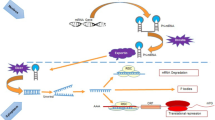
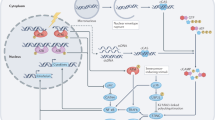
Abstract
Ageing is a multifactorial and integrated gradual deterioration affecting the most of biological process of cells. MiRNAs are differentially expressed in the cellular senescence and play important role in regulating of genes expression involved in features of ageing. The perception of miRNAs functions in ageing regulation can be useful in clarifying the mechanisms underlying ageing and designing of therapeutic strategies. The preservation of genomic integrity through DNA damage response (DDR) is related to the process of cellular senescence. The recent studies have shown that miRNAs has directly regulated the expression of numerous proteins in DDR pathways. In this review study, DDR pathways, miRNA biogenesis and functions, current finding on DDR regulations, molecular biology of ageing and the role of miRNAs in these processes have been studied. Finally, a brief explanation about the therapeutic function of miRNAs in ageing regarding its regulation of DDR has been provided.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alberts B, Johnson A, Lewis J, Raff M, Roberts K, Walter P (2002) Components of the cell-cycle control system. Garland Science, New York
Alers S, Löffler AS, Wesselborg S, Stork B (2012) Role of AMPK-mTOR-Ulk1/2 in the regulation of autophagy: cross talk, shortcuts, and feedbacks. Mol Cell Biol 32:2–11
Awasthi P, Foiani M, Kumar A (2015) ATM and ATR signaling at a glance. J Cell Sci 128:4255–4262
Bai X-Y, Ma Y, Ding R, Fu B, Shi S, Chen X-M (2011) miR-335 and miR-34a Promote renal senescence by suppressing mitochondrial antioxidative enzymes. J Am Soc Nephrol 22:1252–1261
Bao J et al (2018) MiR-126 negatively regulates PLK-4 to impact the development of hepatocellular carcinoma via ATR/CHEK1 pathway. Cell Death Dis 9:1045
Bartel DP (2009) MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 136:215–233
Bates DJ et al (2010) MicroRNA regulation in Ames dwarf mouse liver may contribute to delayed aging. Aging Cell 9:1–18
Bethke A, Fielenbach N, Wang Z, Mangelsdorf DJ, Antebi A (2009) Nuclear hormone receptor regulation of microRNAs controls developmental progression. Science 324:95–98
Bhaumik D et al (2009) MicroRNAs miR-146a/b negatively modulate the senescence-associated inflammatory mediators IL-6 and IL-8. Aging 1:402
Bjedov I, Toivonen JM, Kerr F, Slack C, Jacobson J, Foley A, Partridge L (2010) Mechanisms of life span extension by rapamycin in the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster. Cell Metab 11:35–46
Boehm M, Slack F (2005) A developmental timing microRNA and its target regulate life span in C. elegans. Science 310:1954–1957
Bohnsack MT, Czaplinski K, Görlich D (2004) Exportin 5 is a RanGTP-dependent dsRNA-binding protein that mediates nuclear export of pre-miRNAs. RNA 10:185–191
Boon RA et al (2013) MicroRNA-34a regulates cardiac ageing and function. Nature 495:107
Bratic A, Larsson N-G (2013) The role of mitochondria in aging. J Clin Investig 123:951
Cannell IG et al (2010) p38 MAPK/MK2-mediated induction of miR-34c following DNA damage prevents Myc-dependent DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci 107:5375–5380
Capparelli C et al (2012) CDK inhibitors (p16/p19/p21) induce senescence and autophagy in cancer-associated fibroblasts, “fueling” tumor growth via paracrine interactions, without an increase in neo-angiogenesis. Cell Cycle 11:3599–3610
