Abstract
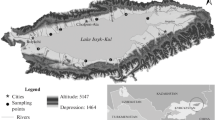
The High Oum-Er-Rbia basin, located in the Moroccan Middle Atlas, is a karstic region with significant water sources that have essential functions regarding agriculture, hydropower production, industrial and drinking water. The region contains abundant wetlands, especially springs, rivers and natural lakes. These systems are highly sensitive to the effects of climate change, experiencing considerable lake level, water chemistry, and biological fluctuations in response to regional hydrological balances. This study focuses on the hydrogeochemical processes and mechanisms that control the chemical composition and variability of Azigza Lake, a typical tectono-karstic lake system of the region. Water monitoring was implemented from July 2013 to October 2014 with a monthly water sampling for physicochemical measurements and major ion concentration analyses of lake water and the surrounding groundwater. Both waters show a relatively low salinity due to the fresh input from the Lower Jurassic karst formation. Lake waters are slightly alkaline and of the calcium-magnesium-bicarbonate type. The geochemistry of the lake waters is mainly controlled by carbonate weathering through water–rock interaction and, to a lesser extent, by cation exchange and precipitation of carbonate minerals. The hydrochemistry of the lake showed clear responses to seasonal changes in precipitation and evaporation, with higher conductivity during the wet period. During the beginning of the wet season, groundwater evolution could be explained by a simple first flush stormwater. The rapid response of lake water to subsurface and underground waters confirms the dominance of an underground conduct flow regime. These changes and behaviors highlight the sensitivity of Azigza system to regional hydrological and climatic changes.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abba H, Nassali H, Benabid M, El Ibaoui H, Chillasse L (2012) Approche physicochimique des eaux du lac dayet Aoua (Maroc). J Appl Biosci 58:4262–4270
Adallal R, Vallet-Coulomb C, Vidal L, Benkaddour A, Rhoujjati A, Sonzogni C (2019) Modelling lake water and isotope mass balance variations of Lake Azigza in the Moroccan Middle Atlas under Mediterranean climate. Reg Environ Change 19:2697–2709. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10113-019-01566-9
Ahmed M, Aqnouy M, El Messari JS (2021) Sustainability of Morocco’s groundwater resources in response to natural and anthropogenic forces. J Hydrol 603:126866. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2021.126866
Amrani S, Hinaje S (2014) Hydrodynamisme et minéralisation des eaux souterraines de la nappe phréatique plio-quaternaire du plateau Timahdite-Almis Guigou (moyen Atlas, Maroc). Eur Sci J 10:174–189
Amraoui F, Razack M, Bouchaou L (2003) Turbidity dynamics in karstic systems. Example of Ribaa and Bittit springs in the Middle Atlas (Morocco). Hydrol Sci J 48(6):971–984. https://doi.org/10.1623/hysj.48.6.971.51418
Amraoui F, Razack M, Bouchaou L (2005) Impact of a long drought period on a large carbonate aquifer: the Liassic aquifer of the Saïs plain and Middle Atlas plateau (Morocco). In: Regional hydrological impacts of climatic change: hydroclimatic variability, IAHS Publ. 296, IAHS, Wallingford, UK, pp 184–193
Benamar A, Mahjoubi FZ, Kzaibe F (2019) Evaluation of water quality of Oum Er Rbia River (Morocco) using water quality index (WQI) method. J Appl Surf Interfaces. https://doi.org/10.48442/IMIST.PRSM/jasi-v5i1-3.15437
Benkaddour A, Lamb H, Leng M, Gasse F (2005) Stable isotope records of Holocene environmental change from Moroccan lakes: an emerging synthesis. In: PAGES 2nd open science meeting: paleoclimate, environmental sustainability and our future, PAGES, p 549
Benkaddour A, Rhoujjati A, Nourelbait M (2008) Hydrologie et sédimentation actuelles au niveau des lacs Iffer et Aguelmam Azigza (Moyen Atlas, Maroc). In: Le Quaternaire Marocain Dans Son Contexte Méditerranéen: Actes de La Quatrième Rencontre Des Quaternaristes Marocains (RQM4). Faculté des Sciences d’Oujda, Oujda, pp 108–118
Bouchaou L, Michelot JL, Chauve P, Mania J, Mudry J (1995) Apports des isotopes stables à l’étude des modalités d’alimentation des aquifères du Tadla (Maroc) sous climat semi-aride. C.R. Acad. Sci Paris, Série II a 320:95–101
