Abstract
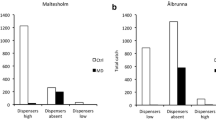
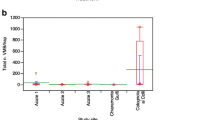
Megaplatypus mutatus (= Platypus mutatus) (Chapuis) is an ambrosia beetle native to South America that attacks live trees, mining deeply into the xylem through large tunnels. This activity weakens the structural integrity of the tree, causing severe stem-breakage and mortality. Attacks are initiated by pioneer males that select a host tree and build short nuptial galleries, to which they attract females using a sexual pheromone. Previously, we showed the potential for the strategy of pheromone-mediated mating disruption of M. mutatus in commercial poplar and hazelnut plantations in South America and Europe using polyethylene reservoir dispensers for pheromones. In the present work we replaced the polymeric reservoir dispensers by monolithic dispensers made by dispersion of the pheromone in natural waxes and the addition of kaolin and we found that: prior to pheromone deployment, the mean number of galleries per tree did not differ significantly between the control and treated plots and the same was observed after the mating disruption treatment for the control plot but not for treated plots, where the mean number of galleries were reduced. These findings confirm that mating disruption is a viable tool for management of M. mutatus in poplar plantations. Using natural wax dispensers has obvious advantages from an environmental point of view.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achinelli FG, Liljersthröm G, Aparicio A, Delgado M, Jouanny M, Mastrandrea C (2005) Daños por taladrillo (Megaplatypus mutatus (= Platypus sulcatus)) en plantaciones de álamo (P. deltoides spp.) de Alberti, Buenos Aires: análisis preliminar de la magnitud y distribución de fustes quebrados. Rev Asoc For Arg 59(1):8–11
Alfaro R, Humble LM, Gonzalez P, Villaverde R, Allegro G (2007) The threat of the ambrosia beetle Megaplatypus mutatus (Chapuis) [= Platypus mutatus Chapuis] to world poplar resources. Forestry 80:471–479
Allegro G, Della Beffa G (2001) Un nuovo problema entomologico per la pioppicoltura Italiana: Platypus mutatus Chapuis (Coleoptera, Platypodidae). Sherwood Foreste ed alberi oggi. 66:31–34
Bessa-Gomes C, Legendre S, Clobert J (2004) Allee effects, mating systems and the extinction risk in population with two sexes. Ecol Lett 7:802–812
Dolinko A, Ceriani-Nakamurakare E (2015) Pheromone dispenser locator. Computer software. Vers. 2.2. Retrieved 2015, from http://cerianinaka.wix.com/dolinko-system
EPPO/OEPP Pest Risk Analysis Reporting Service (2004) First report of Platypus mutatus in Italy: addition to the EPPO Alert List No. 04 2004/061
European and Mediterranean Plant Protection Organisation (2007) Report of the 39th meeting of the panel on phytosanitary measures (Paris, 2007-03-06/09) 07-13694. http://archives.eppo.org/EPPOStandards/PM1_GENERAL/pm1-02(16)_A1A2_2007.pdf. Accessed Sept 2007
Funes H, Zerba E, González-Audino P (2009) Comparison of three types of traps baited with sexual pheromones for ambrosia beetle M. mutatus in poplar plantations. J Econ Entomol 102:1546–1550
Funes H, Zerba E, González-Audino P (2011) Mating disruption of the ambrosia beetle Megaplatypus mutatus in poplar and hazelnut plantations using reservoir systems for pheromones. Ent Exp Appl 139:226–234
Funes H, Zerba E, González-Audino P (2013) Effect of release rate and enantiomeric composition on response to pheromones of Megaplatypus mutatus (Chapuis) in poplar plantations of Argentina and Italy. Bull Entomol Res 103:564–569
Gatti Liguori P, Zerba E, Alzogaray R, Gonzalez-Audino P (2008) 3-Pentanol: a new attractant present in volatile emissions from the ambrosia beetle, Megaplatypus mutatus. J Chem Ecol 34:1446–1451
Giménez R, Etiennot AE (2003) Host range of Platypus mutatus (Chapuis, 1865) (Coleoptera, Platypodidae). Entomotropica 18:89–94
Gonzalez Audino P, Villaverde R, Alfaro R, Zerba E (2005) Identification of volatile emissions from Platypus mutatus (= sulcatus) (Coleoptera, Platypodidae) and their behavioral activity. J Econ Entomol 98:1506–1509
Gonzalez-Audino P, Griffo R, Gatti P, Allegro G, Zerba E (2013) Pheromone detection of the introduced forest pest Megaplatypus mutatus (= Platypus mutatus) (Chapuis) (Platypodinae, Curculionidae) in Italy. Agrofor Syst 87:109–115
González-Audino P, Gatti-Liguori P, Zerba E (2011) Traslucent pheromone traps increase trapping efficiency of ambrosia beetle Megaplatypus mutatus. Crop Prot 30:745–747
Griffo R, Pesapane G, Funes H, Gonzalez-Audino P, Germinara GS (2012) Diffusione e controllo di platipo in Campania. L’Informatore Agrario 31:66–68
Hasewaga M, Leal WS, Sawada M (1993) Field evaluation of anomala Schondeldti Ohaus (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae) synthetic sex pheromone. J Chem Ecol 19:1453–1459
Kydonieus AF, Beroza M (1982) Controlled Release Technologies. In: Kydonieus AF, Beroza M, Zweig G (eds) Insect suppression with controlled release pheromone systems, vol 1, 1st edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 137–138
Santoro FH (1962) b) La copula en Platypus sulcatus Chapuis (Coleoptera, Platypodidae). Rev Invest Forest 3:25–27
Santoro FH (1963) Bioecologia de Platypus sulcatus Chapuis (Coleoptera: Platypodidae). Rev Invest Forest 4:47–78
Sower LL, Overhulser DL, Daterman GE, Saterman C, Laws DE, Koerber TW (1982) Control of Eucosma sonomana by mating disruption with synthetic sex attractant. J Econ Entomol 75:315–318
Tojo K (1985) Intrinsic release rate from matrix-type drug delivery systems. J Pharmacol Sci 74:685–687
Tremblay E, Espinosa B, Mancini D, Caprio G (2000) Un coleottero proveniente dal Sudamerica minaccia i pioppi. Informatore Agrario 56:89–90
Wood SL (1993) Revision of the genera of Platypodidae (Coleoptera). Great Basin Naturalist 53:259–281
Acknowledgments
We are very grateful to Enrique Prada and Carlos Nicora from Establecimiento ¨Maria Dolores¨, Papel Prensa S.A, Alberti, Buenos Aires, Argentina. This study received financial support from the ANPCyT PICT 2010-305 of Argentina and Prestamo BID SAFO I 103. PGA, MS and CC are members of CONICET.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ceriani-Nakamurakare, E., Slodowicz, M., Carmaran, C. et al. Development of natural waxes dispensers for pheromones and use in mating disruption of the ambrosia beetle Megaplatypus mutatus in poplar (Populus spp) plantations. Agroforest Syst 91, 415–421 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10457-016-9938-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10457-016-9938-7