Card DAG, Hebbar PB, Li L, Trotter KW, Komatsu Y, Mishina Y, Archer TK (2008) Oct4/Sox2-regulated miR-302 targets cyclin D1 in human embryonic stem cells. Mol Cell Biol 28:6426–6438
Cascales HS, Müllers E, Lindqvist A (2017) How the cell cycle enforces senescence. Aging (Albany NY) 9:2022
Chang S, Sharan SK (2012) Epigenetic control of an oncogenic microRNA, miR-155, by BRCA1. Oncotarget 3:5
Chang S et al (2011) Tumor suppressor BRCA1 epigenetically controls oncogenic microRNA-155. Nat Med 17:1275
Chang L et al (2012) miR-3928 activates ATR pathway by targeting Dicer. RNA Biol 9:1247–1254
Chen L-H, Chiou G-Y, Chen Y-W, Li H-Y, Chiou S-H (2010) MicroRNA and aging: a novel modulator in regulating the aging network. Ageing Res Rev 9:S59–S66
Chen X, Zhang J, Liu Z, Zhang S, Sun T (2018) Specific microRNA signatures responsible for immune disturbance related to hip fracture in aged rats. J Orthop Surg Res 13:17
Choi YE, Pan Y, Park E, Konstantinopoulos P, De S, D'Andrea A, Chowdhury D (2014) MicroRNAs down-regulate homologous recombination in the G1 phase of cycling cells to maintain genomic stability. Elife 3:e02445
Cortez MA et al (2015) In vivo delivery of miR-34a sensitizes lung tumors to radiation through RAD51 regulation. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 4:e270
Denli AM, Tops BB, Plasterk RH, Ketting RF, Hannon GJ (2004) Processing of primary microRNAs by the Microprocessor complex. Nature 432:231–235
Devi KP, Rajavel T, Daglia M, Nabavi SF, Bishayee A, Nabavi SM (2017) Targeting miRNAs by polyphenols: novel therapeutic strategy for cancer. In: Seminars in Cancer Biology. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Di Francesco A, De Pittà C, Moret F, Barbieri V, Celotti L, Mognato M (2013) The DNA-damage response to γ-radiation is affected by miR-27a in A549 cells. Int J Mol Sci 14:17881–17896
López-Otín C, Blasco MA, Partridge L, Serrano M, Kroemer G (2013) The Hallmarks of Aging. Cell 153:1194–217
Elia L et al (2009) Reciprocal regulation of microRNA-1 and insulin-like growth factor-1 signal transduction cascade in cardiac and skeletal muscle in physiological and pathological conditions. Circulation 120:2377–2385
Fang C et al (2017) MiR-488 inhibits proliferation and cisplatin sensibility in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells by activating the eIF3a-mediated NER signaling pathway. Sci Rep 7:40384
Farooqi AA, Majeed SMK, Mansoor Q, Ismail M (2015) Population-specific genetic variation at microRNA-629-binding site in the 3'-UTR of NBS1 gene in prostate cancer patients. J Exp Therap Oncol 11:161–163
Filipowicz W, Bhattacharyya SN, Sonenberg N (2008) Mechanisms of post-transcriptional regulation by microRNAs: are the answers in sight? Nat Rev Genet 9:102–114
Frenk S, Houseley J (2018) Gene expression hallmarks of cellular ageing. Biogerontology 19:1–20
Gabbianelli R, Malavolta M (2018) Epigenetics in ageing and development. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Galluzzi L et al (2010) miR-181a and miR-630 regulate cisplatin-induced cancer cell death. Cancer Res 70:1793–1803
Gao S et al (2017) MicroRNA-155, induced by FOXP3 through transcriptional repression of BRCA1, is associated with tumor initiation in human breast cancer. Oncotarget 8:41451
Garcia AI et al (2011) Down-regulation of BRCA1 expression by miR-146a and miR-146b-5p in triple negative sporadic breast cancers. EMBO Mol Med 3:279–290
