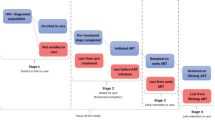
Abstract
The continuum of care for successful HIV treatment includes HIV testing, linkage, engagement in care, and retention on antiretroviral therapy (ART). Loss to follow-up (LTFU) is a significant disruption to this pathway and a common outcome in sub-Saharan Africa. This review of literature identified interventions that have reduced LTFU in the HIV care continuum. A search was conducted utilizing terms that combined the disease state, stages of the HIV care continuum, interventions, and LTFU in sub-Saharan Africa and articles published between January 2010 and July 2015. Thirteen articles were included in the final review. Use of point of care CD4 testing and community-supported programs improved linkage, engagement, and retention in care. There are few interventions directed at LTFU and none that span across the entire continuum of HIV care. Further research could focus on devising programs that include a series of interventions that will be effective through the entire continuum.
Resumen
La continuidad de la atención para el éxito del tratamiento del VIH incluye la prueba del VIH, la vinculación y el compromiso en el cuidado y mantenimiento de la terapia antirretroviral (TAR). Las pérdidas durante el seguimiento (LTFU) es una alteración significativa de esta vía y un resultado común en el África subsahariana. Esta revisión de la literatura identificó intervenciones que han reducido LTFU en el continuo de la atención del VIH. Se realizó una búsqueda utilizando términos que combinaban el estado de la enfermedad, las etapas del continuo de la atención del VIH, las intervenciones y LTFU en el África subsahariana y los artículos publicados entre enero de 2010 y julio de 2015. Trece artículos fueron incluidos en la revisión final. El uso del punto de atención pruebas de CD4 y los programas apoyados por la comunidad mejorar la articulación, compromiso, y la retención de los pacientes. Hay pocas intervenciones dirigidas a LTFU y ninguno que se extienden a lo largo de todo el continuo de la atención del VIH. La investigación adicional podría centrarse en la elaboración de programas que incluyen una serie de intervenciones que serán efectivas a través de toda la cadena.

Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Gardner EM, McLees MP, Steiner JF, Del Rio C, Burman WJ. The spectrum of engagement in HIV care and its relevance to test-and-treat strategies for prevention of HIV infection. Clin Infect Dis. 2011;52(6):793–800.
Rosen S, Fox MP. Retention in HIV care between testing and treatment in sub-Saharan Africa: a systematic review. PLoS Med. 2011;8(7):e1001056.
Mugavero MJ, Norton WE, Saag MS. Health care system and policy factors influencing engagement in HIV medical care: piecing together the fragments of a fractured health care delivery system. Clin Infect Dis. 2011;15(52 Suppl 2):S238–46.
Ulett KB, Willig JH, Lin H, Routman JS, Abroms S, Allison J, et al. The therapeutic implications of timely linkage and early retention in HIV care. AIDS Patient Care STDS. 2009;23(1):41–9.
Mugavero MJ, Lin HY, Willig JH, Westfall AO, Ulett KB, Routman JS, et al. Missed visits and mortality among patients establishing initial outpatient HIV treatment. Clin Infect Dis. 2009;48(2):248–56.
Giordano TP, Gifford AL, White AC Jr, Suarez-Almazor ME, Rabeneck L, Hartman C, et al. Retention in care: a challenge to survival with HIV infection. Clin Infect Dis. 2007;44(11):1493–9.
Bradley H, Hall HI, Wolitski RJ, Van Handel MM, Stone AE, LaFlam M, et al. Vital signs: HIV diagnosis, care, and treatment among persons living with HIV—United States, 2011. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2014;63(47):1113–7.
Genberg BL, Naanyu V, Wachira J, Hogan JW, Sang E, Nyambura M, et al. Linkage to and engagement in HIV care in western Kenya: an observational study using population-based estimates from home-based counselling and testing. Lancet HIV. 2015;2(1):e20–6.
Jani IV, Sitoe NE, Alfai ER, Chongo PL, Quevedo JI, Rocha BM, et al. Effect of point-of-care CD4 cell count tests on retention of patients and rates of antiretroviral therapy initiation in primary health clinics: an observational cohort study. The Lancet. 2011;378(9802):1572–9.
Assefa Y, Damme WV, Mariam DH, Kloos H. Toward universal access to HIV counseling and testing and antiretroviral treatment in Ethiopia: looking beyond HIV testing and ART initiation. AIDS Patient Care STDS. 2010;24(8):521–5.
Udeagu CC, Webster TR, Bocour A, Michel P, Shepard CW. Lost or just not following up: public health effort to re-engage HIV-infected persons lost to follow-up into HIV medical care. AIDS. 2013;27(14):2271–9.
Bandura A. Health promotion by social cognitive means. Health Educ Behav. 2004;31(2):143.
Brinkhof MW, Pujades-Rodriguez M, Egger M. Mortality of patients lost to follow-up in antiretroviral treatment programmes in resource-limited settings: systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2009;4(6):e5790.
