Abstract
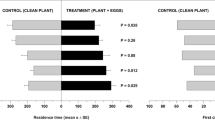
We used a Y-tube olfactometer to assess the sub-lethal effects of the acaricide fenbutatin oxide on the olfactory response of the predatory mite Iphiseiodes zuluagai towards odours from: (1) air or undamaged coffee plants; (2) undamaged or red spider mite Oligonychus ilicis-infested coffee plants; (3) undamaged or false spider mite Brevipalpus phoenicis-infested coffee plants. Predatory mite adult females were exposed to residues of fenbutatin oxide or distilled water on leaf discs during a period of 72 h prior experiments. When exposed to distilled water (control treatments), predatory mites significantly preferred undamaged plants over air, O. ilicis-infested plants over undamaged plants, and they did not prefer B. phoenicis-infested plants over undamaged plants. However, predatory mites that had been exposed to residues of fenbutatin oxide were neither attracted towards undamaged plants nor to O. ilicis-infested plants. Thus, fenbutatin oxide affected negatively the olfactory response of I. zuluagai. We conclude that sub-lethal-effect studies should be considered in pesticide selectivity programs since the ability of predatory mites to locate their prey may be negatively affected by non-lethal concentrations of pesticides.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrei E (1999) Compêndio de defensivos agrícolas. Andrei, São Paulo
Bowie MH, Worner SP, Krips OE, Penman DR (2001) Sublethal effects of esfenvalerate residues on pyrethroid resistent Typhlodromus pyri (Acari: Phytoseiidae) and its prey Panonychus ulmi and Tetranychus urticae (Acari: Tetranychidae). Exp Appl Acarol 25:311–319. doi:10.1023/A:1017927502679
Dempster JP (1968) The sublethal effect of DDT on the rate of feeding by ground beetle Harpalus rufipes. Entomol Exp Appl 11:51–54. doi:10.1007/BF00295305
Dicke M, de Boer JG, Höfte M, Rocha-Granados MC (2003) Mixed blends of herbivore-induced plant volatiles and foraging success of carnivorous arthropods. Oikos 101:38–48. doi:10.1034/j.1600-0706.2003.12571.x
Flechtmann CHW (1983) Ácaros de importância agrícola. Nobel, São Paulo
Gardiner MM, Eigenbrode SD, Cervantes DE, Barbour JD (2005) Response of Neoseiulus fallacis Garmen and Galendromus occidentalis Nesbitt (Acari: Phytoseiidae) to Tetranychus urticae Koch (Acari: Tetranychidae)-damaged hop Humulus lupulus (L.) (Urticales: Cannabaceae). Agric For Entomol 7:245–251. doi:10.1111/j.1461-9555.2005.00267.x
Hassan SA, Bigler F, Bogenshutz H, Boller E, Brun J, Calis JNM, Coremans-Pelseneer J, Duso C, Grove A, Heimbach U, Helver N, Hokkanen H, Lewis GB, Mansur F, Moreth L, Polgar L, Samsoe-Petersen L, Sauphanor B, Staubli A, Sterk G, Vainio A, van de Veire M, Viggiani G, Vogt H (1994) Results of the sixth join pesticide testing programme of the IOBC/WPRS—working group “Pesticides and Beneficial Organisms”. Entomophaga 39:107–119. doi:10.1007/BF02373500
Hurlbert SH (1984) Pseudoreplication and the design of ecological field experiments. Ecol Monogr 54:187–211. doi:10.2307/1942661
Jagers op Akkerhuis G, Sabelis MW, Tjallingii WF (1985) Ultrastructure of chemoreceptors on the pedipalps and first tarsi of Phytoseiulus persimilis. Exp Appl Acarol 1:235–251
Janssen A (1999) Plants with spider-mite prey attract more predatory mites than clean plants under greenhouse conditions. Entomol Exp Appl 90:191–198. doi:10.1023/A:1003551931509
Kitajima W, Chagas CM, Rodrigues JCV (2003) Brevipalpus-transmitted plant virus and virus-like diseases: cytopathology and some recent cases. Exp Appl Acarol 30:135–160. doi:10.1023/B:APPA.0000006546.55305.e3