Gasparini P et al (2014) Protective role of miR-155 in breast cancer through RAD51 targeting impairs homologous recombination after irradiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci 111:4536–4541
Ghorai A, Ghosh U (2014) miRNA gene counts in chromosomes vary widely in a species and biogenesis of miRNA largely depends on transcription or post-transcriptional processing of coding genes. Front Genet 5:100
Gu S, Rong H, Zhang G, Kang L, Yang M, Guan H (2016) Functional SNP in 3′-UTR MicroRNA-binding site of ZNF350 confers risk for age-related cataract. Hum Mutat 37:1223–1230
Guo X et al (2013) Estrogen receptor α regulates ATM expression through miRNAs in breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 19:4994–5002
Guo P, Lan J, Ge J, Nie Q, Guo L, Qiu Y, Mao Q (2014) MiR-26a enhances the radiosensitivity of glioblastoma multiforme cells through targeting of ataxia–telangiectasia mutated. Exp Cell Res 320:200–208
Harrison DE et al (2009) Rapamycin fed late in life extends lifespan in genetically heterogeneous mice. Nature 460:392–395
Harte MT et al (2014) NF-κB is a critical mediator of BRCA1-induced chemoresistance. Oncogene 33:713
Herranz D, Muñoz-Martin M, Cañamero M, Mulero F, Martinez-Pastor B, Fernandez-Capetillo O, Serrano M (2010) Sirt1 improves healthy ageing and protects from metabolic syndrome-associated cancer. Nat Commun 1:3
Herzog R, Zendedel A, Lammerding L, Beyer C, Slowik A (2017) Impact of 17beta-estradiol and progesterone on inflammatory and apoptotic microRNA expression after ischemia in a rat model. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 167:126–134
Heyn H et al (2011) MicroRNA miR-335 is crucial for the BRCA1 regulatory cascade in breast cancer development. Int J Cancer 129:2797–2806
Hoey C et al (2018) Mi RNA-106a and prostate cancer radioresistance: a novel role for LITAF in ATM regulation. Mol Oncol 12:1324–1341
Holzenberger M et al (2003) IGF-1 receptor regulates lifespan and resistance to oxidative stress in mice. Nature 421:182–187
Houtkooper RH, Pirinen E, Auwerx J (2012) Sirtuins as regulators of metabolism and healthspan. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 13:225–238
Hu Z, Klein JD, Mitch WE, Zhang L, Martinez I, Wang XH (2014) MicroRNA-29 induces cellular senescence in aging muscle through multiple signaling pathways. Aging (Albany NY) 6:160
Hu B et al (2017) MiR-21-mediated radioresistance is via promoting repair of DNA double strand breaks. J Biol Chem M116:772392
Huang J-W et al (2013a) Systematic screen identifies miRNAs that target RAD51 and RAD51D to enhance chemosensitivity. Mol Cancer Res 11:1564–1573
Huang T, Alvarez A, Hu B, Cheng S-Y (2013b) Noncoding RNAs in cancer and cancer stem cells. Chin J Cancer 32:582
Huertas P, Jackson SP (2009) Human CtIP mediates cell cycle control of DNA end resection and double strand break repair. J Biol Chem 284:9558–9565
Hühn D, Kousholt A, Sørensen CS, Sartori A (2015) miR-19, a component of the oncogenic miR-17∼ 92 cluster, targets the DNA-end resection factor CtIP. Oncogene 34:3977
Ibrahim YH et al (2012) PI3K inhibition impairs BRCA1/2 expression and sensitizes BRCA-proficient triple-negative breast cancer to PARP inhibition. Cancer Discov 2(11):1036–1047
Jackson SP, Bartek J (2009) The DNA-damage response in human biology and disease. Nature 461:1071
Joaquin á, Watson R (2003) Cell cycle regulation by the B-Myb transcription factor. Cell Mol Life Sci 60:2389–2401
