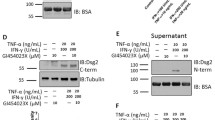
Abstract
Recent data indicates that chronic inflammation of the intestine such as Crohn's or ulcerative colitis puts those individuals at heightened risk for colorectal adenocarcinoma. In this study, we examine the effect of the inflammatory mediator PGE2 and associated signalling on detachment-induced cell death (anoikis) in intestinal epithelial cells. Treatment of detached IEC-18 with 0.01–0.05 μM PGE2 increased cell viability as well as induced aggregation. As EP4 prostaglandin receptors on IEC are coupled to adenylate cyclase, we next treated cells with agents that promote cAMP signalling (Forskolin, dbcAMP, and etazolate), all of which promoted IEC aggregation as well as survival. We next treated detached IECs with specific inhibitors of adenylate cyclase or PKA, which accelerated anoikis. To explore the mechanism of cell-cell adhesion, we next treated detached IECs with an anti-E-cadherin blocking antibody which dispersed aggregates induced by dbcAMP, and an adenovirus expressing a dominant negative E-cadherin (EcadΔEC) prevented aggregate formation. Interestingly EcadΔEC prevented aggregation of IEC induced by dbcAMP but did not significantly reduce viability. This suggests that cAMP signalling is important in both aggregate formation and promoting viability but these are distinct events. Taken together, these data support a mechanism whereby elevated PGE2 levels characteristic of colitis prevent anoikis by activating an AC-, cAMP-, and PKA-dependent signalling pathway. The delay of apoptosis by PGE2 may be one mechanism by which inflammation may contribute to carcinogenesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kolios G, Petoumenos C, Nakos A. Mediators of inflammation: Production and implication in inflammatory bowel disease. Hepato-Gastroenterology 1998; 45: 1601–1609.
Valentijn AJ, Metcalfe AD, Kott J, Streuli CH, Gilmore AP. Spatial and temporal changes in Bax subcellular localization during anoikis. J Cell Biol 2003; 162: 599–612.
Grossmann J, Artinger M, Grasso AW,et al. Hierarchical cleavage of focal adhesion kinase by caspases alters signal transduction during apoptosis of intestinal epithelial cells. Gastroenterology 2001; 120: 79–88.
Grossmann J, Mohr S, Lapetina EG, Fiocchi C, Levine AD. Sequential and rapid activation of select caspases during apoptosis of normal intestinal epithelial cells. Am J Physiol: Gastrointest Liver Physiol 1998; 274: G1117–G1124.
Nishihara H, Kizaka-Kondoh S, Insel PA, Eckmann L. Inhibition of apoptosis in normal and transformed intestinal epithelial cells by cAMP through induction of inhibitor of apoptosis protein (IAP)-2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2003; 100: 8921–8926.
Zou T, Rao JN, Guo X,et al. NF-kappaB-mediated IAP expression induces resistance of intestinal epithelial cells to apoptosis after polyamine depletion. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 2004; 286: C1009–C1018.
Harada H, Grant S. Apoptosis regulators. Rev Clin Exp Hematol 2003; 7: 117–138.
Douma S, Van Laar T, Zevenhoven J, Meuwissen R, Van Garderen E, Peeper DS. Suppression of anoikis and induction of metastasis by the neurotrophic receptor TrkB. Nature 2004; 430: 1034–1039.
Frisch SM, Francis H. Disruption of epithelial cell-matrix interactions induces apoptosis. J Cell Biol 1994; 124: 619–626.
Swan EA, Jasser SA, Holsinger FC, Doan D, Bucana C, Myers JN. Acquisition of anoikis resistance is a critical step in the progression of oral tongue cancer. Oral Oncol 2003; 39: 648–655.
Fernandez Y, Gu B, Martinez A, Torregrosa A, Sierra A. Inhibition of apoptosis in human breast cancer cells: Role in tumor progression to the metastatic state. Int J Cancer 2002; 101: 317–326.
Bates RC, Buret A, van Helden DF, Horton MA, Burns GF. Apoptosis induced by inhibition of intercellular contact. J Cell Biol 1994; 125: 403–415.
