Abstract
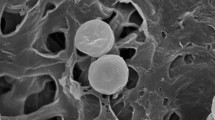
Two novel Gram-stain positive actinobacteria, designated PS-14-16T and RS-7-1, were isolated from the rhizosphere of a mangrove and sea sediment, respectively, and their taxonomic positions were investigated by a polyphasic approach. Both strains were observed to form vegetative hyphae in the early phase of growth but the hyphae eventually fragment into short rods to coccoid cells. The peptidoglycan type of both strains was found to be A4α. Their predominant menaquinone was identified as MK-9(H4) and the major fatty acid as anteiso-C15:0. The DNA G+C content was determined to be 68.4–68.5 mol%. 16S rRNA gene sequencing revealed that strains PS-14-16T and RS-7-1 were related to members of the family Cellulomonadaceae. Their nearest phylogenetic neighbour was found to be Sediminihabitans luteus, which is currently the only species of the genus Sediminihabitans, with a similarity of 97.94 %. However, strains PS-14-16T and RS-7-1 were distinguishable from the members of the genus Sediminihabitans and the other genera within the family Cellulomonadaceae in terms of chemotaxonomic characteristics and phylogenetic relationship. The results of DNA–DNA hybridization experiments indicated that strains PS-14-16T and RS-7-1 belong to the same species. Strains PS-14-16T and RS-7-1 are concluded to represent a novel genus and species of the family Cellulomonadaceae, for which the name Tropicihabitans flavus gen. nov., sp. nov. is proposed. The type strain of T. flavus is PS-14-16T (=NBRC 110109T = IanCC A 516T).


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bergey DH, Harrison FC, Breed RS, Hammer BW, Huntoon FM (1923) Bergey’s manual of determinative bacteriology, 1st edn. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore
Blunt JW, Copp BR, Hu WP, Munro MH, Northcote PT, Prinsep MR (2007) Marine natural products. Nat Prod Rep 24:31–86
Ezaki T, Hashimoto Y, Yabuuchi E (1989) Fluorometric deoxyribonucleic acid-deoxyribonucleic acid hybridization in microdilution wells as an alternative to membrane filter hybridization in which radioisotopes are used to determine genetic relatedness among bacterial strains. Int J Syst Bacteriol 39:224–229
Felsenstein J (1981) Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: a maximum likelihood approach. J Mol Evol 17:368–376
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:738–791
Fitch WM (1971) Toward defining the course of evolution: minimum change for specific tree topology. Syst Zool 20:406–416
Hamada M, Iino T, Iwami T, Harayama S, Tamura T, Suzuki K et al (2010) Mobilicoccus pelagius gen. nov., sp. nov. and Piscicoccus intestinalis gen. nov., sp. nov., two new members of the family Dermatophilaceae, and reclassification of Dermatophilus chelonae (Masters, 1995) as Austwickia chelonae gen. nov., comb. nov. J Gen Appl Microbiol 56:427–436
Hamada M, Tamura T, Shibata C, Yamamura H, Hayakawa M, Suzuki K (2012a) Sediminihabitans luteus gen. nov., sp. nov., a new member of the family Cellulomonadaceae isolated from sea sediment. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 102:325–333
Hamada M, Yamamura H, Komukai C, Tamura T, Suzuki K, Hayakawa M (2012b) Luteimicrobium album sp. nov., a novel actinobacterium isolated from lichen collected in Japan, and emended description of the genus Luteimicrobium. J Antibiot 65:427–431
Hamada M, Shibata C, Tamura T, Suzuki K (2013a) Zhihengliuella flava sp. nov., an actinobacterium isolated from sea sediment, and emended description of the genus Zhihengliuella. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63:4760–4764
Hamada M, Tamura T, Shibata C, Yamamura H, Hayakawa M, Schumann P, Suzuki K (2013b) Paraoerskovia sediminicola sp. nov., an actinobacterium isolated from sea sediment, and emended description of the genus Paraoerskovia. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63:2637–2641
Khan ST, Harayama S, Tamura T, Ando K, Takagi M, Kazuo S (2009) Paraoerskovia marina gen. nov., sp. nov., an actinobacterium isolated from marine sediment. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:2094–2098
Khan ST, Komaki H, Motohashi K, Kozone I, Takagi M, Kazuo S (2011) Streptomyces associated with a marine sponge Haliclona sp.; biosynthetic genes for secondary metabolites and products. Environ Microbiol 13:391–403
Kim OS, Cho YJ, Lee K, Yoon SH, Kim M, Na H, Park SC, Jeon YS, Lee JH, Yi H, Won S, Chun J (2012) Introducing EzTaxon-e: a prokaryotic 16S rRNA gene sequence database with phylotypes that represent uncultured species. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:716–721
Krasil’nikov NA, Kalakoutskii LV, Krasil’nikov NF (1961) A new genus of Actinomycetales, Promicromonospora, gen. nov. Bull Acad Sci USSR 1:107–112