Joo JH, Hong IK, Kim NK, Choi E (2018) Trichosanthes kirilowii extract enhances repair of UVB radiation-induced DNA damage by regulating BMAL1 and miR-142-3p in human keratinocytes. Mol Med Rep 17:877–883
Jung HJ, Suh Y (2014) Circulating miRNAs in ageing and ageing-related diseases. J Genet Genomics 41:465–472
Kanellopoulou C, Monticelli S (2008) A role for microRNAs in the development of the immune system and in the pathogenesis of cancer. In: Seminars in cancer biology. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 79–88
Kawai S, Amano A (2012) BRCA1 regulates microRNA biogenesis via the DROSHA microprocessor complex. J Cell Biol 197:201–208
Kim YK, Kim VN (2007) Processing of intronic microRNAs. EMBO J 26:775–783
Kroemer G, Galluzzi L, Brenner C (2007) Mitochondrial membrane permeabilization in cell death. Physiol Rev 87:99–163
Kumaraswamy E et al (2015) BRCA1 regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) expression in human breast cancer cells involves microRNA-146a and is critical for its tumor suppressor function. Oncogene 34:4333
La Rocca G, Badin M, Shi B, Xu SQ, DeAngelis T, Sepp-Lorenzinoi L, Baserga R (2009a) Mechanism of growth inhibition by MicroRNA 145: The role of the IGF-I receptor signaling pathway. J Cell Physiol 220:485–491
La Rocca G, Shi B, Badin M, De Angelis T, Sepp-Lorenzino L, Baserga R (2009b) Growth inhibition by microRNAs that target the insulin receptor substrate-1. Cell Cycle 8:2255–2259
Lamming DW (2014) Diminished mTOR signaling: a common mode of action for endocrine longevity factors. Springerplus 3:735
Lau NC, Lim LP, Weinstein EG, Bartel DP (2001) An abundant class of tiny RNAs with probable regulatory roles in Caenorhabditis elegans. Science 294:858–862
Lee Y, Kim M, Han J, Yeom KH, Lee S, Baek SH, Kim VN (2004) MicroRNA genes are transcribed by RNA polymerase II. EMBO J 23:4051–4060
Lee J et al (2010) A pathway involving FXR and shp positively regulates hepatic SIRT1 levels via MIR-34A inhibition. J Biol Chemistry:jbc M109:094524
Lee J-H et al (2015) MicroRNA-22 suppresses DNA repair and promotes genomic instability through targeting of MDC1. Can Res 75(7):1298–1310
Li G, Luna C, Qiu J, Epstein DL, Gonzalez P (2009) Alterations in microRNA expression in stress-induced cellular senescence. Mech Ageing Dev 130:731–741
Li T, Ma J, Han X, Jia Y, Yuan H, Shui S, Guo D (2018) MicroRNA-320 Enhances radiosensitivity of glioma through down-regulation of Sirtuin type 1 by directly targeting Forkhead box protein M1. Transl Oncol 11:205–212
Liao X-H et al (2015) STAT3 regulated ATR via microRNA-383 to control DNA damage to affect apoptosis in A431 cells. Cell Signal 27:2285–2295
Lima RT, Busacca S, Almeida GM, Gaudino G, Fennell DA, Vasconcelos MH (2011) MicroRNA regulation of core apoptosis pathways in cancer. Eur J Cancer 47:163–174
Lin F et al (2012) miR-26b promotes granulosa cell apoptosis by targeting ATM during follicular atresia in porcine ovary. PLoS ONE 7:e38640
Liu Y, Liu Q (2011) ATM signals miRNA biogenesis through KSRP. Mol Cell 41:367–368
Liu Q, Wang G, Chen Y, Li G, Yang D, Kang J (2014) A miR-590/Acvr2a/Rad51b axis regulates DNA damage repair during mESC proliferation. Stem Cell Rep 3:1103–1117
Liu G, Xue F, Zhang W (2015) miR-506: a regulator of chemo-sensitivity through suppression of the RAD51-homologous recombination axis. Chin J Cancer 34:44
