Abstract
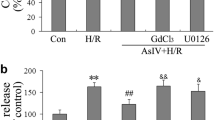
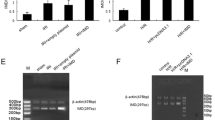
Intermedin (IMD) is a novel member of the calcitonin/calcitonin gene-related peptide family. We investigated the cardioprotective mechanism of IMD1–53 in the in vivo rat model of myocardial ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury and in vitro primary neonatal cardiomyocyte model of hypoxia/reoxygenation (H/R). Myocardial infarct size was measured by 2,3,5-triphenyl tetrazolium chloride staining. Cardiomyocyte viability was determined by trypan blue staining, cell injury by lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) leakage, and cardiomyocyte apoptosis by terminal deoxyribonucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick-end labeling assay, Hoechst staining, gel electrophoresis and caspase 3 activity. The translocation of mitochondrial cytochrome c of myocardia and expression of apoptosis-related factors Bcl-2 and Bax, phosphorylated Akt and phosphorylated GSK-3β were determined by western blot analysis. IMD1–53 (20 nmol/kg) limited the myocardial infarct size in rats with I/R; the infarct size was decreased by 54%, the apoptotic index by 30%, and caspase 3 activity by 32%; and the translocation of cytochrome c from mitochondria to cytosol was attenuated. IMD1–53 increased the mRNA and protein expression of Bcl-2 and ratio of Bcl-2 to Bax by 81 and 261%, respectively. IMD1–53 (1 × 10−7 mol/L) inhibited the H/R effect in cardiomyocytes by reducing cell death by 43% and LDH leakage by 16%; diminishing cellular apoptosis; decreasing caspase 3 activity by 50%; and increasing the phosphorylated Akt and GSK-3β by 41 and 90%, respectively. The cytoprotection of IMD1–53 was abolished with LY294002, a PI3K inhibitor. In conclusion, IMD1–53 exerts cardioprotective effect against myocardial I/R injury through the activation of the Akt/GSK-3β signaling pathway to inhibit mitochondria-mediated myocardial apoptosis.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Roh J, Chang CL, Bhalla A, Klein C, Hsu SY (2004) Intermedin is a calcitonin/calcitonin gene-related peptide family peptide acting through the calcitonin receptor-like receptor/receptor activity-modifying protein receptor complexes. J Biol Chem 279:7264–7274
Takei Y, Inoue K, Ogoshi M, Kawahara T, Bannai H, Miyano S (2004) Identification of novel adrenomedullin in mammals: a potent cardiovascular and renal regulator. FEBS Lett 556:53–58
Yang JH, Jia YX, Pan CS, Zhao J, Ouyang M, Yang J et al (2005) Effects of intermedin (1–53) on cardiac function and ischemia/reperfusion injury in isolated rat hearts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 327:713–719
Jia YX, Yang JH, Pan CS, Geng B, Zhang J, Xiao Y et al (2006) Intermedin 1–53 protects the heart against isoproterenol-induced ischemic injury in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 549:117–123
Yang JH, Pan CS, Jia YX, Zhang J, Zhao J, Pang YZ et al (2006) Intermedin 1–53 activates l-arginine/nitric oxide synthase/nitric oxide pathway in rat aortas. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 341:567–572
Parcellier A, Tintignac LA, Zhuravleva E, Hemmings BA (2008) PKB and the mitochondria: AKTing on apoptosis. Cell Signal 20:21–30
Fujio Y, Nguyen T, Wencker D, Kitsis RN, Walsh K (2000) Akt promotes survival of cardiomyocytes in vitro and protects against ischemia–reperfusion injury in mouse heart. Circulation 101:660–667
Forde JE, Dale TC (2007) Glycogen synthase kinase 3: a key regulator of cellular fate. Cell Mol Life Sci 64:1930–1944
Yin H, Chao L, Chao J (2004) Adrenomedullin protects against myocardial apoptosis after ischemia/reperfusion through activation of Akt-GSK signaling. Hypertension 43:109–116
Park SS, Zhao H, Mueller RA, Xu Z (2006) Bradykinin prevents reperfusion injury by targeting mitochondrial permeability transition pore through glycogen synthase kinase 3beta. J Mol Cell Cardiol 40:708–716
Esumi K, Nishida M, Shaw D, Smith TW, Marsh JD (1991) NADH measurements in adult rat myocytes during simulated ischemia. Am J Physiol 260:H1743–1752
Lee YS, Kang YJ, Kim HJ, Park MK, Seo HG, Lee JH et al (2006) Higenamine reduces apoptotic cell death by induction of heme oxygenase-1 in rat myocardial ischemia–reperfusion injury. Apoptosis 11:1091–1100
Chang L, Xu J, Yu F, Zhao J, Tang X, Tang C (2004) Taurine protected myocardial mitochondria injury induced by hyperhomocysteinemia in rats. Amino Acids 27:37–48
Baxter GF, Mocanu MM, Brar BK, Latchman DS, Yellon DM (2001) Cardioprotective effects of transforming growth factor-beta1 during early reoxygenation or reperfusion are mediated by p42/p44 MAPK. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 38:930–939
Kuwasako K, Cao YN, Nagoshi Y, Tsuruda T, Kitamura K, Eto T (2004) Characterization of the human calcitonin gene-related peptide receptor subtypes associated with receptor activity-modifying proteins. Mol Pharmacol 65:207–213
Boatright KM, Renatus M, Scott FL, Sperandio S, Shin H, Pedersen IM et al (2003) A unified model for apical caspase activation. Mol Cell 11:529–541
Lassus P, Opitz-Araya X, Lazebnik Y (2002) Requirement for caspase-2 in stress-induced apoptosis before mitochondrial permeabilization. Science 297:1352–1354
Hausenloy DJ, Yellon DM (2007) Reperfusion injury salvage kinase signalling: taking a RISK for cardioprotection. Heart Fail Rev 12:217–234
Jonassen AK, Sack MN, Mjøs OD, Yellon DM (2001) Myocardial protection by insulin at reperfusion requires early administration and is mediated via Akt and p70s6 kinase cell-survival signaling. Circ Res 89:1191–1198
Uchiyama T, Engelman RM, Maulik N, Das DK (2004) Role of Akt signaling in mitochondrial survival pathway triggered by hypoxic preconditioning. Circulation 109:3042–3049
Gross ER, Hsu AK, Gross GJ (2004) Opioid-induced cardioprotection occurs via glycogen synthase kinase beta inhibition during reperfusion in intact rat hearts. Circ Res 94:960–966
Nishihara M, Miura T, Miki T, Tanno M, Yano T, Naitoh K et al (2007) Modulation of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore complex in GSK-3beta-mediated myocardial protection. J Mol Cell Cardiol 43:564–570
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant No. 30770869, 30871013) and the State Major Basic Research Development Program of the People’s Republic of China (grant No. 2006CB503807).
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, JQ., Teng, X., Cai, Y. et al. Activation of Akt/GSK-3β signaling pathway is involved in intermedin1–53 protection against myocardial apoptosis induced by ischemia/reperfusion. Apoptosis 14, 1299–1307 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-009-0398-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-009-0398-7