Abstract
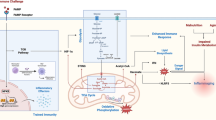
The Toll/interleukin-1 receptor/resistance protein (TIR) domain is a protein–protein interaction domain consisting of 125–200 residues, widely distributed in animals, plants and bacteria but absent from fungi, archea and viruses. In plants and animals, these domains are found in proteins with functions in innate immune pathways, while in bacteria, some TIR domain-containing proteins interfere with the innate immune pathways in the host. TIR domains function as protein scaffolds, mostly involving self-association and homotypic interactions with other TIR domains. In the last 15 years, the three-dimensional structures of TIR domains from several mammalian, plant and bacterial proteins have been reported. These structures, jointly with functional data including the identification of interacting proteins, have started to provide insight into the molecular basis of the assembly of animal and plant immune signaling complexes, and for host immunosuppression by bacterial pathogens. This review focuses on the current knowledge of the structures of the TIR domains and how the structure relates to function.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gay NJ, Keith FJ (1991) Drosophila Toll and IL-1 receptor. Nature 351:355–356
Whitham S, Dinesh-Kumar SP, Choi D, Hehl R, Corr C, Baker B (1994) The product of the tobacco mosaic virus resistance gene N: similarity to Toll and the interleukin-1 receptor. Cell 78:1101–1115
O’Neill L (2000) The Toll/interleukin-1 receptor domain: a molecular switch for inflammation and host defence. Biochem Soc Trans 28:557–563
Spear AM, Loman NJ, Atkins HS, Pallen MJ (2009) Microbial TIR domains: not necessarily agents of subversion? Trends Microbiol 17:393–398
Burns K, Martinon F, Esslinger C et al (1998) MyD88, an adapter protein involved in interleukin-1 signaling. J Biol Chem 273:12203–12209
Van der Biezen EA, Jones JD (1998) Plant disease-resistance proteins and the gene-for-gene concept. Trends Biochem Sci 23:454–456
Meyers BC, Morgante M, Michelmore RW (2002) TIR-X and TIR-NBS proteins: two new families related to disease resistance TIR-NBS-LRR proteins encoded in Arabidopsis and other plant genomes. Plant J 32:77–92
Ve T, Gay NJ, Mansell A, Kobe B, Kellie S (2012) Adaptors in Toll-like receptor signaling and their potential as therapeutic target. Curr Drug Target 13:1360–1374
Dinarello CA (2011) Interleukin-1 in the pathogenesis and treatment of inflammatory diseases. Blood 117:3720–3732
Kawai T, Akira S (2010) The role of pattern-recognition receptors in innate immunity: update on Toll-like receptors. Nat Immunol 11:373–384
Boraschi D, Tagliabue A (2013) The interleukin-1 receptor family. Semin Immunol 25:394–407
Kang JY, Lee JO (2011) Structural biology of the Toll-like receptor family. Annu Rev Biochem 80:917–941
O’Neill LA, Bowie AG (2007) The family of five: TIR-domain-containing adaptors in Toll-like receptor signalling. Nat Rev Immunol 7:353–364
Medzhitov R, Preston-Hurlburt P, Kopp E et al (1998) MyD88 is an adaptor protein in the hToll/IL-1 receptor family signaling pathways. Mol Cell 2:253–258
Muzio M, Natoli G, Saccani S, Levrero M, Mantovani A (1998) The human Toll signaling pathway: divergence of nuclear factor kappaB and JNK/SAPK activation upstream of tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6 (TRAF6). J Exp Med 187:2097–2101
Kawai T, Adachi O, Ogawa T, Takeda K, Akira S (1999) Unresponsiveness of MyD88-deficient mice to endotoxin. Immunity 11:115–122
Takeuchi O, Hoshino K, Akira S (2000) Cutting edge: TLR2-deficient and MyD88-deficient mice are highly susceptible to Staphylococcus aureus infection. J Immunol 165:5392–5396
Barton GM, Kagan JC, Medzhitov R (2006) Intracellular localization of Toll-like receptor 9 prevents recognition of self DNA but facilitates access to viral DNA. Nat Immunol 7:49–56