Lu H-J et al (2018) microRNA-136 inhibits proliferation and promotes apoptosis and radiosensitivity of cervical carcinoma through the NF-κB pathway by targeting E2F1. Life Sci 199:167–178
MacFarlane L-A, Murphy RP (2010) MicroRNA: biogenesis, function and role in cancer. Curr Genomics 11:537–561
Majidinia M, Yousefi B (2016) DNA damage response regulation by microRNAs as a therapeutic target in cancer. DNA Repair 47:1–11
Majidinia M, Yousefi B (2017) DNA repair and damage pathways in breast cancer development and therapy. DNA Repair 54:22–29
Majidinia M, Darband SG, Kaviani M, Nabavi SM, Jahanban-Esfahlan R, Yousefi B (2018) Cross-regulation between Notch signaling pathway and miRNA machinery in cancer. DNA Repair 66:30–41
Manic G, Obrist F, Sistigu A, Vitale I (2015) Trial watch: targeting ATM–CHK2 and ATR–CHK1 pathways for anticancer therapy. Mol Cell Oncol 2:e1012976
Mansour WY et al (2013) Aberrant overexpression of miR-421 downregulates ATM and leads to a pronounced DSB repair defect and clinical hypersensitivity in SKX squamous cell carcinoma. Radiother Oncol 106:147–154
Maréchal A, Zou L (2013) DNA damage sensing by the ATM and ATR kinases. Cold Spring Harbor Perspect Biol 5:a012716
Martin NT et al (2013) ATM–dependent miR-335 targets CtIP and modulates the DNA damage response. PLoS Genet 9:e1003505
Martinez I, Cazalla D, Almstead LL, Steitz JA, DiMaio D (2011) miR-29 and miR-30 regulate B-Myb expression during cellular senescence. Proc Natl Acad Sci 108:522–527
Martins R, Lithgow GJ, Link W (2016) Long live FOXO: unraveling the role of FOXO proteins in aging and longevity. Aging Cell 15:196–207
Matamala N et al (2016) MicroRNA deregulation in triple negative breast cancer reveals a role of miR-498 in regulating BRCA1 expression. Oncotarget 7:20068
Melton C, Judson RL, Blelloch R (2010) Opposing microRNA families regulate self-renewal in mouse embryonic stem cells. Nature 463:621–626
Menghini R et al (2009) MicroRNA 217 modulates endothelial cell senescence via silent information regulator 1. Circulation 120:1524–1532
Mersch J et al (2015) Cancers associated with BRCA 1 and BRCA 2 mutations other than breast and ovarian. Cancer 121:269–275
Mirza-Aghazadeh-Attari M, Darband SG, Kaviani M, Mihanfar A, Attari JA, Yousefi B, Majidinia M (2018) DNA damage response and repair in colorectal cancer: defects, regulation and therapeutic implications. DNA Repair 69:34–52
Mitomo S et al (2008) Downregulation of miR-138 is associated with overexpression of human telomerase reverse transcriptase protein in human anaplastic thyroid carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Sci 99:280–286
Miyaki S et al (2009) MicroRNA-140 is expressed in differentiated human articular chondrocytes and modulates interleukin-1 responses. Arthritis Rheum 60:2723–2730
Moskwa P et al (2011) miR-182-mediated downregulation of BRCA1 impacts DNA repair and sensitivity to PARP inhibitors. Mol Cell 41:210–220
Mueller AC, Sun D, Dutta A (2013) The miR-99 family regulates the DNA damage response through its target SNF2H. Oncogene 32:1164
Naccarati A et al (2012) Polymorphisms in miRNA-binding sites of nucleotide excision repair genes and colorectal cancer risk. Carcinogenesis 33:1346–1351
Nagaraja AK et al (2010) A link between mir-100 and FRAP1/mTOR in clear cell ovarian cancer. Mol Endocrinol 24:447–463
Nishino J, Kim I, Chada K, Morrison SJ (2008) Hmga2 promotes neural stem cell self-renewal in young but not old mice by reducing p16 Ink4a and p19 Arf expression. Cell 135:227–239
