Abstract
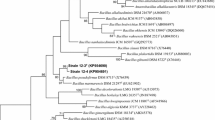
A rod shaped, non-motile, endospore forming, Gram-stain positive and moderately halotolerant strain, designated as NCCP-168T, was isolated from salt mines sampled in the Karak district of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Province in Pakistan. To delineate its taxonomic position, the strain was subjected to polyphasic characterization. Cells of strain NCCP-168T can grow at 10–40 ○C (optimum at 30–35 ○C), in a pH range of 5.0–9.0 (optimum at pH 8.0) and in 0–17 % (w/v) NaCl on agar medium. The phylogenetic analysis based on the 16S rRNA gene sequence showed that strain NCCP-168T belongs to the genus Bacillus with the highest similarity to Bacillus seohaeanensis BH724T (97.1 %), and less than 97 % similarity with other closely related taxa (95.6 % with B. subtilis subsp. subtilis NCIB3610T). DNA–DNA relatedness between strain NCCP-168T and the type strains of closely related species was lower than 30 %. Chemotaxonomic data (major menaquinone, MK-7; cell wall peptidoglycan type, A1γ [meso-diaminopimelic acid]; major fatty acids, iso-C15:0 29.9 %, anteiso-C15:0 29.3 %, iso-C16:0 11.4 %, iso-C14:0 8.9 % and anteiso-C17:0 7.0 %; major polar lipids, diphosphatidylglycerol, phosphatidylglycerol and phosphatidylethanolamine) support the affiliation of strain NCCP-168T with genus Bacillus. On the basis of phenotypic, chemotaxonomic and phylogenetic data, strain NCCP-168T can be distinguished from the closely related taxa and thus represents a novel species in the genus Bacillus, for which the name Bacillus pakistanensis sp. nov. is proposed, with the type strain NCCP-168T (= KCTC 13786T = DSM 24834T = JCM 18975T).

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed I, Yokota A, Fujiwara T (2007a) Gracilibacillus boraciitolerans sp. nov., a highly boron-tolerant and moderately halotolerant bacterium isolated from soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57 (Pt 4):796–802. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.64284-0
Ahmed I, Yokota A, Fujiwara T (2007b) A novel highly boron tolerant bacterium, Bacillus boroniphilus sp. nov., isolated from soil, that requires boron for its growth. Extremophiles 11:217–224. doi:10.1007/s00792-006-0027-0
Arahal DR, Ventosa A (2002) Moderately halophilic and halotolerant species of Bacillus and related genera, Applications and systematics of bacillus and relatives. Blackwell, Oxford, pp 83–99
Chang YH, Han JI, Chun JS, Lee KC, Rhee MS, Kim YB, Bae KS (2002) Comamonas koreensis sp. nov., a non-motile species from wetland in Woopo Korea. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 52:377–381. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.01734-0
Chen YG, Liu ZX, Peng DJ, Zhang YQ, Wang YX, Tang SK, Li WJ, Cui XL, Liu YQ (2009) Virgibacillus litoralis sp. nov., a moderately halophilic bacterium isolated from saline soil. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 96(3):323–329. doi:10.1007/s10482-009-9349-0
Ezaki T, Hashimoto Y, Yabuuchi E (1989) Fluorometric deoxyribonucleic acid-deoxyribonucleic acid hybridization in microdilution wells as an alternative to membrane filter hybridization in which radioisotopes are used to determine genetic relatedness among bacterial strains. Int J Syst Bacteriol 39(3):224–229. doi:10.1099/00207713-39-3-224
Garabito MJ, Márquez C, Ventosa A (1998) Halotolerant Bacillus diversity in hypersaline environments. Can J Microbiol 44:95–102. doi:10.1139/w97-125
Groth I, Schumann P, Weiss N, Martin K, Rainey FA (1996) Agrococcus jenensis gen. nov., sp. nov., a new genus of actinomycetes with diaminobutyric acid in the cell wall. Int J Syst Bacteriol 46(1):234–239. doi:10.1099/00207713-46-1-234
Ishikawa M, Ishizaki S, Yamamoto Y, Yamasato K (2002) Paraliobacillus ryukyuensis gen. nov., sp. nov., a new Gram-positive, slightly halophilic, extremely halotolerant, facultative anaerobe isolated from a decomposing marine alga. J Gen Appl Microbiol 48(5):269–279. doi:10.2323/jgam.48.269
Jung MY, Kim J-S, Paek WK, Styrak I, Park I-S, Sin Y, Paek J, Park KA, Kim H, Kim HL, Chang Y-H (2012) Description of Lysinibacillus sinduriensis sp. nov., and transfer of Bacillus massiliensis and Bacillus odysseyi to the genus Lysinibacillus as Lysinibacillus massiliensis comb. nov. and Lysinibacillus odysseyi comb. nov. with emended description of the genus Lysinibacillus. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62(10):2347–2355. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.033837-0
Kämpfer P, Rossello-Mora R, Falsen E, Busse HJ, Tindall BJ (2006) Cohnella thermotolerans gen. nov., sp. nov., and classification of ‘Paenibacillus hongkongensis’ as Cohnella hongkongensis sp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:781–786. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.63985-0
Kim OS, Cho YJ, Lee K, Yoon SH, Kim M, Na H, Park SC, Jeon YS, Lee JH, Yi H, Won S, Chun J (2012) Introducing EzTaxon-e: a prokaryotic 16S rRNA gene sequence database with phylotypes that represent uncultured species. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:716–721. doi:10.1099/Ijs.0.038075-0
Lee JC, Lim JM, Park DJ, Jeon CO, Li WJ, Kim CJ (2006) Bacillus seohaeanensis sp. nov., a halotolerant bacterium that contains l-lysine in its cell wall. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56(8):1893–1898. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.64237-0