Fitzgerald KA, Palsson-McDermott EM, Bowie AG et al (2001) Mal (MyD88-adapter-like) is required for Toll-like receptor-4 signal transduction. Nature 413:78–83
Horng T, Barton GM, Flavell RA, Medzhitov R (2002) The adaptor molecule TIRAP provides signalling specificity for Toll-like receptors. Nature 420:329–333
Horng T, Barton GM, Medzhitov R (2001) TIRAP: an adapter molecule in the Toll signaling pathway. Nat Immunol 2:835–841
Yamamoto M, Sato S, Hemmi H et al (2002) Essential role for TIRAP in activation of the signalling cascade shared by TLR2 and TLR4. Nature 420:324–329
Bonham KS, Orzalli MH, Hayashi K et al (2014) A promiscuous lipid-binding protein diversifies the subcellular sites of Toll-like receptor signal transduction. Cell 156:705–716
Hoebe K, Du X, Georgel P et al (2003) Identification of Lps2 as a key transducer of MyD88-independent TIR signalling. Nature 424:743–748
Oshiumi H, Matsumoto M, Funami K, Akazawa T, Seya T (2003) TICAM-1, an adaptor molecule that participates in Toll-like receptor 3-mediated interferon-beta induction. Nat Immunol 4:161–167
Yamamoto M, Sato S, Hemmi H et al (2003) Role of adaptor TRIF in the MyD88-independent Toll-like receptor signaling pathway. Science 301:640–643
Kagan JC, Su T, Horng T, Chow A, Akira S, Medzhitov R (2008) TRAM couples endocytosis of Toll-like receptor 4 to the induction of interferon-beta. Nat Immunol 9:361–368
Oshiumi H, Sasai M, Shida K, Fujita T, Matsumoto M, Seya T (2003) TIR-containing adapter molecule (TICAM)-2, a bridging adapter recruiting to Toll-like receptor 4 TICAM-1 that induces interferon-beta. J Biol Chem 278:49751–49762
Gerdts J, Summers DW, Sasaki Y, DiAntonio A, Milbrandt J (2013) Sarm1-mediated axon degeneration requires both SAM and TIR interactions. J Neurosci 33:13569–13580
Osterloh JM, Yang J, Rooney TM et al (2012) dSarm/Sarm1 is required for activation of an injury-induced axon death pathway. Science 337:481–484
Xu Y, Tao X, Shen B et al (2000) Structural basis for signal transduction by the Toll/interleukin-1 receptor domains. Nature 408:111–115
Li C, Zienkiewicz J, Hawiger J (2005) Interactive sites in the MyD88 Toll/interleukin (IL) 1 receptor domain responsible for coupling to the IL1beta signaling pathway. J Biol Chem 280:26152–26159
Slack JL, Schooley K, Bonnert TP et al (2000) Identification of two major sites in the type I interleukin-1 receptor cytoplasmic region responsible for coupling to pro-inflammatory signaling pathways. J Biol Chem 275:4670–4678
Alaidarous M, Ve T, Casey LW et al (2014) Mechanism of bacterial interference with TLR4 signaling by Brucella Toll/interleukin-1 receptor domain-containing protein TcpB. J Biol Chem 289:654–668
Bernoux M, Ve T, Williams S et al (2011) Structural and functional analysis of a plant resistance protein TIR domain reveals interfaces for self-association, signaling, and autoregulation. Cell Host Microbe 9:200–211
Gautam JK, Ashish ComeauLD, Krueger JK, Smith MF Jr (2006) Structural and functional evidence for the role of the TLR2 DD loop in TLR1/TLR2 heterodimerization and signaling. J Biol Chem 281:30132–30142
Valkov E, Stamp A, Dimaio F et al (2011) Crystal structure of Toll-like receptor adaptor MAL/TIRAP reveals the molecular basis for signal transduction and disease protection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:14879–14884
Williams SJ, Sohn KH, Wan L et al (2014) Structural basis for assembly and function of a heterodimeric plant immune receptor. Science 344:299–303
Jang TH, Park HH (2014) Crystal structure of TIR domain of TLR6 reveals novel dimeric Interface of TIR-TIR interaction for Toll-like receptor signaling pathway. J Mol Biol 426:3305–3313
Khan JA, Brint EK, O’Neill LA, Tong L (2004) Crystal structure of the Toll/interleukin-1 receptor domain of human IL-1RAPL. J Biol Chem 279:31664–31670
