Abstract
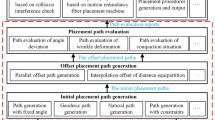
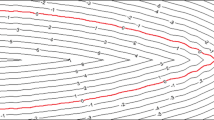
Path planning for fiber placement is one of the research hotspots on composite fiber placement forming technology. The problem how to realize adaptive planning of placement path has great significance in improving the efficiency of automatic fiber placement and shortening product manufacturing period. Firstly, with the numerical simulation of moving interface, the iterative generation and wave propagation of reference path are simulated on the mesh surface, and the mesh dynamic representation (MDR) of fiber placement paths is realized. Then, through improvement on proposed algorithm, an optimal reference path which assures all the fiber directions to meet the requirements of product structure design is sought automatically, and thus adaptive planning of placement path is realized. The simulated automatic fiber placement mechanism can generate a series of equidistant paths through the equidistant propagation of reference path, by which the overlap and gap of fiber tows are avoided, and the quality of fiber placement is improved. Finally, the simple and complex surfaces for fiber placement are analyzed with finite element in the numerical experiment, and the obtained equidistant paths and fiber directions show the efficiency of the proposed method.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Crosky A., Grant C., Kelly D. W., et al: Fiber placement processes for composites manufacture. In: Boisse P. (eds.) Advances in Composites Manufacturing & Process Design, pp. 79-92. Elsevier, Paris France (2015)
Blom, A.W., Stickler, P.B., Gürdal, Z.: Optimization of a composite cylinder under bending by tailoring stiffness properties in circumferential direction. Compos. Part B. 41(2), 157–165 (2010)
Parnas, L., Oral, S., Ceyhan, Ü.: Optimum design of composite structures with curved fiber courses. Compos. Sci. Technol. 63(7), 1071–1082 (2003)
Blom, A.W., Tatting, B.F., Hol, J.M.A.M., Gürdal, Z.: Fiber path definitions for elastically tailored conical shells. Compos. Part B. 40(1), 77–84 (2009)
Lu M., Zhou L. S., Wang X. P.: Optimization of fiber steering in composite laminates using a curve projection algorithm. CMES. 22(16), 1993-1996 (2011)
Yan, L., Wang, F.Z., Shi, Y.Y.: Path planning algorithm for fiber placement based on non-equidistant offset. Acta Aeronautica ET Astronautica Sinica. 36(11), 3715–3723 (2015)
Shirinzadeh, B., Cassidy, G., Oetomo, D., Alici, G., Ang Jr, M.H.: Trajectory generation for open-contoured structures in robotic fiber placement. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 23(4), 380–394 (2007)
Waldhart C., Gurdal Z., Ribbens C.: Analysis of tow placed, parallel fiber, variable stiffness laminates. In: AIAA/ASME/ASCE/AHS/ASC, 37th SDM Conf., Salt Lake City, UT, U.S.A. (2013)
Lu, M., Zhou, L.S., Wang, X.P.: Trajectory generation for cylindrical structures in robotic multi-fiber placement. Acta Aeronautica ET Astronautica Sinica. 32(1), 181–186 (2011)
Dang X. D., Xiao J., Huan D. J.: Realization of parallel equidistant trajectory planning algorithm for automatic fiber placement. WHUJNS. 53(5), 613-616 (2007)
Schueler, K., Miller, J., Hale, R.: Approximate geometric methods in application to the modeling of fiber placed composite. J. Comput. Inf. Sci. Eng. 4(3), 251–256 (2004)
Pei, J.Z., Wang, X.P., Pei, J.Y., et al.: Path planning based on ply orientation information for automatic fiber placement on mesh surface. Appl. Compos. Mater. 10, 1–14 (2018)
Treister, E., Haber, E.: A fast marching algorithm for the factored eikonal equation. J. Comput. Phys. 324, 210–225 (2016)
Mesuda, Y., Inui, S., Horiba, Y.: Virtual draping by mapping. Comput. Ind. 95, 93–101 (2018)
Qian, J., Zhang, Y.T., Zhao, H.K.: Fast sweeping methods for eikonal equations on triangular meshes. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 45(1), 83–107 (2007)
Bacigalupoa, A., Lepidi, M.: Acoustic wave polarization and energy flow in periodic beam lattice materials. Int. J. Solids Struct. 147, 183–203 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2018.05.025
Volpe, F.A., Létourneau, P.D., Zhao, A.: Huygens–Fresnel wavefront tracing. Comput. Phys. Commun. 212, 123–131 (2017)
Yan, J., Cheng, C.: Dynamic representation method of target in remote sensed images based on global subdivision grid. Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium. IEEE. 2014:3097–3100 (2014)
Wang, X., Samulyak, R., Jiao, X., Yu, K.: AP-cloud: adaptive particle-in-cloud method for optimal solutions to Vlasov–Poisson equation. J. Comput. Phys. 316, 682–699 (2016)
Zhou, C.Y.: Finite element analysis and application of SAMCEF, pp. 133–147. Mechanical Industry Press, Beijing (2015)
Acknowledgments
First of all, thank the reviewers for their hard review, and give them the highest respect and heartfelt thanks. Secondly, this work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under grant No. 51575266.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, L., Wang, X., Pei, J. et al. Adaptive Path Planning of Fiber Placement Based on Improved Method of Mesh Dynamic Representation. Appl Compos Mater 26, 785–803 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10443-018-9751-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10443-018-9751-8