Abstract
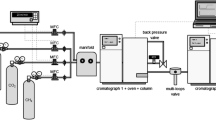
Granular activated carbon (GAC) and more recently activated carbon fibers (ACF) are used for the treatment of volatile organic compounds (VOC) in industrial processes. The purpose of this study was to investigate the adsorption kinetics of ACF to eliminate VOC from polluted air. This approach is carried out by modeling experimental breakthrough curves with two kinds of models: an equilibrium model and a mass transfer model based on a linear driving force (LDF) in conjunction with the Langmuir equilibrium model. The results show the influence of the intraparticle diffusion on the adsorption kinetics of ACF, in spite of their small fiber diameter. Moreover, external diffusion kinetics is fast because of the influence of the large external surface area of ACF on the VOC mass transfer.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- a :
-
External surface area of adsorbent particles per unit adsorbent volume, m2/m3
- C i :
-
Bulk-fluid phase concentration of component i, kg/m3
- C is :
-
Fluid phase concentration of component i on the surface of particles, kg/m3
- C in :
-
Inlet bulk-fluid phase concentration of component i, kg/m3
- \(\overline{C_{i}}\) :
-
Average concentration of component i in the fluid phase inside the particle, kg/m3
- D e :
-
Effective intraparticular diffusion coefficient, m2/s
- D K :
-
Knudsen diffusion, m2/s
- D m :
-
Molecular diffusivity of the component i in the carrier, m2/s
- D z :
-
Axial dispersion coefficient, m2/s
- d f :
-
Fiber diameter, m
- K :
-
Langmuir isotherm parameter, m3/kg
- k f :
-
External diffusion coefficient, m/s
- k p :
-
Intraparticular diffusion parameter, 1/s
- L :
-
Column length, m
- Pe :
-
Peclet number
- \(\overline{q_{i}}\) :
-
Average solid phase concentration of component i (amount adsorbed), kg/kg
- q im :
-
Langmuir isotherm parameter, kg/kg
- q is :
-
Concentration of component i on the surface of the particle, kg/kg
- r f :
-
Fiber radius, m
- T :
-
Temperature, K
- t :
-
Dimensional time
- u :
-
Interstitial velocity of fluid, m/s
- Y :
-
Dimensionless axial coordinate
- z :
-
Axial coordinate, m
- ε :
-
Bed void volume fraction
- ε p :
-
Particle porosity
- ρ p :
-
Density of the adsorbent, kg/m3
- ρ f :
-
Density of the fluid, kg/m3
- τ :
-
Dimensionless time
References
Bird, R.B., Stewart, W.E., Lightfoot, E.N.: Transport Phenomena. Wiley, New York (1960)
Brasquet, C., Le Cloirec, P.: Adsorption onto activated carbon fibers: application to water and air treatments. Carbon 35, 1307–1313 (1997)
Chapra, S.C., Canale, R.P.: Numerical Methods for Engineers. McGraw-Hill, New York (2002)
Cheng, T., Jiang, Y., Zhang, Y., Liu, S.: Prediction of breakthrough curves for adsorption in activated carbon in a fixed bed. Carbon 42(15), 3081–3085 (2004)
Chuang, C.L., Chiang, P.C., Chang, E.E.: Modeling of VOC adsorption onto activated carbon. Chemosphere 53, 17–27 (2003)
Crittenden, J.C., Weber, W.J.: Predictive model for design of fixed-bed adsorbers: single-component model verification. J. Environ. Eng. 104(2), 433–443 (1978)
Finlayson, B.A.: Nonlinear Analysis in Chemical Engineering. McGraw-Hill, New York (1980)
Furuya, E.G., Chang, H.T., Miura, Y., Yokomura, H., Tajima, S., Yamashita, S., Noll, K.E.: Intraparticle mass transport mechanism in activated carbon adsorption of phenols. J. Environ. Eng. 122(10), 909–916 (1996)
Khan, F.K., Ghoshal, A.K.: Removal of volatile organic compounds from polluted air. J. Loss Prevent. Proc. 13, 527–545 (2000)
Langmuir, L.: The adsorption of gases on plane surface of glass, mica and platinium. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 40, 1361–1366 (1918)
Le Cloirec, P.: Les Composés Organiques Volatils dans l’Environnement. Lavoisier, Paris (1998)
Markovska, L., Meshko, V., Noveski, V., Marinkovski, M.: Solid diffusion control of the adsorption of basic dyes onto granular activated carbon and natural zeolite in fixed bed columns. J. Serbian Chem. Soc. 463–475 (2001)
Mocho, P., Bourhis, J.C., Le Cloirec, P.: Regeneration of activated carbon loaded with VOC by induction heating. Carbon 34, 851–856 (1996)
Pré, P., Delage, F., Le Cloirec, P.: A model to predict the adsorber thermal behavior during treatment of volatile organic compounds onto wet activated carbon. Environ. Sci. Technol. 36, 4681–4688 (2002)
Rong, H., Ryu, Z., Zheng, J., Zhang, Y.: Effect of air oxydation of Rayon-based activated carbon fibers on the adsorption behavior for formaldehyde. Carbon 40, 2291–2300 (2002)
Ruthven, D.M.: Principles of Adsorption and Adsorption Processes. Wiley, New York (1984)
Ryu, Z., Zheng, J., Wang, M.: Porous structure of pan-based activated carbon fibers. Carbon 36(4), 427–433 (1998)
Salden, A., Eigenberge, G.: Multifunctional adsorber/reactor concept for waste air purification. Chem. Eng. Sci. 56, 1605–1611 (2001)
Scott, D.S., Dullien, F.A.L.: Diffusion of ideal gases in capillaries and porous solid. AIChE J. 8, 113–118 (1962)
Tien, C.: Adsorption Calculations and Modeling. Butterworth-Heinemann, Washington (1994)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fournel, L., Mocho, P., Brown, R. et al. Modeling breakthrough curves of volatile organic compounds on activated carbon fibers. Adsorption 16, 147–153 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10450-010-9207-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10450-010-9207-4