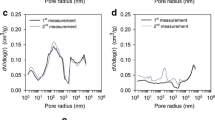
Abstract
Preparation of activated carbon is carried out from an abundant and very cheap waste by-product from wastewater treatment plant: sewage sludge. The first step of preparation consists in a carbonization process under a 10 mL min− 1 nitrogen flow, at 600∘C during 1 hour. The second step is a physical activation, performed with carbon dioxide. The experimental conditions of the activation were optimized using experimental design methodology. Three factors were studied: activation temperature (from 700 to 900∘C), activation duration (from 30 to 120 min) and CO2 flow rate (from 0.7 to 2.9 L min− 1). The porous carbonaceous materials were characterized in terms of physico-chemical and structural properties (specific surface area, pore volumes, surface pH, surface functional groups) and adsorption properties in aqueous and gaseous phase, these characteristics constituting the responses of the experimental design. A surface response methodology enabled to define optimum values for the 3 factors (at 900∘C during 30 min for a CO2 flow rate of 2.9 L min− 1) which involve an adsorbent with a specific surface area of 260 m2 g− 1 and a pore size distribution comprising meso and micropores. Adsorption capacities of organic pollutants (phenol, dyes, VOC) are proportional to the specific surface area, apart from copper adsorption capacities (up to 80 mg g− 1) due to an ion-exchange mechanism with Ca2 + ions present in the raw material. In order to decrease the high ash content in the produced material (51 wt.%) and thus to improve the pore development, carbonized sludge were washed with an acid (HCl, 3 M) at room temperature before the activation step. This oxidation pre-treatment allowed to reach a 410 m2 g− 1 specific surface area with an ash content of 26.4 wt.%.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baçaoui, A., A. Yaacoubi, A. Dahbi, C. Bennouna, R. Phan Tan Luu, F.J. Maldonado-Hodar, J. Rivera-Utrilla, and C. Moreno-Castilla, “Optimization of Conditions for the Preparation of Activated Carbons from Olive-Waste Cakes,” Carbon,39, 425–432 (2001).
Bagreev, A., T.J. Bandosz, and D.C. Locke, “Pore Structure and Surface Chemistry of Adsorbents Obtained by Pyrolysis of Sewage Sludge-Derived Fertilizer,” Carbon, 39, 1971–1979 (2001).
Bagreev, A., J.A. Menendez, I. Dukhno, Y. Tarasenko, and T.J. Bandosz, “Bituminous Coal-Based Activated Carbons Modified with Nitrogen as Adsorbents of Hydrogen Sulfide,” Carbon, 42, 469–476 (2004).
Bansal, R.C., J.B. Donnet, and F. Stoeckli, Active Carbon, Marcel Dekker, New York, 1988.
Boehm, H.P., “Chemical Identification of Surface Groups,” Advances Catalysis, 16, 179–274 (1966).
Box, G.E.P., W.G. Hunter, and J.S. Hunter, Statistics for Experimenters, an Introduction to Design, Data Analysis and Model Building, Wiley, New-York, 1978.
Brasquet, C., B. Rousseau, H. Estrade-Szwarckopf, and P. Le Cloirec, “Observation of Activated Carbon Fibers with SEM and AFM—Correlation with Adsorption Data in Aqueous Solution,” Carbon, 38, 407–422 (2000).
Chiang, P.C. and J.H., You, “Use of Sewage Sludge for Manufactoring Adsorbents,” Can. J Chem. Eng., 65, 922–927 (1987).
Hassler, J.W., Activated Carbon:Industrial, Commercial and Environmental, Chemical Publishing Co. Inc., New York, 1974.
Linares-Solano, A., I. Martin-Gullon, C. Salinas-Martinez de Lecea, and B. Serrano-Talavera, “Activated Carbons from Bituminous Coal:Effect of Mineral Matter Content,” Fuel, 79, 635–643 (2000).
Ricou, P., I. Lecuyer, and P. Le Cloirec, “Experimental Design Methodology Applied to Adsorption of Metallic Ions Onto Fly Ash,” Wat. Res., 35, 965–976 (2001).
Rio, S., C. Faur-Brasquet, L. Le Coq, and P. Le Cloirec, “Preparation and Caracterization of Activated Carbon from Sewage Sludge,” Wat. Sci. Tech., 49(1), 139–146 (2004).
Tay, J.H., X.G. Chen, S. Jeyaseelan, and N. Graham, “A Comparative Study of Anaerobically Digested and Undigested Sewage Sludges in Preparation of Activated Carbons,” Chemosphere, 44, 53–57 (2001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rio, S., Faur-Brasquet, C., Le Coq, L. et al. Production and Characterization of Adsorbent Materials from an Industrial Waste. Adsorption 11 (Suppl 1), 793–798 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10450-005-6025-1
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10450-005-6025-1