/000490027
Levy JMM, Towers CG, Thorburn A (2017) Targeting autophagy in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 17:528–542. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc.2017.53
Li YJ et al (2017) Autophagy and multidrug resistance in cancer. Chin J Cancer 36:52. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40880-017-0219-2
Li H et al (2018) miR-519a enhances chemosensitivity and promotes autophagy in glioblastoma by targeting STAT3/Bcl2 signaling pathway. J Hematol Oncol 11:70. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-018-0618-0
Li YH, Xu KC, Huang GM, Zang HL (2020) The function and molecular mechanism of CEP55 in anaplastic thyroid cancer. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 24:9549–9555. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_202009_23040
Li Y, Zhu Z, Hou X, Sun Y (2021) LncRNA AFAP1-AS1 promotes the progression of colorectal cancer through miR-195-5p and WISP1. J Oncol 2021:6242798. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/6242798
Liang R et al (2018) SNHG6 functions as a competing endogenous RNA to regulate E2F7 expression by sponging miR-26a-5p in lung adenocarcinoma. Biomed Pharmacother 107:1434–1446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.08.099
Liu L, Mei Q, Zhao J, Dai Y, Fu Q (2016) Suppression of CEP55 reduces cell viability and induces apoptosis in human lung cancer. Oncol Rep 36:1939–1945. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2016.5059
Liu X et al (2020) MiR-195-5p inhibits malignant progression of cervical cancer by targeting YAP1. Onco Targets Ther 13:931–944. https://doi.org/10.2147/ott.S227826
Lu T, Wang R, Cai H, Cui Y (2020) Long non-coding RNA DLEU2 promotes the progression of esophageal cancer through miR-30e-5p/E2F7 axis. Biomed Pharmacother 123:109650. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109650
Lv L et al (2016) Upregulation of CD44v6 contributes to acquired chemoresistance via the modulation of autophagy in colon cancer SW480 cells. Tumour Biol 37:8811–8824. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4755-6
Ma T et al (2018) USP9X inhibition improves gemcitabine sensitivity in pancreatic cancer by inhibiting autophagy. Cancer Lett 436:129–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2018.08.010
Michaud M et al (2011) Autophagy-dependent anticancer immune responses induced by chemotherapeutic agents in mice. Science (New York) 334:1573–1577. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1208347
Mulcahy Levy JM, Thorburn A (2020) Autophagy in cancer: moving from understanding mechanism to improving therapy responses in patients. Cell Death Differ 27:843–857. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-019-0474-7
Qi J, Liu G, Wang F (2018) High levels of centrosomal protein 55 expression is associated with poor clinical prognosis in patients with cervical cancer. Oncol Lett 15:9347–9352. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2018.8448
Saha S, Panigrahi DP, Patil S, Bhutia SK (2018) Autophagy in health and disease: A comprehensive review. Biomed Pharmacother 104:485–495. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.05.007
Sui X et al (2013) Autophagy and chemotherapy resistance: a promising therapeutic target for cancer treatment. Cell Death Dis 4:e838. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2013.350
Tian S, Guo X, Yu C, Sun C, Jiang J (2017) miR-138-5p suppresses autophagy in pancreatic cancer by targeting SIRT1. Oncotarget 8:11071–11082. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.14360
Wang M et al (2018) Long non-coding RNA H19 confers 5-Fu resistance in colorectal cancer by promoting SIRT1-mediated autophagy. Cell Death Dis 9:1149. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-018-1187-4
Wang Y et al (2021) Circ-AASDH functions as the progression of early stage lung adenocarcinoma by targeting miR-140-3p to activate E2F7 expression. Transl Lung Cancer Res 10:57–70. https://doi.org/10.21037/tlcr-20-1062
Wu T et al (2015) Autophagy facilitates lung adenocarcinoma resistance to cisplatin treatment by activation of AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway. Drug Des Dev Ther 9:6421–6431. https://doi.org/10.2147/dddt.S95606
Wu S et al (2019) Correlation between EZH2 and CEP55 and lung adenocarcinoma prognosis. Pathol Res Pract 215:292–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prp.2018.11.016