Chi BH, Musonda P, Lembalemba MK, Chintu NT, Gartland MG, Mulenga SN, et al. Universal combination antiretroviral regimens to prevent mother-to-child transmission of HIV in rural Zambia: a two-round cross-sectional study. Bull World Health Organ. 2014;92(8):582–92.
Lessells RJ, Mutevedzi PC, Cooke GS, Newell ML. Retention in HIV care for individuals not yet eligible for antiretroviral therapy: rural KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2011;56(3):e79–86.
Ingle SM, May M, Uebel K, Timmerman V, Kotze E, Bachmann M, et al. Outcomes in patients waiting for antiretroviral treatment in the Free State Province, South Africa: prospective linkage study. AIDS. 2010;24(17):2717–25.
Larson BA, Brennan A, McNamara L, Long L, Rosen S, Sanne I, et al. Early loss to follow up after enrolment in pre-ART care at a large public clinic in Johannesburg, South Africa. Trop Med Int Health. 2010;15(s1):43–7.
Kranzer K, Zeinecker J, Ginsberg P, Orrell C, Kalawe NN, Lawn SD, et al. Linkage to HIV care and antiretroviral therapy in Cape Town, South Africa. PLoS One. 2010;5(11):e13801.
McGuire M, Munyenyembe T, Szumilin E, Heinzelmann A, Le Paih M, Bouithy N, et al. Vital status of pre-ART and ART patients defaulting from care in rural Malawi. Trop Med Int Health. 2010;15(s1):55–62.
Fox MP, Rosen S. Patient retention in antiretroviral therapy programs up to three years on treatment in sub-Saharan Africa, 2007–2009: systematic review. Trop Med Int Health. 2010;15(s1):1–15.
Wang B, Losina E, Stark R, Munro A, Walensky RP, Wilke M, et al. Loss to follow-up in a community clinic in South Africa: roles of gender, pregnancy and CD4 count. SAMJ S Afr Med J. 2011;101(4):253–7.
Grol R. Successes and failures in the implementation of evidence-based guidelines for clinical practice. Med Care. 2001;39(8):II-46–54.
Bemelmans M, Van Den Akker T, Ford N, Philips M, Zachariah R, Harries A, et al. Providing universal access to antiretroviral therapy in Thyolo, Malawi through task shifting and decentralization of HIV/AIDS care. Trop Med Int Health. 2010;15(12):1413–20.
McCollum ED, Preidis GA, Kabue MM, Singogo EB, Mwansambo C, Kazembe PN, et al. Task shifting routine inpatient pediatric HIV testing improves program outcomes in urban Malawi: a retrospective observational study. PLoS One. 2010;5(3):e9626.
Silvestri DM, Modjarrad K, Blevins ML, Halale E, Vermund SH, McKinzie JP. A comparison of HIV detection rates using routine opt-out provider-initiated HIV testing and counseling versus a standard of care approach in a rural African setting. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2011;56(1):e9–32.
Thornton RL. The Demand for, and Impact of, Learning HIV Status. Am Econ Rev. 2008;98(5):1829–63.
Faal M, Naidoo N, Glencross DK, Venter WD, Osih R. Providing immediate CD4 count results at HIV testing improves ART initiation. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2011;58(3):e54–9.
Nsigaye R, Wringe A, Roura M, Kalluvya S, Urassa M, Busza J, et al. From HIV diagnosis to treatment: evaluation of a referral system to promote and monitor access to antiretroviral therapy in rural Tanzania. J Int AIDS Soc. 2009;12(1):1.
Kohler PK, Chung MH, McGrath CJ, Benki-Nugent SF, Thiga JW, John-Stewart GC. Implementation of free cotrimoxazole prophylaxis improves clinic retention among antiretroviral therapy-ineligible clients in Kenya. AIDS. 2011;25(13):1657–61.
Lester RT, Ritvo P, Mills EJ, Kariri A, Karanja S, Chung MH, et al. Effects of a mobile phone short message service on antiretroviral treatment adherence in Kenya (WelTel Kenya1): a randomised trial. The Lancet. 2010;376(9755):1838–45.
Pop-Eleches C, Thirumurthy H, Habyarimana JP, Zivin JG, Goldstein MP, de Walque D, et al. Mobile phone technologies improve adherence to antiretroviral treatment in a resource-limited setting: a randomized controlled trial of text message reminders. AIDS. 2011;25(6):825–34.
Govindasamy D, Ford N, Kranzer K. Risk factors, barriers and facilitators for linkage to antiretroviral therapy care: a systematic review. AIDS. 2012;26(16):2059–67.
Kranzer K, Govindasamy D, Ford N, Johnston V, Lawn SD. Quantifying and addressing losses along the continuum of care for people living with HIV infection in sub-Saharan Africa: a systematic review. J Int AIDS Soc. 2012;15(2):1–15.
Simoni JM, Amico KR, Smith L, Nelson K. Antiretroviral adherence interventions: translating research findings to the real world clinic. Curr HIV/AIDS Rep. 2010;7(1):44–51.