Waterhouse CCM, Joseph RR, Stadnyk AW. Endogenous IL-1 and type II IL-1 receptor expression modulate anoikis in intestinal epithelial cells. Exper Cell Res 2001; 269: 109–116.
Smida RS, Honore S, Rognoni JB, Martin PM, Penel C. Up-regulation of alpha 2 beta 1 integrin cell-surface expression protects A431 cells from epidermal growth factor-induced apoptosis. Int J Cancer 2000; 87: 360–367.
Rainaldi G, Calcabrini A, Arancia G, Santini MT. Differential expression of adhesion molecules (CD44, ICAM-1 and LFA-3) in cancer cells grown in monolayer or as multicellular spheroids. Anticancer Res 1999; 19: 1769–1778.
Kantak SS, Kramer RH. E-cadherin regulates anchorage-independent growth and survival in oral squamous cell carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem 1998; 273: 16953–16961.
Shen X, Kramer RH. Adhesion-mediated squamous cell carcinoma survival through ligand-independent activation of epidermal growth factor receptor. Am J Pathol 2004; 165: 1315–1329.
Jabbour HN, Kelly RW, Boddy SC. Autocrine/paracrine regulation of apoptosis in epithelial cells by prostaglandin E2. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 2002; 67: 357–363.
Munkholm P. Review article: the incidence and prevalence of colorectal cancer in inflammatory bowel disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2003; 18(Suppl 2): 1–5.
Hanakawa Y, Amagai M, Shirakata Y, Sayama K, Hashimoto K. Different effects of dominant negative mutants of desmocollin and desmoglein on the cell-cell adhesion of keratinocytes. J Cell Sci 2000; 113 (Pt 10): 1803–1811.
Korchak HM, Rich AM, Wilkenfeld C, Rutherford LE, Weissmann G. A carbocyanine dye, DiOC6(3), acts as a mitochondrial probe in human neutrophils. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1982; 108: 1495–1501.
Turunen JP, Mattila P, Renkonen R. cAMP mediates IL-1-induced lymphocyte penetration through endothelial monolayers. J Immunol 1990; 145: 4192–4197.
Zhang YH, Lin JX, Yip YK, Vilcek J. Enhancement of cAMP levels and of protein kinase activity by tumor necrosis factor and interleukin 1 in human fibroblasts: role in the induction of interleukin 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1988; 85: 6802–6805.
Bonazzi A, Bolla M, Buccellati C, et al. Effect of endogenous and exogenous prostaglandin E(2) on interleukin-1 beta-induced cyclooxygenase-2 expression in human airway smooth-muscle cells. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2000; 162: 2272–2277.
Rauk PN, Chiao JP. Interleukin-1 stimulates human uterine prostaglandin production through induction of cyclooxygenase-2 expression. Am J Reprod Immunol 2000; 43: 152–159.
Endo T, Ogushi F, Sone S, et al. Induction of cyclooxygenase-2 is responsible for interleukin-1 beta-dependent prostaglandin E2 synthesis by human lung fibroblasts. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 1995; 12: 358–365.
Mitchell MD, Edwin SS, Lundin-Schiller S, Silver RM, Smotkin D, Trautman MS. Mechanism of interleukin-1 beta stimulation of human amnion prostaglandin biosynthesis: Mediation via a novel inducible cyclooxygenase. Placenta 1993; 14: 615–625.
Ding M, Kinoshita Y, Kishi K, et al. Distribution of prostaglandin E receptors in the rat gastrointestinal tract. Prostaglandins 1997; 53: 199–216.
Nitta M, Hirata I, Toshina K, et al. Expression of the EP4 prostaglandin E2 receptor subtype with rat dextran sodium sulphate colitis: colitis suppression by a selective agonist, ONO-AE1-329. Scand J Immunol 2002; 56: 66–75.
Takafuji V, Cosme R, Lublin D, Roche JK. Prostanoid receptors in intestinal epithelium: Selective expression, function, and change with inflammation. Prostaglandins, Leukotrienes, and Essential Fatty Acids 2000; 63: 223–235.