Nyman T, Stenmark P, Flodin S, Johansson I, Hammarstrom M, Nordlund P (2008) The crystal structure of the human Toll-like receptor 10 cytoplasmic domain reveals a putative signaling dimer. J Biol Chem 283:11861–11865
Enokizono Y, Kumeta H, Funami K et al (2013) Structures and interface mapping of the TIR domain-containing adaptor molecules involved in interferon signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:19908–19913
Lin Z, Lu J, Zhou W, Shen Y (2012) Structural insights into TIR domain specificity of the bridging adaptor Mal in TLR4 signaling. PLoS ONE 7:e34202
Ohnishi H, Tochio H, Kato Z et al (2009) Structural basis for the multiple interactions of the MyD88 TIR domain in TLR4 signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:10260–10265
Snyder GA, Cirl C, Jiang J et al (2013) Molecular mechanisms for the subversion of MyD88 signaling by TcpC from virulent uropathogenic Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:6985–6990
Snyder GA, Deredge D, Waldhuber A et al (2014) Crystal structures of the Toll/interleukin-1 receptor (TIR) domains from the Brucella protein TcpB and host adaptor TIRAP reveal mechanisms of molecular mimicry. J Biol Chem 289:669–679
Woo JR, Kim S, Shoelson SE, Park S (2013) X-ray crystallographic structure of TIR-domain from the human TIR-domain containing adaptor protein/MyD88 adaptor-like protein (TIRAP/MAL). Bull Korean Chem Soc 33:3091–3094
Dangl JL, Horvath DM, Staskawicz BJ (2013) Pivoting the plant immune system from dissection to deployment. Science 341:746–751
Jones JDG, Dangl JL (2006) The plant immune system. Nature 444:323–329
Krasileva KV, Dahlbeck D, Staskawicz BJ (2010) Activation of an Arabidopsis resistance protein is specified by the in planta association of its leucine-rich repeat domain with the cognate oomycete effector. Plant Cell 22:2444–2458
Swiderski MR, Birker D, Jones JD (2009) The TIR domain of TIR-NB-LRR resistance proteins is a signaling domain involved in cell death induction. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 22:157–165
Caplan JL, Mamillapalli P, Burch-Smith TM, Czymmek K, Dinesh-Kumar SP (2008) Chloroplastic protein NRIP1 mediates innate immune receptor recognition of a viral effector. Cell 132:449–462
Zhu Z, Xu F, Zhang Y et al (2010) Arabidopsis resistance protein SNC1 activates immune responses through association with a transcriptional corepressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:13960–13965
Chan SL, Mukasa T, Santelli E, Low LY, Pascual J (2010) The crystal structure of a TIR domain from Arabidopsis thaliana reveals a conserved helical region unique to plants. Protein Sci 19:155–161
Zhang Q, Zmasek CM, Cai X, Godzik A (2011) TIR domain-containing adaptor SARM is a late addition to the ongoing microbe-host dialog. Dev Comp Immunol 35:461–468
Cirl C, Wieser A, Yadav M et al (2008) Subversion of Toll-like receptor signaling by a unique family of bacterial Toll/interleukin-1 receptor domain-containing proteins. Nat Med 14:399–406
Newman RM, Salunkhe P, Godzik A, Reed JC (2006) Identification and characterization of a novel bacterial virulence factor that shares homology with mammalian Toll/interleukin-1 receptor family proteins. Infect Immun 74:594–601
Salcedo SP, Marchesini MI, Lelouard H et al (2008) Brucella control of dendritic cell maturation is dependent on the TIR-containing protein Btp1. PLoS Pathog 4:e21
Chan SL, Low LY, Hsu S et al (2009) Molecular mimicry in innate immunity: crystal structure of a bacterial TIR domain. J Biol Chem 284:21386–21392
Kaplan-Turkoz B, Koelblen T, Felix C et al (2013) Structure of the Toll/interleukin 1 receptor (TIR) domain of the immunosuppressive Brucella effector BtpA/Btp1/TcpB. FEBS Lett 587:3412–3416
Fekonja O, Bencina M, Jerala R (2012) Toll/interleukin-1 receptor domain dimers as the platform for activation and enhanced inhibition of Toll-like receptor signaling. J Biol Chem 287:30993–31002
