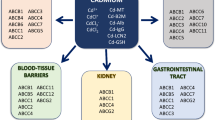
We created a physiologically substantiated kinetic model of cadmium transport and toxicity in intestinal cell model (Caco-2 cells). Transcriptome profiling of Caco-2 cells revealed high content of transporter DMT1 and ZIP14 and intensive expression of some calcium channels of the CACN family. The mathematical model describing three types of transporters, as well as intracellular cadmium binding with metallothionein and excretion through the basolateral membrane allowed us to construct cadmium uptake and transport curves that approximated the previously obtained experimental data. Using the proposed model, we determined toxic intracellular cadmium concentration leading to cell death and impairing the integrity of cell monolayer and described cadmium transport in this case.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Blais, S. Lecoeur, G. Milhaud, D. Tomé, and M. Kolf-Clauw, Cadmium uptake and transepithelial transport in control and long-term exposed Caco-2 cells: the role of metallothionein. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol., 160, No. 1, 76-85 (1999).
G. B. Cardin, M. Mantha, and C. Jumarie, Resistance to cadmium as a function of Caco-2 cell differentiation: role of reactive oxygen species in cadmium- but not zinc-induced adaptation mechanisms. Biometals, 22, No. 5, 753-769 (2009).
F. Elisma and C. Jumarie, Evidence for cadmium uptake through Nramp2: metal speciation studies with Caco-2 cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 285, No. 3, 662-668 (2001).
M. Erk and B. Raspor, Evaluation of cadmium-metallothionein stability constants based on voltammetric measurements. Anal. Chim. Acta, 360, Nos. 1-3, 189-194, doi: 10.1016/S0003-2670(97)00729-0 (1998).
M. B. Esch, T. L. King, and M. L. Shuler, The role of body-ona-chip devices in drug and toxicity studies. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng., 13, 55-72 (2011).
S. Himeno, T. Yanagiya, and H. Fujishiro, The role of zinc transporters in cadmium and manganese transport in mammalian cells. Biochimie, 91, No. 10, 1218-1222 (2009).
C. Jumarie, P. G. Campbell, A. Berteloot, M. Houde, and F. Denizeau, Caco-2 cell line used as an in vitro model to study cadmium accumulation in intestinal epithelial cells. J. Membr. Biol., 158, No. 1, 31-48 (1997).
C. Jumarie, P. G. Campbell, M. Houde, and F. Denizeau, Evidence for an intracellular barrier to cadmium transport through Caco-2 cell monolayers. J. Cell. Physiol., 180, No. 2, 285-297 (1999).
S. Lecoeur, C. Huynh-Delerme, A. Blais, A. Duché, D. Tomé, and M. Kolf-Clauw, Implication of distinct proteins in cadmium uptake and transport by intestinal cells HT-29. Cell Biol. Toxicol., 18, No. 6, 409-423 (2002).
R. Leyva-Ramos, J. R. Rangel-Mendez, L. A. Bernal-Jacome, and M. S. Berber Mendoza, Intraparticle diffusion of cadmium and zinc ions during adsorption from aqueous solution on activated carbon. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol., 80, No. 8, 924-933, doi: 10.1002/jctb.1263 (2005).
J. Luevano and C. Damodaran, A review of molecular events of cadmium-induced carcinogenesis. J. Environ. Pathol. Toxicol. Oncol., 33, No. 3, 183-194 (2014).
D. V. Maltseva, E. A. Ryabenko, S. V. Sizova, D. V. Yashin, S. A. Khaustova, and M. Y. Shkurnikov, Effect of exercise on the expression of HSPBP1, PGLYRP1, and HSPA1A genes in human leukocytes. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med., 153, No. 6, 866-868 (2012).
C. Marchetti, Role of calcium channels in heavy metal toxicity. ISRN Toxicol., 2013, doi: 10.1155/2013/184360 (2013).
E. M. Materne, A. G. Tonevitsky, and U. Marx, Chip-based liver equivalents for toxicity testing – organotypicalness versus cost-efficient high throughput. Lab Chip., 13, No. 18, 3481- 3495 (2013).
V. Matović, A. Buha, D. Dukić-Ćosić, and Z. Bulat, Insight into the oxidative stress induced by lead and/or cadmium in blood, liver and kidneys. Food Chem. Toxicol., 78, 130-140 (2015).
J. Miękisz, J. Gomułkiewicz, and S. Miękisz, Mathematical models of ion transport through cell membrane channels. Mathematica Applicanda, 42, No. 1, 39-62, doi: 10.14708/ma.v42i1.469 (2014).
J. M. Moulis, Cellular mechanisms of cadmium toxicity related to the homeostasis of essential metals. Biometals, 23, No. 5, 877-896 (2010).
Y. Nevo and N. Nelson, The NRAMP family of metal-ion transporters. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1763, No. 7, 609-620 (2006).
H. Ohrvik, E. Tydén, P. Artursson, A. Oskarsson, and J. Tallkvist, Cadmium transport in a model of neonatal intestinal cells correlates to MRP1 and not DMT1 or FPN1. ISRN Toxicol., 2013, doi: 10.1155/2013/892364 (2013).
D. A. Sakharov, D. V. Maltseva, E. A. Riabenko, M. U. Shkurnikov, H. Northoff, A. G. Tonevitsky, and A. I. Grigoriev, Passing the anaerobic threshold is associated with substantial changes in the gene expression profile in white blood cells. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol., 112, No. 3, 963-972 (2012).
D. A. Sakharov, A. V. Stepanov, M. Y. Shkurnikov, and A. G. Tonevitskii, Short-term highly intense physiological stress causes an increase in the expression of heat shock protein inhuman leukocytes. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med., 147, No. 3, 361-365 (2009).
T. R. Samatov, M. U. Shkurnikov, S. A. Tonevitskaya, and A. G. Tonevitsky, Modelling the metastatic cascade by in vitro microfluidic platforms. Prog. Histochem. Cytochem., 49, No. 4, 21-29 (2015).
S. Soodvilai, J. Nantavishit, C. Muanprasat, and V. Chatsudthipong, Renal organic cation transporters mediated cadmium-induced nephrotoxicity. Toxicol. Lett., 204, No. 1, 38-42 (2011).
A. G. Tonevitsky, D. V. Maltseva, A. Abbasi, T. R. Samatov, D. A. Sakharov, M. U. Shkurnikov, A. E. Lebedev, V. V. Galatenko, A. I. Grigoriev, and H. Northoff, Dynamically regulated miRNA-mRNA networks revealed by exercise. BMC Physiol., 13, 9, doi: 10.1186/1472-6793-13-9 (2013).
E. Van Kerkhove, V. Pennemans, and Q. Swennen, Cadmium and transport of ions and substances across cell membranes and epithelia. Biometals, 23, No. 5, 823-855 (2010).
L. Verheyen, F. Degryse, T. Niewold, and E. Smolders, Labile complexes facilitate cadmium uptake by Caco-2 cells. Sci. Total Environ., 426, 90-99 (2012).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Kletochnye Tekhnologii v Biologii i Meditsine, No. 1, pp. 54-59, January, 2016
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gerasimenko, T.N., Senyavina, N.V., Anisimov, N.U. et al. A Model of Cadmium Uptake and Transport in Caco-2 Cells. Bull Exp Biol Med 161, 187–192 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-016-3373-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-016-3373-7