Norbury CJ, Zhivotovsky B (2004) DNA damage-induced apoptosis. Oncogene 23:2797
Olivieri F et al (2012) Age-related differences in the expression of circulating microRNAs: miR-21 as a new circulating marker of inflammaging. Mech Ageing Dev 133:675–685
Pandey R, Bhattacharya A, Bhardwaj V, Jha V, Mandal AK, Mukerji M (2016) Alu-miRNA interactions modulate transcript isoform diversity in stress response and reveal signatures of positive selection. Sci Rep 6:32348
Pardini B et al (2013) Variation within 3'UTRs of base excision repair genes and response to therapy in colorectal cancer patients: a potential modulation of microRNAs binding. Clin Cancer Res 19:6044–6056
Patel N, Garikapati KR, Pandita RK, Singh DK, Pandita TK, Bhadra U, Bhadra MP (2017) miR-15a/miR-16 down-regulates BMI1, impacting Ub-H2A mediated DNA repair and breast cancer cell sensitivity to doxorubicin. Sci Rep 7:4263
Persengiev S, Kondova I, Otting N, Koeppen AH, Bontrop RE (2011) Genome-wide analysis of miRNA expression reveals a potential role for miR-144 in brain aging and spinocerebellar ataxia pathogenesis. Neurobiol Aging 32:2316.e2317–2316.e2327.
Petrovic N, Davidovic R, Bajic V, Obradovic M, Isenovic RE (2017) MicroRNA in breast cancer: the association with BRCA1/2. Cancer Biomark 19:119–128
Pitto L et al (2009) miR-290 acts as a physiological effector of senescence in mouse embryo fibroblasts. Physiol Genomics 39:210–218
Qin Y et al (2017) Epigenetic silencing of miR-137 induces drug resistance and chromosomal instability by targeting AURKA in multiple myeloma. Leukemia 31:1123
Rane S et al (2009) Downregulation of miR-199a derepresses hypoxia-inducible factor-1α and Sirtuin 1 and recapitulates hypoxia preconditioning in cardiac myocytes. Circ Res 104:879–886
Ren B, Cam H, Takahashi Y, Volkert T, Terragni J, Young RA, Dynlacht BD (2002) E2F integrates cell cycle progression with DNA repair, replication, and G2/M checkpoints. Genes Dev 16:245–256
Reznick RM et al (2007) Aging-associated reductions in AMP-activated protein kinase activity and mitochondrial biogenesis. Cell Metab 5:151–156
Robida-Stubbs S et al (2012) TOR signaling and rapamycin influence longevity by regulating SKN-1/Nrf and DAF-16/FoxO. Cell Metab 15:713–724
Rodriguez A, Griffiths-Jones S, Ashurst JL, Bradley A (2004) Identification of mammalian microRNA host genes and transcription units. Genome Res 14:1902–1910
Sala A (2005) B-MYB, a transcription factor implicated in regulating cell cycle, apoptosis and cancer. Eur J Cancer 41:2479–2484
Saleh L et al (2017) Ibrutinib downregulates a subset of miRNA leading to upregulation of tumor suppressors and inhibition of cell proliferation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia 31:340
Salminen A, Kaarniranta K (2012) AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) controls the aging process via an integrated signaling network. Ageing Res Rev 11:230–241
Selman C, Partridge L, Withers DJ (2011) Replication of extended lifespan phenotype in mice with deletion of insulin receptor substrate 1. PLoS ONE 6:e16144
Shan Z-X et al (2009) Upregulated expression of miR-1/miR-206 in a rat model of myocardial infarction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 381:597–601
Shariati-Kohbanani M et al (2016) DNA Methylation and microRNA patterns are in association with the expression of BRCA1 in ovarian cancer. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand) 62:16–23
