Abstract
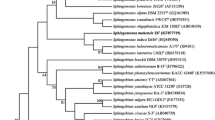
A strictly aerobic and facultatively psychrophilic bacterium, strain 3-0-1T, was isolated from Lake Yamdrok on the Tibetan Plateau, China. Cells were Gram-negative and short-rod-shaped. Strain 3-0-1T formed circular, opaque, yellow colonies, and grew at 0–5 % (w/v) NaCl, pH 5.0–11.0 and 5–35 °C. Phylogenetic analysis based on 16S rRNA gene sequences of various species with validly published names showed that strain 3-0-1T belongs to the genus Sphingobacterium, family Sphingobacteriaceae, sharing the highest similarity with Sphingobacterim nematocida M-SX103T (96.62 %) and less than 95 % similarity with all the other species in the genus Sphingobactrium. The predominant isoprenoid quinone of strain 3-0-1T was identified as menaquinone 7 (MK-7), the major polar lipid was identified as phosphatidylethanolamine and the DNA G+C content was determined to be 42.5 mol%. The predominant cellular fatty acids were identified as summed feature 3 (C16:1 ω7c and/or C16:1 ω6c) (>30 %), iso-C15:0 (>20 %) and iso-C17:0 3-OH (>10 %). Based on the variability of phylogenetic and phenotypic characteristics, strain 3-0-1T represents a novel species of the genus Sphingobacterium, for which the name Sphingobacterium yamdrokense sp. nov. is proposed. The type strain is 3-0-1T (=JCM 19397T = CGMCC 1.12560T).


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Breznak JA, Costilow RN (1994) Physicochemical factors in growth. Meth Gen Mol Bacteriol 137–154
Collins M, Jones D (1980) Lipids in the classification and identification of coryneform bacteria containing peptidoglycans based on 2, 4-diaminobutyric acid. J Appl Bacteriol 48(3):459–470
Dong X, Cai M (2001) Determinative manual for routine bacteriology. Scientific Press, Beijing, pp 370–390 (English translation)
Embley T (1991) The linear PCR reaction: a simple and robust method for sequencing amplified rRNA genes. Lett Appl Microbiol 13(3):171–174
Gerhardt P, Murray R, Wood WA, Krieg NR (1994) Methods for general and molecular bacteriology. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC
Holmes B, Owen RJ, Hollis DG (1982) Flavobacterium spiritivorum, a new species isolated from human clinical specimens. Int J Syst Bacteriol 32(2):157–165
Komagata K, Suzuki KI (1988) Lipid and cell-wall analysis in bacterial systematics. Methods Microbiol 19:161–207
Liu J, Yang LL, Xu CK, Xi JQ, Yang FX, Zhou F, Zhou Y, Mo MH, Li WJ (2012) Sphingobacterium nematocida sp. nov., a nematicidal endophytic bacterium isolated from tobacco. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62(Pt 8):1809–1813
Liu Y, Yao T, Jiao N, Zhu L, Hu A, Liu X, Gao J, Chen Z (2013) Salinity impact on bacterial community composition in five high-altitude lakes from the Tibetan plateau, Western China. Geomicrobiol J 30(5):462–469
Mandel M, Igambi L, Bergendahl J, Dodson M, Scheltgen E (1970) Correlation of melting temperature and cesium chloride buoyant density of bacterial deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol 101(2):333–338
Minnikin D, O’donnell A, Goodfellow M, Alderson G, Athalye M, Schaal A, Parlett J (1984) An integrated procedure for the extraction of bacterial isoprenoid quinones and polar lipids. J Microbiol Meth 2(5):233–241
Reasoner D, Geldreich E (1985) A new medium for the enumeration and subculture of bacteria from potable water. Appl Environ Microbiol 49(1):1–7
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28(10):2731–2739
Yabuuchi E, Kaneko T, Yano I, Moss CW, Miyoshi N (1983) Sphingobacterium gen. nov., Sphingobacterium spiritivorum comb. nov., Sphingobacterium multivorum comb. nov., Sphingobacterium mizutae sp. nov., and Flavobacterium indologenes sp. nov.: glucose-nonfermenting Gram-negative rods in CDC groups IIK-2 and IIb. Int J Syst Bacteriol 33(3):580–598
Yoo SH, Weon HY, Jang HB, Kim BY, Kwon SW, Go SJ, Stackebrandt E (2007) Sphingobacterium composti sp. nov., isolated from cotton-waste composts. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57(7):1590–1593
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41425004, 41171050, 41201059) and the National Basic Research Program of China (2012CB956100).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, N., Liu, Y., Gu, Z. et al. Sphingobacterium yamdrokense sp. nov., isolated from Lake Yamdrok. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 107, 1331–1336 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-015-0428-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-015-0428-0