Bouchaou L, Chauve P, Mudry J, Mania J, Hsissou Y (1997) Fonctionnement et structure d’un hydrosystème karstique en zone montagneuse sous climat semiaride : cas de l’Atlas de Beni Mellal (Maroc). J Africa Earth Sci 25(2):225–236
Bouchaou L, Mangin A, Chauve P (2002) Turbidity mechanism of water from a karstic spring: example of the Ain Asserdoune spring (Beni Mellal Atlas, Morocco). J Hydrol 265(1–4):34–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-1694(02)00098-7
Bouchaou L, Michelot JL, Qurtobi M, Zine N, Gaye CB, Aggarwal PK, Marah H, Zerouali A, Taleb H, Vengosh A (2009) Origin and residence time of groundwater in the Tadla basin (Morocco) using multiple isotopic and geochemical tools. J Hydrol 379(3–4):323–338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2009.10.019
Brauer A (2004) Annually laminated lake sediments and their palaeoclimatic relevance. In: Fischer H et al (eds) The climate in historical times towards a synthesis of holocene proxy data and climate models. Springer, Berlin, pp 109–128. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-10313-5_7
Cao J, Yuan D, Groves C, Huang F, Yang H, Lu Q (2012) Carbon fluxes and sinks: the consumption of atmospheric and soil CO2 by carbonate rock dissolution. Acta Geol Sin Engl Ed 86:963–972. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1755-6724.2012.00720.x
Cejudo E, Acosta-González G, Ortega-Camacho D, Tun-Rosado GE (2020) Changes in the hydrochemistry of a karstic lake in Yucatan, Mexico. Environ Earth Sci 79(5):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-020-8838-3
Chillasse L, Dakki M (2004) Potentialités et statuts de conservation des zones humides du MoyenAtlas (Maroc), avec référence aux influences de la sécheresse. Sécheresse 15:337–345
Cui BL, Li XY (2015) Runoff processes in the Qinghai Lake Basin, Northeast Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China: insights from stable isotope and hydrochemistry. Quat Int 380:123–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quaint.2015.02.030
Cui BL, Li XY, Wei XH (2016) Isotope and hydrochemistry reveal evolutionary processes of lake water in Qinghai Lake. J Great Lakes Res 42(3):580–587. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jglr.2016.02.007
El Fartati M, Hinaje S, Chaouni AA, Yaagoub D, Amrani S, Gharmane Y (2021) Hydrogeology of the Tazouta basin and its relationship with the Neogene-Quaternary brittle tectonics (Folded Middle Atlas, Morocco). Arab J Geosci 14(19):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-08453-w
El Jihad MD (2010) Les difficultés de gestion des ressources « naturelles » et de développement rural dans un milieu anthropisé : l’expérience du Projet Oued Srou (Maroc central). Norois. Environnement, Aménagement, Société 216:25–45
El Khalki Y, Hafid A (2002) Turbidité, indicateur du fonctionnement perturbé du géosystème karstique de l’Atlas de Beni Mellal (Moyen Atlas méridional, Maroc). Karstologia 40(1):39–44. https://doi.org/10.3406/karst.2002.2506
Etebaai I, Damnati B, Raddad H, Benhardouz H, Benhardouz O, Miche H, Taieb M (2012) Impacts climatiques et anthropiques sur le fonctionnement hydrogéochimique du Lac Ifrah (Moyen Atlas marocain). Hydrol Sci J 57:547–561. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667.2012.660158
Flower R, Foster IDL (1992) Climatic implications of recent changes in lake level at Lac Azigza (Morocco). Bulletin De La Sociéte Géologique De France 163:91–96
Flower RJ, Stevenson AC, Dearing JA, Foster IDL, Airey A, Rippey B, Wilson JPF, Appleby PG (1989) Catchment disturbance inferred from paleolimnological studies of three contrasted sub-humid environments in Morocco. J Paleolimnol 1:293–322. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00184003
Gayral P, Panouse JB (1954) L’Aguelmame Azigza : Recherches Physiques et Biologiques. Bulletin De La Société Des Sciences Naturelles Et Physiques Du Maroc 36:135–159
Gibbs RJ (1970) Mechanisms Controlling World Water Chemistry. Science 170:1088–1090. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.170.3962.1088
Haddout S, Jamali A, Rhazi M, Aghfir M (2018) Finite volume coastal ocean model for water-level fluctuation due to climate change in Aguelmam Sidi Ali Lake (Middle Atlas, Morocco). In : Annales de Limnologie-International Journal of Limnology, vol 54, p 5. EDP Sciences. https://doi.org/10.1051/limn/2017033
