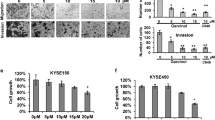
We studied the mechanism underlying the effect of baicalein on the growth of transplanted esophageal cancer in NOG mice and its effect on the expression of PAK4. For that purpose, we developed a new model of transplanted esophageal cancer (human esophageal cancer OE19 cells (107 cells/ml) were inoculated to NOG mice). Three experimental groups with transplanted esophageal cancer cells received baicalein in different doses (1, 1.5, and 2 mg/kg). In 32 days, the tumors were resected, and the expression of PAK4 and the level of activated PAK4 were assayed by reverse transcription PCR and Western blotting, respectively. The results showed a dose-depending anti-tumor effect of baicalein on the transplanted esophageal cancer in NOG mice: this effect of baicalein (determined by the size and weight of the tumor) increased with increasing the dose of the substance. Furthermore, the anti-tumor effect of baicalein was also confirmed by reduction of PAK4 expression. Thus, baicalein can inhibit tumor growth by inhibiting activation of PAK4. Therefore, our results showed that baicalein could inhibit the growth of esophageal cancer cells by inhibiting the activity of PAK4, which can be an important mechanism of its antitumor effect.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nik Salleh NNH, Othman FA, Kamarudin NA, Tan SC. The Biological Activities and Therapeutic Potentials of Baicalein Extracted from Oroxylum indicum: A Systematic Review. Molecules. 2020;25(23):5677. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25235677
D’amico R, Fusco R, Gugliandolo E, Cordaro M, Siracusa R, Impellizzeri D, Peritore AF, Crupi R, Cuzzocrea S, Di Paola R. Effects of a new compound containing Palmitoylethanolamide and Baicalein in myocardial ischaemia/reperfusion injury in vivo. Phytomedicine. 2019;54:27-42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2018.09.191
Qiao D, Jin J, Xing J, Zhang Y, Jia N, Ren X, Lin Z, Jin N, Chen L, Piao Y. Baicalein Inhibits Gastric Cancer Cell Proliferation and Migration through a FAK Interaction via AKT/mTOR Signaling. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2021;49(2):525-541. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0192415X21500245
Lin H, Hao Y, Wan X, He J, Tong Y. Baicalein inhibits cell development, metastasis and EMT and induces apoptosis by regulating ERK signaling pathway in osteosarcoma. J. Recept. Signal Transduct. Res. 2020;40(1):49-57. https://doi.org/10.1080/10799893.2020.1713807
Yan W, Ma X, Zhao X, Zhang S. Baicalein induces apoptosis and autophagy of breast cancer cells via inhibiting PI3K/AKT pathway in vivo and vitro. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2018;12:3961-3972. https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S181939
Park YG, Choi J, Jung HK, Kim B, Kim C, Park SY, Seol JW. Baicalein inhibits tumor progression by inhibiting tumor cell growth and tumor angiogenesis. Oncol. Rep. 2017;38(5):3011-3018. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2017.6007
Rane CK, Minden A. P21 activated kinase signaling in cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2019;54:40-49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2018.01.006
Naїja A, Merhi M, Inchakalody V, Fernandes Q, Mestiri S, Prabhu KS, Uddin S, Dermime S. The role of PAK4 in the immune system and its potential implication in cancer immunotherapy. Cell. Immunol. 2021;367:104408. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellimm.2021.104408
Nekrasova T, Minden A. PAK4 is required for regulation of the cell-cycle regulatory protein p21, and for control of cell-cycle progression. J. Cell. Biochem. 2011;112(7):1795-1806. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.23092
Liu Y, Xiao H, Tian Y, Nekrasova T, Hao X, Lee HJ, Suh N, Yang CS, Minden A. The pak4 protein kinase plays a key role in cell survival and tumorigenesis in athymic mice. Mol. Cancer Res. 2008;6(7):1215-1224. https://doi.org/10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-08-0087
Liu Y, Chen N, Cui X, Zheng X, Deng L, Price S, Karantza V, Minden A. The protein kinase Pak4 disrupts mammary acinar architecture and promotes mammary tumorigenesis. Oncogene. 2010;29(44):5883-5894. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.329
Fu Y, Fang L, Yin Q, Wu Q, Sui W, Sun Y, Zhao X, Wu Y, Zhou L. Interfering with pak4 Protein Expression Affects Osteosarcoma Cell Proliferation and Migration. Bio-med. Res. Int. 2021;2021:9977001. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/ 9977001
Wei Y, Wu W, Jiang Y, Zhou H, Yu Y, Zhao L, Wu X, Lu X, Yuan Q, Wang Z, Dong Z, He L, Zhao J, Liu K. Nuplazid suppresses esophageal squamous cell carcinoma growth in vitro and in vivo by targeting PAK4. Br. J. Cancer. 2022;126(7):1037-1046. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41416-021-01651-z
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Byulleten’ Eksperimental’noi Biologii i Meditsiny, Vol. 174, No. 10, pp. 489-492, October, 2022
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Sun, X., Liu, J. et al. Baicalein Inhibits the Growth of Transplanted Esophageal Cancer in Mice and the Effect on the Expression of PAK4. Bull Exp Biol Med 174, 478–481 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-023-05733-1
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-023-05733-1