Xiang S et al (2019) E2F1 and E2F7 differentially regulate KPNA2 to promote the development of gallbladder cancer. Oncogene 38:1269–1281. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-018-0494-7
Xu H et al (2015) MicroRNA-195-5p acts as an anti-oncogene by targeting PHF19 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Rep 34:175–182. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2015.3957
Xu R, Liu S, Chen H, Lao L (2016) MicroRNA-30a downregulation contributes to chemoresistance of osteosarcoma cells through activating Beclin-1-mediated autophagy. Oncol Rep 35:1757–1763. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2015.4497
Yang Y, Klionsky DJ (2020) Autophagy and disease: unanswered questions. Cell Death Differ 27:858–871. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-019-0480-9
Yang R et al (2020a) E2F7-EZH2 axis regulates PTEN/AKT/mTOR signalling and glioblastoma progression. Br J Cancer 123:1445–1455. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41416-020-01032-y
Yang L, He Y, Zhang Z, Wang W (2020b) Upregulation of CEP55 predicts dismal prognosis in patients with liver cancer. Biomed Res Int 2020:4139320. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/4139320
Ye X et al (2020) TNNC1 reduced gemcitabine sensitivity of nonsmall-cell lung cancer by increasing autophagy. Med Sci Monit 26:e922703. https://doi.org/10.12659/msm.922703
Yuan C et al (2021) Effects of MicroRNA-195-5p on biological behaviors and radiosensitivity of lung adenocarcinoma cells via targeting HOXA10. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2021:4522210. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/4522210
Zhang M et al (2019) SOCS5 inhibition induces autophagy to impair metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Cell Death Dis 10:612. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-019-1856-y
Zhao H, Ding F, Zheng G (2020) LncRNA TMPO-AS1 promotes LCN2 transcriptional activity and exerts oncogenic functions in ovarian cancer. FASEB J 34:11382–11394. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.201902683R
Zhao Y, Zhang W, Yang Y, Dai E, Bai Y (2021) Diagnostic and prognostic value of microRNA-2355-3p and contribution to the progression in lung adenocarcinoma. Bioengineered 12:4747–4756. https://doi.org/10.1080/21655979.2021.1952367
Funding
This study was supported in part by grants from to investigate the value and mechanism of CEP55 gene as a diagnostic and independent prognostic factor in LUAD (2021RC033).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conception and design: LF. Administrative support: ZL. Provision of study materials or patients: LD. Collection and assembly of data: TZ. Data analysis and interpretation: JD. Manuscript writing: All authors. Final approval of manuscript: All authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
The study was approved by Shaoxing People’s Hospital Experimental Animal Ethics Committee, approval number [2022Z052]. The methods were carried out in accordance with the approved guidelines.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.

10528_2023_10330_MOESM1_ESM.jpg
Supplementary file1 (JPG 1758 KB)—Supplementary Fig. 1 Effect of E2F7 knockdown/CEP55 overexpression on the functions of LUAD cells. A, B The mRNA and protein expression of E2F7 of HCC827 cells in each group; C The proliferation ability of each transfected group; D The apoptosis of HCC827 cells in each group; E The expression of apoptosis-related proteins in LUAD cells; F Immunofluorescence assay of E2F7 and LC3 protein expression in HCC827 cells in each group; G The expression of autophagy-related proteins in HCC827 cells; H, I The cell viability and IC50 values respond to 24 h and 48 h of gemcitabine treatment (0, 0.001, 0.01, 0.1, 1, 5, 10 μg/mL), respectively. *, **, ***, **** meant P<0.05, 0.01, 0.001, 0.0001, respectively (one-way ANOVA)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Fu, L., Li, Z., Wu, Y. et al. Hsa-miR-195-5p Inhibits Autophagy and Gemcitabine Resistance of Lung Adenocarcinoma Cells via E2F7/CEP55. Biochem Genet 61, 1528–1547 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-023-10330-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-023-10330-y