Alpaugh ML, Barsky SH. Reversible model of spheroid formation allows for high efficiency of gene delivery ex vivo and accurate gene assessment in vivo. Hum Gene Ther 2002; 13: 1245–1258.
Desoize B, Gimonet D, Jardiller JC. Cell culture as spheroids: An approach to multicellular resistance. Anticancer Res 1998; 18: 4147–4158.
Bates RC, Goldsmith JD, Bachelder RE, et al. Flt-1-dependent survival characterizes the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of colonic organoids. Current Biology 2003; 13: 1721–1727.
Xing H, Gao QL, Yang XK, et al. Resistance of multicellular spheroids to taxol in human ovarian cancer and its mechanism. Ai Zheng 2003; 22: 826–830.
Ferrandez A, Prescott S, Burt RW. COX-2 and colorectal cancer. Curr Pharm Des 2003; 9: 2229–2251.
Oshimoto H, Okamura S, Yoshida M, Mori M. Increased activity and expression of phospholipase D2 in human colorectal cancer. Oncol Res 2003; 14: 31–37.
Yu HG, Huang JA, Yang YN, et al. Inhibition of cytosolic phospholipase A2 mRNA expression: A novel mechanism for acetylsalicylic acid-mediated growth inhibition and apoptosis in colon cancer cells. Regul Pept 2003; 114: 101–107.
Wendum D, Svrcek M, Rigau V, et al. COX-2, inflammatory secreted PLA2, and cytoplasmic PLA2 protein expression in small bowel adenocarcinomas compared with colorectal adenocarcinomas. Mod Pathol 2003; 16: 130–136.
Kunikata T, Tanaka A, Miyazawa T, Kato S, Takeuchi K. 16,16-Dimethyl prostaglandin E2 inhibits indomethacin-induced small intestinal lesions through EP3 and EP4 receptors. Dig Dis Sci 2002; 47: 894–904.
Belley A, Chadee K. Prostaglandin E(2) stimulates rat and human colonic mucin exocytosis via the EP(4) receptor. Gastroenterology 1999; 117: 1352–1362.
Yan SR, Joseph RR, Rosen K, et al. Activation of NF-kB following detachment delays apoptosis in intestinal epithelial cells. Oncogene 2005 (in press).
Hintermann E, Yang N, O’Sullivan D, Higgins JM, Quaranta V. Integrin alpha6beta4-erbB2 complex inhibits haptotaxis by up-regulating E-cadherin cell-cell junctions in keratinocytes. J Biol Chem 2005; 280: 8004–8015.
Okamoto R, Irie K, Yamada A, Katata T, Fukuhara A, Takai Y. Recruitment of E-cadherin associated with alpha- and beta-catenins and p120 to the nectin-based cell-cell adhesion sites by the action of 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate in MDCK cells. Genes Cells 2005; 10: 435–445.
Fouquet S, Lugo-Martinez VH, Faussat AM, et al. Early loss of E-cadherin from cell-cell contacts is involved in the onset of Anoikis in enterocytes. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 43061–43069.
Day ML, Zhao X, Vallorosi CJ, et al. E-cadherin mediates aggregation-dependent survival of prostate and mammary epithelial cells through the retinoblastoma cell cycle control pathway. J Biol Chem 1999; 274: 9656–9664.
Nightingale J, Chaudhary KS, Abel PD, et al. Ligand activation of the androgen receptor downregulates E-cadherin-mediated cell adhesion and promotes apoptosis of prostatic cancer cells. Neoplasia 2003; 5: 347–361.
Bergin E, Levine JS, Koh JS, Lieberthal W. Mouse proximal tubular cell-cell adhesion inhibits apoptosis by a cadherin-dependent mechanism. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 2000; 278: F758–F768.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Joseph, R.R., Yazer, E., Hanakawa, Y. et al. Prostaglandins and activation of AC/cAMP prevents anoikis in IEC-18. Apoptosis 10, 1221–1233 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-005-2049-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-005-2049-y