Abstract
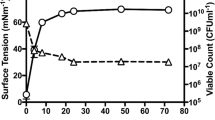
Quorum sensing (QS) is a bacterial communication system in which bacteria coordinate the expression of certain genes in response to the presence of small signal molecules. Some signal molecules called autoinducers are found to regulate several phenotypes of bacteria. The molecules used for the QS system of Vibrio anguillarum are supposed to regulate their pathogenic genes. However, it is not well understood how exactly the virulence gene of V. anguillarum is regulated by the QS molecules to date. To address this question, one of the QS molecules of the NB10 strain of V. anguillarum called N-acyl homoserine lactones (AHLs) was disrupted by a lactonase enzyme to verify its role on their virulence. The effects of AHLs degradation in vitro were investigated by measuring its effect on growth and virulence factors production (lipase, phospholipase, and caseinase) and in vivo by verifying its effect on sea bass and Artemia larvae infection. Lactonase enzyme degraded AHLs of NB10; yet that degradation had no effect on the cell growth and production of the tested virulence factors. Similarly, challenge tests demonstrated that larval mortality was not significantly lower by lactonase treatment. Therefore, these observations indicated that virulence gene expression of V. anguillarum and its virulence are not regulated by the AHL-mediated QS system; either different molecules or other factors are associated with the virulence regulation of V. anguillarum towards the tested life stages of sea bass and Artemia.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akinbowale OL, Peng H, Barton MD (2007) Diversity of tetracycline resistance genes in bacteria from aquaculture sources in Australia. J Appl Microbiol 103:2016–2025
Abuaita BH, Withey JH (2009) Bicarbonate induces Vibrio cholerae virulence gene expression by enhancing ToxT activity. Infect Immun 77:4111–4120
Allison D, Ruiz B, SanJose C, Jaspe A, Gilbert P (1998) Extracellular products as mediators of the formation and detachment of Pseudomonas fluorescens biofilms. FEMS Microbiol Lett 167:179–184
Beck von Bodman S, Farrand SK (1995) Capsular polysaccharide biosynthesis and pathogenicity in Erwinia stewartii require induction by an N-acyl homoserine lactone autoinducer. J Bacteriol 177:5000–5008
Buchholtz C, Nielsen KF, Milton DL, Larsen JL, Gram L (2006) Profiling of acylated homoserine lactones of Vibrio anguillarum in vitro and in vivo: influence of growth conditions and serotype. Syst Appl Microbiol 29:433–445
Bruhn JB, Dalsgaard I, Nielsen KF, Buchholtz C et al (2005) Quorum sensing signal molecules (acylated homoserine lactones) in Gram-negative fish pathogenic bacteria. Dis Aquat Org 65:43–52
Buch C, Sigh J, Nielsen J, Larsen JL, Gram L (2003) Production of acylated homoserine lactones by different serotypes of Vibrio anguillarum both in culture and during infection of rainbow trout. Syst Appl Microbiol 26:338–349
Costa JM, Loper JE (1997) EcbI and EcbR: homologs of LuxI and LuxR affecting antibiotic and exoenzyme production by Erwinia carotovora sub sp. Beta vasculorum. Can J Microbiol 43:1164–1171
Croxatto A, Lauritz J, Chen C, Milton DL (2007) Vibrio anguillarum colonization of rainbow trout integument requires a DNA locus involved in exopolysaccharide transport and biosynthesis. Environ Microbiol 9:370–382
Defoirdt T, Bossier P, Sorgeloos P, Verstraete W (2005) The impact of mutations in the quorum sensing systems of Aeromonas hydrophila, Vibrio anguillarum and Vibrio harveyi on their virulence towards gnotobiotically cultured Artemia franciscana. Environ Microbiol 7:1239–1247
Dierckens K, Rekecki A, Laureau S, Sorgeloos P et al (2009) Development of a bacterial challenge test for gnotobiotic sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) larvae. Environ Microbiol 11:526–533
Donabedian H (2003) Quorum sensing and its relevance to infectious disease. J Inf Secur 46:207–214
Dong YH, JL X, Li XZ, Zhang LH (2000) AiiA, an enzyme that inactivates the acylhomoserine lactone quorum-sensing signal and attenuates the virulence of Erwinia carotovora. P Natl Acad Sci USA 97:3526–3531
Dong YH, Wang LH, JL X, Zhang HB et al (2001) Quenching quorum-sensing-dependent bacterial infection by an N-acyl homoserine lactonase. Nature 411:813–817
Dong YH, Gusti AR, Zhang Q, JL X, Zhang LH (2002) Identification of quorum-quenching N-acyl homoserine lactonases from Bacillus species. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:1754–1759
Dong YH, Zhang XF, JL X, Zhang LH (2004) Insecticidal Bacillus thuringiensis silences Erwinia carotovora virulence by a new form of microbial antagonism, signal interference. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:954–960
Eberl L, Winson MK, Sternberg C, Stewart GSAB et al (1996) Involvement of N-acyl-L-homoserine lactone autoinducers in controlling the multicellular behaviour of Serratia liquefaciens. Mol Microbiol 20:127–136
Gilk SD, Cockrell DC, Luterbach C, Hansen B et al (2013) Bacterial colonization of host cells in the absence of cholesterol. PLoS Pathog 9
Gotoh K, Kodama T, Hiyoshi H, Izutsu K et al (2010) Bile acid induced virulence gene expression of Vibrio parahaemolyticus reveals a novel therapeutic potential for bile acid sequestrants. PLoS One 5(10):e13365
Hsiao A, Liu Z, Joelsson A, Zhu J (2006) Vibrio cholerae virulence regulator-coordinated evasion of host immunity. P Natl Acad Sci USA 103:14542–14547