Song L et al (2011) miR-18a impairs DNA damage response through downregulation of ataxia telangiectasia mutated (ATM) kinase. PLoS ONE 6:e25454
Strum JC et al (2009) MicroRNA 132 regulates nutritional stress-induced chemokine production through repression of SirT1. Mol Endocrinol 23:1876–1884
Su Z, Yang Z, Xu Y, Chen Y, Yu Q (2015) MicroRNAs in apoptosis, autophagy and necroptosis. Oncotarget 6:8474
Sun C-C, Li S-J, Yuan Z-P, Li D-J (2016) MicroRNA-346 facilitates cell growth and metastasis, and suppresses cell apoptosis in human non-small cell lung cancer by regulation of XPC/ERK/Snail/E-cadherin pathway. Aging (Albany NY) 8:2509
Tamminga J, Kathiria P, Koturbash I, Kovalchuk O (2008) DNA damage-induced upregulation of miR-709 in the germline downregulates BORIS to counteract aberrant DNA hypomethylation. Cell Cycle 7:3731–3736
Tang BL (2016) Sirt1 and the mitochondria. Mol Cells 39:87
Tanic M, Zajac M, Gómez-López G, Benítez J, Martínez-Delgado B (2012) Integration of BRCA1-mediated miRNA and mRNA profiles reveals microRNA regulation of TRAF2 and NFκB pathway. Breast Cancer Res Treat 134:41–51
Tardif G, Hum D, Pelletier J-P, Duval N, Martel-Pelletier J (2009) Regulation of the IGFBP-5 and MMP-13 genes by the microRNAs miR-140 and miR-27a in human osteoarthritic chondrocytes. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 10:148
Terry LJ, Shows EB, Wente SR (2007) Crossing the nuclear envelope: hierarchical regulation of nucleocytoplasmic transport. Science 318:1412–1416
Tong HL, Jiang RY, Zhang WW, Yan YQ (2017) MiR-2425-5p targets RAD9A and MYOG to regulate the proliferation and differentiation of bovine skeletal muscle-derived satellite cells. Sci Rep 7:418
Treiber T, Treiber N, Meister G (2012) Regulation of microRNA biogenesis and function. Thromb Haemost 107:605
Tsai Y-S, Lin C-S, Chiang S-L, Lee C-H, Lee K-W, Ko Y-C (2011) Areca nut induces miR-23a and inhibits repair of DNA double-strand breaks by targeting FANCG. Toxicol Sci 123:480–490
van Almen GC et al (2011) MicroRNA-18 and microRNA-19 regulate CTGF and TSP-1 expression in age-related heart failure. Aging Cell 10:769–779
Wan G, Mathur R, Hu X, Zhang X, Lu X (2011) miRNA response to DNA damage. Trends Biochem Sci 36:478–484
Wan G et al (2013) DNA-damage-induced nuclear export of precursor microRNAs is regulated by the ATM-AKT pathway. Cell Rep 3:2100–2112
Wang X, Qian R, Zhang W, Chen S, Jin H, Hu R (2009) MicroRNA-320 expression in myocardial microvascular endothelial cells and its relationship with insulin-like growth factor-1 in type 2 diabetic rats. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 36:181–188
Wang Y et al (2011a) MicroRNA-138 modulates DNA damage response by repressing histone H2AX expression. Mol Cancer Res 9:1100–1111
Wang Y et al (2011b) Transforming growth factor-β regulates the sphere-initiating stem cell-like feature in breast cancer through miRNA-181 and ATM. Oncogene 30:1470
Wang Y, Huang J-W, Calses P, Kemp CJ, Taniguchi T (2012) MiR-96 downregulates REV1 and RAD51 to promote cellular sensitivity to cisplatin and PARP inhibition. Can Res 72:1037–1046
Wang J et al (2013) Repression of ATR pathway by miR-185 enhances radiation-induced apoptosis and proliferation inhibition. Cell Death Dis 4:e699
Wang Y et al (2015) MiR-499 enhances the cisplatin sensitivity of esophageal carcinoma cell lines by targeting DNA polymerase β. Cell Physiol Biochem 36:1587–1596