Hinaje S, Ait Brahim L (2002) Les bassins lacustres du Moyen Atlas (Maroc): un exemple d’activité tectonique polyphasée associée à des structures d’effondrement. Instituto Geológico e Mineiro 89:283–294
Howell BA, Fryar AE, Benaabidate L, Bouchaou L, Farhaoui M (2019) Variable responses of karst springs to recharge in the Middle Atlas region of Morocco. Hydrogeol J 27(5):1693–1710. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-019-01945-w
Hughes TH, Memon BA, LaMoreaux PE (1994) Landfills in karst terrains. Bull Assoc Eng Geol 31:203–208
Hussein MT (2004) Hydrochemical evaluation of groundwater in the Blue Nile basin, eastern Sudan, using conventional and multivariate techniques. Hydrogeol J 12:144–158. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-003-0265-5
Jouve G, Vidal L, Adallal R, Rhoujjati A, Benkaddour A, Chapron E, Tachikawa K, Bard E, Courp T, Dezileau L, Hebert B, Rapuc W, Simonneau A, Sonzogni C, Sylvestre F (2019) Recent hydrological variability of the Moroccan Middle Atlas Mountains inferred from microscale sedimentological and geochemical analyses of lake sediments. Quat Res 91:414–430. https://doi.org/10.1017/qua.2018.94
Karroum L, El Baghdadi M, Barakat A, Meddah R, Aadraoui M, Oumenskou H, Ennaji W (2019) Hydrochemical characteristics and water quality evaluation of the Srou River and its tributaries (Middle Atlas, Morocco) for drinking and agricultural purposes. Dwt 146:152–164. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2019.23632
Kelts K, Hsü KJ (1978) Freshwater carbonate sedimentation. In: Lakes, pp 295–323. Springer, New York. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4757-1152-3_9
Khalil N, Rouane SE, Mania J, Mudry J (2004) Essai de bilan hydrochimique sur les eaux du Haut Bassin de l’Oum Er Rbia (Moyen Atlas, Maroc). Revue Francaise De Geotechnique 109:75–85. https://doi.org/10.1051/geotech/2004109075
Kiraly L (2003) Karstification and groundwater flow. Speleogenesis Evol Karst Aquifers 1(3):155–192
Lazhar H, Obda K, Amyay M (2020) Hydroclimatic variability of Aguelmam Sidi Ali (Middle Atlas Central, Morocco) over the past four decades. In: Proceedings of the 4th edition of international conference on geo-IT and water resources 2020, Geo-IT and water resources 2020, pp 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1145/3399205.3399215
Lecomte KL, Bicalho CC, Silva-Filho EV (2016) Geochemical characterization in karst basin tributaries of the San Franciscan depression: the Corrente River, western Bahia, NE-Brazil. J S Am Earth Sci 69:119–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsames.2016.03.011
Lepoutre B, Martin J, Chamayou J (1967) Le causse Moyen atlasique. Les Cahiers De La Recherche Agronomique 24:207–226
Martin J (1981) Le Moyen Atlas Central: Etude géomorphologique. Service Géologique du Maroc
Menjour F, Amraoui F, Remmal T (2016) Assessment of the spatio-temporal evolution of Aguelmam Sidi Ali Lake using multitemporal landsat imagery (Middle Atlas-Morocco). In: 6th International conference on cartography and GIS, p 588
Miche H, Saracco G, Mayer A, Qarqori K, Rouai M, Dekayir A, Chalikakis K, Emblanch C (2018) Hydrochemical constraints between the karst Tabular Middle Atlas Causses and the Saïs basin (Morocco): implications of groundwater circulation. Hydrogeol J 26(1):71–87. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-017-1675-0
Muzirafuti A, Boualoul M, Randazzo G, Lanza S, Allaoui A, El Ouardi H, Habibi H, Ouhaddach H (2005) The use of remote sensing for water protection in the karst environment of the Tabular Middle Atlas/the causse of El Hajeb/Morocco. ASTER 2000:16
Naoura J, El Kati I, Benaabidate L (2021) Assessment of Ras El Ma Karst Spring features by structural and functional approaches at the Region of Taza, Morocco. J Ecol Eng. https://doi.org/10.12911/22998993/141477
Nordstrom DK, Blowes DW, Ptacek CJ (2015) Hydrogeochemistry and microbiology of mine drainage: an update. Appl Geochem 57:3–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2015.02.008
Parkhurst DL, Apello C (1999) User’s guide to PHREEQC (V2). US Geol. Surv 312
Piper AM (1944) A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water-analyses. EOS Trans Am Geophys Union 25(6):914–928. https://doi.org/10.1029/TR025i006p00914