Boland A, Cherry MG, Dickson R, editors. Doing a systematic review: a student’s guide. Los Angeles, CA: Sage; 2013.
The World Bank. Country and Lending Groups. 2016. http://data.worldbank.org/about/country-and-lending-groups. Accessed 16 June 2016.
Effective Public Health Practice Project (EPHPP). Quality assessment tool for quantitative studies. 2010. http://www.ephpp.ca/tools.html. Accessed 8 June 2016.
Larson BA, Schnippel K, Ndibongo B, Xulu T, Brennan A, Long L, et al. Rapid point-of-care CD4 testing at mobile HIV testing sites to increase linkage to care: an evaluation of a pilot program in South Africa. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2012;61(2):e13–7.
Leon N, Mathews C, Lewin S, Osler M, Boulle A, Lombard C. A comparison of linkage to HIV care after provider-initiated HIV testing and counselling (PITC) versus voluntary HIV counselling and testing (VCT) for patients with sexually transmitted infections in Cape Town, South Africa. BMC Health Serv Res. 2014;14(1):1.
Wanyenze RK, Hahn JA, Liechty CA, Ragland K, Ronald A, Mayanja-Kizza H, et al. Linkage to HIV care and survival following inpatient HIV counseling and testing. AIDS Behav. 2011;15(4):751–60.
Wanyenze RK, Kamya MR, Fatch R, Mayanja-Kizza H, Baveewo S, Szekeres G, et al. Abbreviated HIV counselling and testing and enhanced referral to care in Uganda: a factorial randomised controlled trial. Lancet Glob Health. 2013;1(3):e137–45.
Bemelmans M, Baert S, Goemaere E, Wilkinson L, Vandendyck M, Cutsem G, et al. Community-supported models of care for people on HIV treatment in sub-Saharan Africa. Trop Med Int Health. 2014;19(8):968–77.
Franke MF, Kaigamba F, Socci AR, Hakizamungu M, Patel A, Bagiruwigize E, et al. Improved retention associated with community-based accompaniment for antiretroviral therapy delivery in rural Rwanda. Clin Infect Dis. 2013;56(9):1319–26.
Lubega M, Tumwesigye NM, Kadobera D, Marrone G, Wabwire-Mangen F, Peterson S, et al. Effect of community support agents on retention of people living with HIV in pre-antiretroviral care: a randomized controlled trial in Eastern Uganda. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2015;70(2):e36–43.
Fatti G, Meintjes G, Shea J, Eley B, Grimwood A. Improved survival and antiretroviral treatment outcomes in adults receiving community-based adherence support: 5-year results from a multicentre cohort study in South Africa. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2012;61(4):e50–8.
Rosen S, Ketlhapile M. Cost of using a patient tracer to reduce loss to follow-up and ascertain patient status in a large antiretroviral therapy program in Johannesburg, South Africa. Trop Med Int Health. 2010;15(s1):98–104.
Djarma O, Nguyen Y, Renois F, Djimassal A, Banisadr F, Andreoletti L. Continuous free access to HAART could be one of the potential factors impacting on loss to follow-up in HAART-eligible patients living in a resource-limited setting: N’djamena, Chad. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2014;108(11):735–8.
Messou E, Kouakou M, Gabillard D, Gouesse P, Kone M, Tchehy A, et al. Medication possession ratio: predicting and decreasing loss to follow-up in antiretroviral treatment programs in Cote d’Ivoire. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2011;1(57 Suppl 1):S34–9.
Wynberg E, Cooke G, Shroufi A, Reid SD, Ford N. Impact of point-of-care CD4 testing on linkage to HIV care: a systematic review. J Int AIDS Soc. 2014;17(1):18809.
Losina E, Touré H, Uhler LM, Anglaret X, Paltiel AD, Balestre E, et al. Cost-effectiveness of preventing loss to follow-up in HIV treatment programs: a Cote d’Ivoire appraisal. PLoS Med. 2009;6(10):e1000173.
Kasteng F, Settumba S, Kallander K, Vassall A, inSCALE Study Group. Valuing the work of unpaid community health workers and exploring the incentives to volunteering in rural Africa. Health Policy Plan. 2016;31(2):205–16.
Acknowledgments
For her help in suggesting search terminology and more efficient ways to search databases, the authors wish to acknowledge Xan Goodman.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
The study was partly funded by the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD), the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH), the President’s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief (PEPFAR) under award number R01HD075050 and R01HD087994.
Conflict of Interest
The authors state that there are no competing interests to declare.
Research Involving Human Subjects or Animals
This research is a systematic review of published literature and deemed excluded by the UNLV IRB.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was not obtained as this was a systematic review of published literature.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Keane, J., Pharr, J.R., Buttner, M.P. et al. Interventions to Reduce Loss to Follow-up During All Stages of the HIV Care Continuum in Sub-Saharan Africa: A Systematic Review. AIDS Behav 21, 1745–1754 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10461-016-1532-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10461-016-1532-5