Logan NA, Berge O, Bishop AH, Busse HJ, De Vos P, Fritze D, Heyndrickx M, Kampfer P, Rabinovitch L, Salkinoja-Salonen MS, Seldin L, Ventosa A (2009) Proposed minimal standards for describing new taxa of aerobic, endospore-forming bacteria. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59(Pt 8):2114–2121. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.013649-0
Minnikin DE, O’Donnell AG, Goodfellow M, Alderson G, Athalye M, Schaal A, Parlett JH (1984) An integrated procedure for the extraction of bacterial isoprenoid quinones and polar lipids. J Microbiol Method 2:233–241. doi:10.1016/0167-7012(84)90018-6
Oren A (1999) Bioenergetic aspects of halophilism. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 63(2):334–348
Quesada E, Ventosa A, Rodriguez-Valera F, Ramos-Cormenzana A (1982) Types and properties of some bacteria isolated from hypersaline soils. J Appl Microbiol 53(2):155–161. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2672.1982.tb04671.x
Quesada E, Béjar V, Ferrer M, Calvo C, Llamas I, Martínez-Checa F, Arias S, Ruiz-García C, Páez R, Martinez-Cánovas M, del Moral A (eds) (2004) Moderately halophilic, exopolysaccharide-producing bacteria. Halophilic Microorganisms. Springer-Verlag Berlin
Roohi A, Ahmed I, Iqbal M, Jamil M (2012) Preliminary isolation and characterization of halotolerant and halophilic bacteria from salt mines of Karak, Pakistan. Pak J Bot 44((SI 1)):365–370
Roohi A, Ahmed I, Khalid N, Iqbal M, Jamil M (2014) Isolation and phylogenetic identification of halotolerant/halophilic bacteria from the salt mines of Karak, Pakistan. Int J Agric Biol (Accepted)
Sasser M (1990) Identification of bacteria by gas chromatography of cellular fatty acids. MIDI Technical Note 101
Schleifer KH, Kandler O (1972) Peptidoglycan types of bacterial cell walls and their taxonomic implications. Bacteriol Rev 36(4):407–477
Shida O, Takagi H, Kadowaki K, Nakamura LK, Komagata K (1997) Transfer of Bacillus alginolyticus, Bacillus chondroitinus, Bacillus curdlanolyticus, Bacillus glucanolyticus, Bacillus kobensis, and Bacillus thiaminolyticus to the genus Paenibacillus and emended description of the genus Paenibacillus. Int J Syst Bacteriol 47(2):289–298. doi:10.1099/00207713-47-2-289
Stackebrandt E, Goebel BM (1994) Taxonomic note: a place for DNA–DNA reassociation and 16S rRNA sequence analysis in the present species definition in bacteriology. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 44(4):846–849. doi:10.1099/00207713-44-4-846
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739. doi:10.1093/molbev/msr121
Tindall BJ (1990) A comparative study of the lipid composition of Halobacterium saccharovorum from various sources. Syst Appl Microbiol 13:128–130. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.65717-0
Ventosa A, Nieto JJ, Oren A (1998) Biology of moderately halophilic aerobic bacteria. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 62(2):504–544
Ventosa A, Mellado E, Sánchez-Porro C, Marquez M (eds) (2008) Halophilic and halotolerant microorganisms from soils. Microbiology of Extreme Soils, Soil Biology. Springer-Verlag, Berlin
Wainø M, Tindall BJ, Schumann P, lngvorsenl K (1999) Gracilibacillus gen. nov., with description of Gracilibacillus halotolerans gen. nov., sp. nov.; transfer of Bacillus dipsosauri to Gracilibacillus dipsosauri comb. nov., and Bacillus salexigens to the genus Salibacillus gen. nov., as Salibacillus salexigens comb. nov. lnt J Syst Bacteriol 49:821–831. doi:10.1099/00207713-49-2-821
Yoon J-H, Kim I-G, Kang KH, Oh T-K, Park Y-H (2003) Bacillus marisflavi sp. nov. and Bacillus aquimaris sp. nov., isolated from sea water of a tidal flat of the Yellow Sea in Korea. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 53(5):1297–1303. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.02365-0
Zhang J, Wang J, Fang C, Song F, Xin Y, Qu L, Ding K (2010) Bacillus oceanisediminis sp. nov., isolated from marine sediment. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60 (Pt 12):2924–2929. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.019851-0
Acknowledgments
This work was partially supported by PSDP Project “Research for Agricultural Development Program (RADP)” under a sub-project (Grant No. CS-55/RADP/PARC) entitled “Establishment of Microbial Bio-Resource Laboratories: National Culture Collection of Pakistan (NCCP)” from Pakistan Agricultural Research Council (PARC), Islamabad, Pakistan. The partial financial support of KRIBB to authors, Aneela Roohi and Saira Abbas in the training course at Korean Collection for Type Cultures, Biological Resources Centre, KRIBB under the umbrella of ACM forum is also gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Aneela Roohi and Iftikhar Ahmed contributed equally to the experimentation.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roohi, A., Ahmed, I., Paek, J. et al. Bacillus pakistanensis sp. nov., a halotolerant bacterium isolated from salt mines of the Karak Area in Pakistan. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 105, 1163–1172 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-014-0177-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-014-0177-5