Plummer LN, Busenberg E (1982) The solubilities of calcite, aragonite and vaterite in CO2–H2O solutions between 0 and 90 °C, and an evaluation of the aqueous model for the system CaCO3-CO2-H2O. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 46(6):1011–1040. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-7037(82)90056-4
Romero-Viana L, Julià R, Camacho A, Vicente E, Miracle M (2008) Climate signal in varve thickness: Lake La Cruz (Spain), a case study. J Paleolimnol 40(2):703–714. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10933-008-9194-6
Sayad A, Chakiri S (2010) Impact de l’évolution du climat sur le niveau de Dayet Aoua dans le Moyen Atlas marocain. Sécheresse 21:245–251. https://doi.org/10.1684/sec.2010.0252
Sayad A, Chakiri S, Martin C, Bejjaji Z, Echarfaoui H (2011) Effet des conditions climatiques sur le niveau du lac Sidi Ali (Moyen Atlas, Maroc). Physio-Géo 5:251–268. https://doi.org/10.4000/physio-geo.2145
Schoeller H (1965) Qualitative evaluation of groundwater resources. In: Methods and techniques of groundwater investigations and development. UNESCO, Paris, pp 54–83
Su Y, Zhu G, Feng Q, Li Z, Zhang F (2009) Environmental isotopic and hydrochemical study of groundwater in the Ejina basin, northwest China. Environ Geol 58:601–614. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-008-1534-3
Tahiri A, Amraoui F, Sinan M (2020) Remote sensing, GIS, and Fieldwork Studies to assess and valorize groundwater resources in the springs area of oum-Er-rabiaa (Moroccan Middle Atlas). Groundw Sustain Dev 11:100440. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsd.2020.100440
Vidal L, Rhoujjati A, Adallal R, Jouve G, Bard E, Benkaddour A, Chapron E, Courp T, Dezileau L, Garcia M, Hebert B, Simmoneau A, Sonzogni C, Sylvestre F, Tachikawa K, Vallet-Coulomb C, Viry E (2016) Past hydrological variability in the Moroccan Middle Atlas inferred from lakes and lacustrine sediments. In: The Mediterranean Region under climate change, pp 57–69
Welch SP (1948) Limnological methods. McGraw Hill Book Co., New York, p 381
White WB (1988) Geomorphology and hydrology of Karst Terrains. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Xiao J, Jin Z, Zhang F, Wang J (2012) Solute geochemistry and its sources of the groundwaters in the Qinghai Lake catchment, NW China. J Asian Earth Sci 52:21–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.02.006
Xu H, Hou Z, An Z, Liu X, Dong J (2010) Major ion chemistry of waters in Lake Qinghai catchments, NE Qinghai-Tibet plateau, China. Quat Int 212(1):35–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quaint.2008.11.001
Zielhofer C (2004) Hydrographical and hydrochemical characteristics of karst water components (southern Franconian Jura)—a contribution to fresh water protection and karst morphogenesis. Zeitschrift Für Geomorphologie Suppl 136:113–134
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by FR-ECCOREV, LABEX OT-Med (# ANR-11-LABX-0061) (PHYMOR project) (France), CNRST (Morocco), PHC Toubkal (Project # 16/38) and Campus France. The authors extend their thanks to SETEL- and SIGEO- CEREGE and IRD-Rabat for logistic support during the field trips (2013 and 2015).
Funding
This study was partly funded by FR-ECCOREV, LABEX OT-Med (# ANR-11-LABX-0061) (PHYMOR project) (France), CNRST (Morocco), PHC Toubkal (Project # 16/38). The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Adallal R and Id Abdellah H processed the experimental data, performed the analysis, drafted the manuscript and designed the figures. Vidal L, Benkaddour A and Rhoujjati A commented on previous versions of the manuscript and supervised the work. Vallet-Coulomb C and Sonzogni C aided in interpreting the results and reviewed the manuscript. All authors provided critical feedback and helped shape the research, analysis and manuscript
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We confirm that there are no known conflict of interest associated with this publication.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Adallal, R., Id Abdellah, H., Benkaddour, A. et al. Hydrogeochemical Processes of the Azigza Lake System (Middle Atlas, Morocco) Inferred from Monthly Monitoring. Aquat Geochem 29, 25–47 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10498-022-09409-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10498-022-09409-6