Abstract
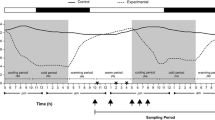
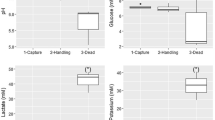
In 2000–2001, an investigation was performed in two Sicilian mariculture sites (Pachino and Castellammare) to monitor physiological and biochemical parameters in sea bream (Sparus aurata) and sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) specimens farmed in off-shore sea cages. Plasma cortisol and glucose levels, tissue lactate concentration, haematocrit and haemoglobin content, lysozyme, haemolytic and haemagglutinating activities were determined. During the experiment, an increase in tissue lactate and plasma cortisol levels and a reduction in haemolytic and haemagglutinating titers, were recorded. Changes occurring in these haematological, immunological and biochemical values suggest that these parameters can be useful indicators in assessing the condition of chronic stress induced by mariculture operations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
B.A. Barton J.D. Morgan M.M. Vijayan (2002) Physiological and condition-related indicators of environmental stress in fish S.M. Adams (Eds) Biological Indicators of Aquatic Ecosystem Stress American Fisheries Society Bethesda, Maryland
N. Hady Kacem J.F. Aldrin B. Romestand (1986) ArticleTitleInfluence immediate du brossage des bacs sur certain parameters sanguins du loup d’elevage, Dicentrarchus labrax L.: Effect du stress Aquaculture 59 53–59
D. Montero M. Marrero M.S. Izquierdo L. Robaina J.M. Vergara L. Tort (1999) ArticleTitleEffect of vitamin E and C dietary supplementation on some immune parameters of gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata) juveniles subjected to crowding stress Aquaculture 171 269–278
J. Ortuño M.A. Esteban J. Meseguer (2001) ArticleTitleEffects of short-term crowding stress on the gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata L.) innate immune response Fish and Shellfish Immunology 11 187–197
E.F. Ossermann D.P. Lawlor (1966) ArticleTitleSerum and urinary lysozyme (Muramidase) in monocytic and monomyelocytic leukaemia Journal of Experimental Medicine 124 921–951
N.W. Pankhurst G. Van der Kraak (1997) Effects of stress on reproduction and growth of fish G.K. Iwama A.D. Pickering J.P. Sumpter C.B. Schreck (Eds) Fish Stress and Health in Aquaculture Cambridge University Press Cambridge, UK 73–93
M. Pavlidis M. Berry P. Divanach M. Kentouri (1997) ArticleTitleDiel pattern of haematocrit, serum metabolites, osmotic pressure, electrolytes and thyroid hormones in sea bass and sea bream Aquaculture International 5 237–247
A.D. Pickering T.G. Pottinger P. Christie (1982) ArticleTitleRecovery of the brown trout, Salmo trutta L., from acute handling stress: A time-course study Journal of Fish Biology 20 229–244
A.D. Pickering T.G. Pottinger (1989) ArticleTitleStress responses and disease resistance in salmonid fish: Effects of chronic elevation of plasma cortisol Fish Physiology and Biochemistry 7 253–258
A. Santulli A. Modica C. Messina L. Ceffa A. Curatolo G. Rivas G. Fabis V. D’Amelio (1999) ArticleTitleBiochemical responses of European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.) to the stress induced by off shore experimental seismic prospecting Marine Pollution Bulletin 38 1105–1114
J.O. Sunyer E. Gomez V. Navarro H. Quesada L. Tort (1995) ArticleTitlePhysiological responses and depression of humoral components of the immune system in gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata) following daily acute stress Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 52 2339–2346
L. Tort E. Gómez D. Montero J.O. Sunyer (1996a) ArticleTitleSerum haemolytic and agglutinating activity as indicators of fish immunocompetence: Their suitability in stress and dietary studies Aquaculture International 4 31–41
L. Tort J.O. Sunyer E. Gómez A. Molinero (1996b) ArticleTitleCrowding stress induces changes in serum haemolytic and agglutinating activity in gilthead seabream Sparus aurata Veterinary Immunology and Immunopathology 51 179–188
M. Visalli G. Maricchiolo V. Micale L. Genovese (2000) ArticleTitleUtilizzo dell’HPLC per la determinazione del cortisolo plasmatico in specie ittiche Biologia Marina Mediterranea 7 933–935
R.M.G. Wells N.W. Pankhurst (1999) ArticleTitleEvaluation of simple instruments for the measurement of blood glucose and lactate, and plasma protein as stress indicators in fish Journal of World Aquaculture Society 30 276–284
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Caruso, G., Genovese, L., Maricchiolo, G. et al. Haematological, biochemical and immunological parameters as stress indicators in Dicentrarchus labrax and Sparus aurata farmed in off-shore cages. Aquacult Int 13, 67–73 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-004-9031-5
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-004-9031-5