Bovijn C, Ulrichts P, De Smet AS et al (2012) Identification of interaction sites for dimerization and adapter recruitment in Toll/interleukin-1 receptor (TIR) domain of Toll-like receptor 4. J Biol Chem 287:4088–4098
Nunez Miguel R, Wong J, Westoll JF et al (2007) A dimer of the Toll-like receptor 4 cytoplasmic domain provides a specific scaffold for the recruitment of signalling adaptor proteins. PLoS ONE 2:e788
Radhakrishnan GK, Yu Q, Harms JS, Splitter GA (2009) Brucella TIR domain-containing protein mimics properties of the Toll-like receptor adaptor protein TIRAP. J Biol Chem 284:9892–9898
Thomas C, Bazan JF, Garcia KC (2012) Structure of the activating IL-1 receptor signaling complex. Nat Struct Mol Biol 19:455–457
Wang D, Zhang S, Li L, Liu X, Mei K, Wang X (2010) Structural insights into the assembly and activation of IL-1beta with its receptors. Nat Immunol 11:905–911
Lin SC, Lo YC, Wu H (2010) Helical assembly in the MyD88-IRAK4-IRAK2 complex in TLR/IL-1R signalling. Nature 465:885–890
Ullah MO, Ve T, Mangan M et al (2013) The TLR signalling adaptor TRIF/TICAM-1 has an N-terminal helical domain with structural similarity to IFIT proteins. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 69:2420–2430
Li J, McQuade T, Siemer AB et al (2012) The RIP1/RIP3 necrosome forms a functional amyloid signaling complex required for programmed necrosis. Cell 150:339–350
Kobe B, Gleichmann T, Horne J, Jennings IG, Scotney PD, Teh T (1999) Turn up the HEAT. Structure 7:R91–R97
Stapleton D, Balan I, Pawson T, Sicheri F (1999) The crystal structure of an Eph receptor SAM domain reveals a mechanism for modular dimerization. Nat Struct Biol 6:44–49
Riedl SJ, Li W, Chao Y, Schwarzenbacher R, Shi Y (2005) Structure of the apoptotic protease-activating factor 1 bound to ADP. Nature 434:926–933
Kobe B, Kajava AV (2001) The leucine-rich repeat as a protein recognition motif. Curr Opin Struct Biol 11:725–732
Deslandes L, Olivier J, Theulieres F et al (2002) Resistance to Ralstonia solanacearum in Arabidopsis thaliana is conferred by the recessive RRS1-R gene, a member of a novel family of resistance genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:2404–2409
Finn RD, Bateman A, Clements J et al (2014) Pfam: the protein families database. Nucleic Acids Res 42:D222–D230
Gouet P, Robert X, Courcelle E (2003) ESPript/ENDscript: extracting and rendering sequence and 3D information from atomic structures of proteins. Nucleic Acids Res 31:3320–3323
Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown NP et al (2007) Clustal W and clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 23:2947–2948
Roberts E, Eargle J, Wright D, Luthey-Schulten Z (2006) MultiSeq: unifying sequence and structure data for evolutionary analysis. BMC Bioinformatics 7:382
Humphrey W, Dalke A, Schulten K (1996) VMD: visual molecular dynamics. J Mol Graph 14(33–38):27–38
Tao X, Xu Y, Zheng Y, Beg AA, Tong L (2002) An extensively associated dimer in the structure of the C713S mutant of the TIR domain of human TLR2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 299:216–221
Acknowledgments
The work in the authors’ laboratory was funded by the National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC, Australia; 1003326, 565526, 1071659) and the Australian Research Council (ARC; DP120100685). BK is an NHMRC Research Fellow (1003325).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Thomas Ve and Simon J Williams are co-first authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ve, T., Williams, S.J. & Kobe, B. Structure and function of Toll/interleukin-1 receptor/resistance protein (TIR) domains. Apoptosis 20, 250–261 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-014-1064-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-014-1064-2