LaSarre B, Federle MJ (2013) Exploiting quorum sensing to confuse bacterial pathogens. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 77(1):73–111
Lee SJ, Park SY, Lee JJ, Yum DY et al (2002) Genes encoding the N-acyl homoserine lactone-degrading enzyme are widespread in many subspecies of Bacillus thuringiensis. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:3919–3924
Li X, Yang Q, Dierckens K, Milton DL, Defoirdt T (2014) RpoS and indole signaling control the virulence of Vibrio anguillarum towards gnotobiotic sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) larvae. PLoS One 9(10):e111801
Lin YH, JL X, Hu J, Wang LH et al (2003) Acyl-homoserine lactone acylase from Ralstonia sp. strain XJ12B represents a novel and potent class of quorum-quenching enzymes. Mol Microbiol 47:849–860
Ma L, Chen J, Liu R, Zhang XH, Jiang YA (2009) Mutation of rpoS gene decreased resistance to environmental stresses, synthesis of extracellular products and virulence of Vibrio anguillarum. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 70:130–136
McGee K, Horstedt P, Milton DL (1996) Identification and characterization of additional flagellin genes from Vibrio anguillarum. J Bacteriol 178:5188–5198
Milton DL (2006) Quorum sensing in vibrios: complexity for diversification. Int J Med Microbiol 296:61–71
Molina L, Constantinescu F, Michel L, Reimmann C et al (2003) Degradation of pathogen quorum-sensing molecules by soil bacteria: a preventive and curative biological control mechanism. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 45:71–81
Natrah FMI, Ruwandeepika HAD, Pawar S, Karunasagar I et al (2011) Regulation of virulence factors by quorum sensing in Vibrio harveyi. Vet Microbiol 154:124–129
Ni N, Li M, Wang J, Wang B (2009) Inhibitors of bacterial quorum sensing. Med Res Rev 29:65–124
Norqvist A, Norrman B, Wolf-Watz H (1990) Identification and characterization of a zinc metallo protease associated with invasion by the fish pathogen Vibrio anguillarum. Infect Immun 58:3731–3736
Paillard C, Leroux F, Borrego JJ (2004) Bacterial disease in marine bivalves: review of recent studies: trends and evolution. Aquat Living Resour 17:477–498
Phillips I, Casewell M, Cox T, Groot BD et al (2004) Does the use of antibiotics in food animals pose a risk to human health? A critical review of published data. J Antimicrob Chemother 53(1):28–52
Rasch M, Buch C, Austin B, Slierendrecht WJ et al (2004) An inhibitor of bacterial quorum sensing reduces mortalities caused by vibriosis in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss, Walbaum). Syst Appl Microbiol 27:350–359
Rock JL, Nelson DR (2006) Identification and characterization of a hemolysin gene cluster in Vibrio anguillarum. Infect Immun 74:2777–2786
Smith VJ, Brown JH, Hauton C (2003) Immunostimulation in crustaceans: does it really protect against infection? Fish Shellfish Immunol 15:71–90
Stork M, Di Lorenzo M, Welch TJ, Crosa JH (2007) Transcription termination within the iron transport-biosynthesis operon of Vibrio anguillarum requires an antisense RNA. J Bacteriol 189:3479–3488
Subasinghe RP, Bondad-Reantaso MG, McGladdery SE (2001) Aquaculture development, health and wealth. In: Subasinghe RP, Bueno P, Phillips MJ, Hough C et al (eds) Aquaculture in the Third Millennium, Bangkok, 20–25 February 2000
Teplitski M, Robinson JB, Bauer WD (2000) Plants secrete substances that mimic bacterial N-acyl homoserine lactone signal activities and affect population density-dependent behaviors in associated bacteria. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 13:637–648
Tinh NTN, Dung NV, Trung CT, Thuy VT (2013) In vitro characterization of a recombinant AHL-lactonase from Bacillus cereus isolated from a striped catfish (Pangasianodon hypophthalmus) pond. Indian J Microbiol 53(4):485–487
Tinh NTN, Dung NV, Thuy VT, Suong NT (2014) Inhibition of quorum sensing-mediated bioluminescence in Vibrio harveyi by a recombinant AHL-lactonase from Bacillus cereus. J Pure Appl Microbiol 8:353–360
Toranzo AE, Magarinos B, Romalde JL (2005) A review of the main bacterial fish diseases in mariculture systems. Aquaculture 246:37–61
Xu F, Byun T, Dussen HJ, Duke KR (2003) Degradation of N-acyl homoserine lactones the bacterial quorum-sensing molecules by acylase. J Biotechnol 101:89–96
Yang H, Chen J, Yang G, Zhang XH, Li Y (2007) Mutational analysis of the zinc metallo protease EmpA of Vibrio anguillarum. FEMS Microbiol Lett 267:56–63
Acknowledgements
This study was carried out under the Scientific Research Fund of Flanders (FWO-Vlaanderen project no 1.5.013.12N) and the Special Research Fund of Ghent University (GOA project no BOF12/GOA/022). In addition, a part of this study was supported by the Vietnamese National Foundation for Science and Technology Development (NAFOSTED), agreement No. 05/2010/HÐ-KHTN. We are also grateful to Artemia Reference Center, Ghent University, Belgium and Research Institute for Aquaculture No. 2, Hochiminh City, Vietnam, for providing technical and logistic supports.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Das, M., Li, X., Dung, N.V. et al. No effect of N-acyl homoserine lactones disruption by lactonase enzyme on the virulence of Vibrio anguillarum towards sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) and brine shrimp (Artemia franciscana). Aquacult Int 26, 363–374 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-017-0214-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-017-0214-2