Wang Y et al (2018a) miR-98-5p contributes to cisplatin resistance in epithelial ovarian cancer by suppressing miR-152 biogenesis via targeting Dicer1. Cell Death Dis 9:447
Wang Y et al (2018b) MiR-149 sensitizes esophageal cancer cell lines to cisplatin by targeting DNA polymerase β. J Cell Mol Med 22:3857–3865
Williams AB, Schumacher B (2016) p53 in the DNA-damage-repair process. Cold Spring Harbor Perspect Med 6:a026070
Wronski A et al (2016) MicroRNA-206 is differentially expressed in Brca1-deficient mice and regulates epithelial and stromal cell compartments of the mouse mammary gland. Oncogenesis 5:e218
Wu Z, Wang P, Song C, Wang K, Yan R, Li J, Dai L (2015) Evaluation of miRNA-binding-site SNPs of MRE11A, NBS1, RAD51 and RAD52 involved in HRR pathway genes and risk of breast cancer in China. Mol Genet Genomics 290:1141–1153
Xie Q-H, He X-X, Chang Y, Sun S-z, Jiang X, Li P-Y, Lin J-S (2011) MiR-192 inhibits nucleotide excision repair by targeting ERCC3 and ERCC4 in HepG2. 2.15 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 410:440–445
Xu N, Papagiannakopoulos T, Pan G, Thomson JA, Kosik KS (2009) MicroRNA-145 regulates OCT4, SOX2, and KLF4 and represses pluripotency in human embryonic stem cells. Cell 137:647–658
Xu D et al (2011) miR-22 represses cancer progression by inducing cellular senescence. J Cell Biol 193:409–424
Xu K, Chen Z, Qin C, Song X (2014) miR-7 inhibits colorectal cancer cell proliferation and induces apoptosis by targeting XRCC2. OncoTargets Ther 7:325
Xu X et al (2015) miR-34a induces cellular senescence via modulation of telomerase activity in human hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting FoxM1/c-Myc pathway. Oncotarget 6:3988
Yang J, Xu Z-P, Huang Y, Hamrick HE, Duerksen-Hughes PJ, Yu Y-N (2004) ATM and ATR: sensing DNA damage. World J Gastroenterol 10:155
Yang H et al (2014) Up-regulation of microRNA-138 induce radiosensitization in lung cancer cells. Tumor Biol 35:6557–6565
Yu X-Y, Song Y-H, Geng Y-J, Lin Q-X, Shan Z-X, Lin S-G, Li Y (2008) Glucose induces apoptosis of cardiomyocytes via microRNA-1 and IGF-1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 376:548–552
Zhang X, Wan G, Berger FG, He X, Lu X (2011) The ATM kinase induces microRNA biogenesis in the DNA damage response. Mol Cell 41:371–383
Zhang P et al (2014a) miR-205 acts as a tumour radiosensitizer by targeting ZEB1 and Ubc13. Nat Commun 5:5671
Zhang X et al (2014b) MicroRNA-181a functions as an oncomir in gastric cancer by targeting the tumour suppressor gene ATM. Pathol Oncol Res 20:381–389
Zou Z et al (2016) miR-30a can inhibit DNA replication by targeting RPA1 thus slowing cancer cell proliferation. Biochem J 473:2131–2139
Zou X, Kang L, Yang M, Wu J, Guan H (2018) MicroRNA binding mediated functional sequence variant in 3′-UTR of DNA repair Gene XPC in age-related cataract. Sci Rep 8:15198
Acknowledgements
The Authors would like to thank Aging Reserch Institute of Tabriz University of Medical Science for fund suppord (Grant no: 62906) and Clinical Research Development Unit, Shohada Hospital, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences for kind advisory supports.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Majidinia, M., Mir, S.M., Mirza-Aghazadeh-Attari, M. et al. MicroRNAs, DNA damage response and ageing. Biogerontology 21, 275–291 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10522-020-09862-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10522-020-09862-2