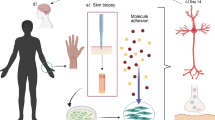
We compared the expression of Aβ42 peptide, τ-protein, and α-synuclein in the substantia nigra and skin fibroblasts of elderly and senile patients with Parkinson’s disease and subjects without neuropathology. Expression of markers in the studied tissues was assessed by immunohistochemical and immunocytochemical methods. The expression of Aβ42 peptide, τ-protein, and α-synuclein in the substantia nigra of elderly and senile patients with Parkinson’s disease was higher by 11-31 times than in subjects without neuropathology. In skin fibroblasts of patients with Parkinson’s disease, the expression of Aβ42 peptide and α-synuclein was 3-14 times higher than in subjects without neuropathology, and expression of τ-protein did not significantly differ in the studied groups. Thus, immunocytochemical analysis of the expression Aβ42 peptide and α-synuclein in skin fibroblasts can be a simple method of early diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease in elderly persons.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Nimer MS, Mshatat SF, Abdulla HI. Saliva α-synuclein and a high extinction coefficient protein: a novel approach in assessment biomarkers of Parkinson’s disease. N. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2014;6(12):633-637.
Burke JF, Albin RL, Koeppe RA, Giordani B, Kilbourn MR, Gilman S, Frey KA. Assessment of mild dementia with amyloid and dopamine terminal positron emission tomography. Brain. 2011;134(Pt 6):1647-1657.
Cheng HC, Ulane CM, Burke RE. Clinical progression in Parkinson disease and the neurobiology of axons. Ann. Neurol. 2010;67(6):715-725.
Cova I, Priori A. Diagnostic biomarkers for Parkinson’s disease at a glance: where are we? J. Neural Transm. (Vienna). 2018;125(10):1417-1432.
Donaghy PC, Firbank MJ, Thomas AJ, Lloyd J, Petrides G, Barnett N, Olsen K, O’Brien JT. Clinical and imaging correlates of amyloid deposition in dementia with Lewy bodies. Mov. Disord. 2018;33(7):1130-1138.
El-Agnaf OM, Salem SA, Paleologou KE, Curran MD, Gibson MJ, Court JA, Schlossmacher MG, Allsop D. Detection of oligomeric forms of alphα-synuclein protein in human plasma as a potential biomarker for Parkinson’s disease. FASEB J. 2006;20(3):419-425.
Foster ER, Campbell MC, Burack MA, Hartlein J, Flores HP, Cairns NJ, Hershey T, Perlmutter JS. Amyloid imaging of Lewy body-associated disorders. Mov. Disord. 2010;25(15):2516-2523.
Gordon R, Singh N, Lawana V, Ghosh A, Harischandra DS, Jin H, Hogan C, Sarkar S, Rokad D, Panicker N, Anantharam V, Kanthasamy AG, Kanthasamy A. Protein kinase Cδ upregulation in microglia drives neuroinflammatory responses and dopaminergic neurodegeneration in experimental models of Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2016;93:96-114.
Htike TT, Mishra S, Kumar S, Padmanabhan P, Gulyás B. Peripheral biomarkers for early detection of Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-018-1151-1154.
Irwin DJ, Xie SX, Coughlin D, Nevler N, Akhtar RS, Mc-Millan CT, Lee EB, Wolk DA, Weintraub D, Chen-Plotkin A, Duda JE, Spindler M, Siderowf A, Hurtig HI, Shaw LM, Grossman M, Trojanowski JQ. CSF tau and β-amyloid predict cerebral synucleinopathy in autopsied Lewy body disorders. Neurology. 2018;90(12):e1038-e1046.
Kotagal V, Spino C, Bohnen NI, Koeppe R, Albin RL. Serotonin, β-amyloid, and cognition in Parkinson disease. Ann. Neurol. 2018;83(5):994-1002.
Lei P, Ayton S, Finkelstein DI, Adlard PA, Masters CL, Bush AI. Tau protein: relevance to Parkinson’s disease. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2010;42(11):1775-1778.
Maetzler W, Liepelt I, Reimold M, Reischl G, Solbach C, Becker C, Schulte C, Leyhe T, Keller S, Melms A, Gasser T, Berg D. Cortical PIB binding in Lewy body disease is associated with Alzheimer-like characteristics. Neurobiol. Dis. 2009;34(1):107-112.
Miller DB, O’Callaghan JP. Biomarkers of Parkinson’s disease: present and future. Metabolism. 2015;64(3, Suppl. 1):S40-S46.
Moussaud S, Jones DR, Moussaud-Lamodière EL, Delenclos M, Ross OA, McLean PJ. Alpha-synuclein and tau: teammates in neurodegeneration. Mol. Neurodegener. 2014;9. ID 43. doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/1750-1326-9-43.
Ono K, Yamada M. Alpha-Synuclein in blood and cerebrospinal fluid of patients with alphα-synucleinopathy. Rinsho Byori. 2014;62(3):241-245.
Paltsev MA, Polyakova VO, Kvetnoy IM, Anderson G, Kvetnaia TV, Linkova NS, Paltseva EM, Rubino R, De Cosmo S, De Cata A, Mazzoccoli G. Morphofunctional and signaling molecules overlap of the pineal gland and thymus: role and significance in aging. Oncotarget. 2016;7(11):11,972-11,983.
Petrou M, Dwamena BA, Foerster BR, MacEachern MP, Bohnen NI, Müller ML, Albin RL, Frey KA. Amyloid deposition in Parkinson’s disease and cognitive impairment: a systematic review. Mov. Disord. 2015;30(7):928-935.
Salama M, Shalash A, Magdy A, Makar M, Roushdy T, Elbalkimy M, Elrassas H, Elkafrawy P, Mohamed W, Abou Donia MB. Tubulin and Tau: possible targets for diagnosis of Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s diseasesb. PLoS One. 2018;13(5). ID e0196436. doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0196436.
Sánchez-Ferro Á, Rábano A, Catalán MJ, Rodríguez-Valcárcel FC, Fernández Díez S, Herreros-Rodríguez J, García-Cobos E, Álvarez-Santullano MM, López-Manzanares L, Mosqueira AJ, Vela Desojo L, López-Lozano JJ, López-Valdés E, Sánchez-Sánchez R, Molina-Arjona JA. In vivo gastric detection of alphasynuclein inclusions in Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2014;30(4):517-524.
Valli M, Strafella AP. New advances in tau imaging in parkinsonism. Int. Rev. Psychiatry. 2017;29(6):628-635.
Venderova K, Park DS. Programmed cell death in Parkinson’s disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2012;2(8). pii: a009365. doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a009365.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Kletochnye Tekhnologii v Biologii i Meditsine, No. 1, pp. 63-68, January, 2019
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zuev, V.A., Dyatlova, A.S., Lin’kova, N.S. et al. Skin Fibroblasts as the Object for Clinical Diagnosis of Parkinson’s Disease in Persons of Different Ages. Bull Exp Biol Med 167, 177–181 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-019-04485-1
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-019-04485-1