Li D, Tian J, Shen Z (2006) Assessment of sublethal effects of clofentezine on life-table parameters in hawthorn spider mite (Tetranychus viennensis). Exp Appl Acarol 38:255–273. doi:10.1007/s10493-006-0016-0
Marcic D (2005) Sublethal effects of tebufenpyrad on the eggs and immatures of two-spotted spider mite, Tetranychus urticae. Exp Appl Acarol 36:177–185. doi:10.1007/s10493-005-3579-2
Marcic D (2007) Sublethal effects of spirodiclofen on life history and life-table parameters of two-spotted spider mite (Tetranychus urticae). Exp Appl Acarol 42:121–129. doi:10.1007/s10493-007-9082-1
Mineiro JLC, Sato ME, Raga A, Arthur V (2008) Population dynamics of phytophagous and predaceous mites on coffee in Brazil, with emphasis on Brevipalpus phoenicis (Acari: Tenuipalpidae). Exp Appl Acarol 44:277–291. doi:10.1007/s10493-008-9149-7
Pallini Filho A, de Moraes GJ, Bueno VHP (1992) Ácaros associados ao cafeeiro (Coffea arabica L.) no sul de Minas Gerais. Cienc Prat 16:303–307
Pallini A, Janssen A, Sabelis MW (1997) Odour-mediated responses of phytophagous mites to conspecific and heterospecific competitors. Oecologia 110:179–185. doi:10.1007/s004420050147
Poletti M, Maia AHN, Omoto C (2007) Toxicity of neonicotinoid insecticides to Neoseiulus californicus and Phytoseiulus macropilis (Acari: Phytoseiidae) and their impact on functional response of Tetranychus urticae (Acari: Tetranychidae). Biol Control 40:30–36. doi:10.1016/j.biocontrol.2006.09.001
Reis PR, Alves EB (1997) Criação do ácaro predador Iphiseiodes zuluagai Denmark & Muma (Acari: Phytoseiidae) em laboratório. Soc Entomol Brasil 26:565–568
Reis PR, Teodoro AV, Pedro Neto M (2000) Predatory activity of phytoseiid mites on the developmental stages of coffee ringspot mite (Acari: Phytoseiidae: Tenuipalpidae). An Soc Entomol Brasil 29:547–553
Sabelis MW, van de Baan HE (1983) Location of distant spider mite colonies by phytoseiid predators: demonstration of specific kairomones emitted by Tetranychus urticae and Panonychus ulmi. Entomol Exp Appl 33:303–314
StatSoft Inc. (1984–2004) Statistica for windows (Software-system for data-analyses) Version 7.0. Tulsa
Stark JD, Banks JE (2003) Population level effects of pesticides and other toxicants on arthropods. Annu Rev Entomol 48:505–519. doi:10.1146/annurev.ento.48.091801.112621
Stark JD, Rangus T (1994) Lethal and sublethal effects of the neem insecticide, Margosan-O, on pea aphid. Pestic Sci 41:155–160. doi:10.1002/ps.2780410212
Stark JD, Tanigoshi L, Bounfour M, Antonelli A (1997) Reproductive potential: its influence on the susceptibility of a species to pesticides. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 37:273–279. doi:10.1006/eesa.1997.1552
Teodoro AV, Fadini MAM, Lemos WP, Guedes RNC, Pallini A (2005) Lethal and sub-lethal selectivity of fenbutatin oxide and sulfur to the predator Iphiseiodes zuluagai (Acari: Phytoseiidae) and its prey, Oligonychus ilicis (Acari: Tetranychidae), in Brazilian coffee plantations. Exp Appl Acarol 36:61–70. doi:10.1007/s10493-005-0507-4
Acknowledgments
We thank Paulo R. Reis for mite identification, and Christoph Gehring, two anonymous reviewers and the editor for helpful comments on the manuscript. Funding was provided by CNPq (Brasília, Brazil).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Teodoro, A.V., Pallini, A. & Oliveira, C. Sub-lethal effects of fenbutatin oxide on prey location by the predatory mite Iphiseiodes zuluagai (Acari: Phytoseiidae). Exp Appl Acarol 47, 293–299 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10493-008-9219-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10493-008-9219-x