Lam KS (2006) Discovery of novel metabolites from marine actinomycetes. Curr Opin Microbiol 9:245–251
Lewis K (2013) Platforms for antibiotic discovery. Nature Rev Drug Discov 12:371–387
Li Y, Chen F, Dong K, Wang G (2013) Actinotalea ferrariae sp. nov., isolated from an iron mine, and emended description of the genus Actinotalea. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63:3398–3403
Ling LL, Schneider T, Peoples AJ, Spoering AL, Engels I, Conlon BP, Mueller A, Schäberle TF, Hughes DE, Epstein S, Jones M, Lazarides L, Steadman VA, Cohen DR, Felix CR, Fetterman KA, Millett WP, Nitti AG, Zullo AM, Chen C, Lewis K (2015) A new antibiotic kills pathogen without detectable ressistance. Nature 517:455–459
Prauser H, Lechevalier MP, Lechevalier HA (1970) Description of Oerskovia gen. n. to harbor Ørskov’s motile Nocardia. Appl Microbiol 19:534
Rocourt J, Wehmeyer U, Stackebrandt E (1987) Transfer of Listeria denitrificans to a new genus, Jonesia gen. nov., as Jonesia denitrificans comb. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol 37:266–270
Saito H, Miura K (1963) Preparation of transforming deoxyribonucleic acid by phenol treatment. Biochim Biophys Acta 72:619–629
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Sasser M (1990) Identification of bacteria by gas chromatography of cellular fatty acids, MIDI Technical Note 101. MIDI Inc, Newark
Schleifer KH, Kandler O (1972) Peptidoglycan types of bacterial cell walls and their taxonomic implications. Bacteriol Rev 36:407–477
Schumann P (2011) Peptidoglycan structure. In: Rainey F, Oren A (eds) Taxonomy of prokaryotes, methods in microbiology, vol 38. Academic Press, London, pp 101–129
Schumann P, Kämpfer P, Busse HJ, Evtushenko LI (2009) Proposed minimal standards for describing new genera and species of the suborderer Micrococcineae. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:1823–1849
Stackebrandt E, Prauser H (1991) The family Cellulomonadaceae. In: Balows A, Trüper HG, Dworkin M, Harder W, Schleifer KH (eds) The prokaryotes, vol 2, 2nd edn. Springer, New York, pp 1323–1345
Stackebrandt E, Schumann P (2000) Description of Bogoriellaceae fam. nov., Dermacoccaceae fam. nov., Rarobacteraceae fam. nov. and Sanguibacteraceae fam. nov. and emendation of some families of the suborder Micrococcineae. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 50:1279–1285
Stackebrandt E, Schumann P (2012) Genus I. Cellulomonas. In: Goodfellow M, Kämpfer P, Busse HJ, Trujillo ME, Suzuki K, Ludwig W, Whitman WB (eds) Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology. The Actinobacteria, part A, vol 5, 2nd edn. Springer, New York, pp 702–710
Stackebrandt E, Rainey FA, Ward-Rainey NL (1997) Proposal for a new hierarchic classification system, Actinobacteria classis nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol 47:479–491
Stackebrandt E, Breymann S, Steiner U, Prauser H, Weiss N, Schumann P et al (2002) Re-evaluation of the status of the genus Oerskovia, reclassification of Promicromonospora enterophila (Jáger, 1983) as Oerskovia enterophila comb. nov. and description of Oerskovia jenensis sp. nov. and Oerskovia paurometabola sp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 52:1105–1111
Tamaoka J, Komagata K (1984) Determination of DNA base composition by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. FEMS Microbiol Lett 25:125–128
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30:2725–2729
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4876–4882
Yamamoto N, Sato SI, Saito K, Hasuo T, Tadenuma M, Suzuki KI, Tamaoka J, Komagata K (1988) Rarobacter faecitabidus gen. nov., sp. nov., a yeast-lysing coryneform bacterium. Int J Syst Bacteriol 38:7–11
Yi H, Schumann P, Chun J et al (2007) Demequina aestuarii gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel actinomycete of the suborder Micrococcineae, and reclassification of Cellulomonas fermentans Bagnara, 1985 as Actinotalea fermentans gen. nov., comb. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:151–156
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Science and Technology Research Partnership for Sustainable Development (SATREPS) which is a research program in collaborated with the Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST) and the Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hamada, M., Shibata, C., Nurkanto, A. et al. Tropicihabitans flavus gen. nov., sp. nov., a new member of the family Cellulomonadaceae . Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 107, 1299–1306 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-015-0424-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-015-0424-4