Abstract
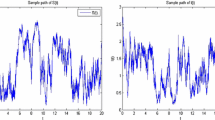
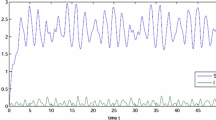
In this paper, we study sufficient conditions for the permanence and ergodicity of a stochastic susceptible-infected-recovered (SIR) epidemic model with Beddington-DeAngelis incidence rate in both of non-degenerate and degenerate cases. The conditions obtained in fact are close to the necessary one. We also characterize the support of the invariant probability measure and prove the convergence in total variation norm of the transition probability to the invariant measure. Some of numerical examples are given to illustrate our results.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, R.M., May, R.M.: Infectious Diseases in Humans: Dynamics and Control. Oxford University Press, Oxford (1991)
Beddington, J.R.: Mutual interference between parasites or predators and its effect on searching efficiency. J. Anim. Ecol. 44, 331–340 (1975)
Bellet, L.R.: Ergodic properties of Markov Process. In: Open Quantum Systems II, pp. 1–39. Springer, Berlin (2006)
Capasso, V., Serio, G.: A generalization of the Kermack-McKendrick deterministic epidemic model. Math. Biosci. 42, 41–61 (1978)
Chen, L., Sun, J.: Global stability and optimal control of an SIRS epidemic model on heterogeneous networks. Physica A 410, 196–204 (2014)
Dang, N.H., Yin, G.: Coexistence and exclusion of stochastic competitive Lotka-Volterra models. J. Differ. Equ. 262, 1192–1225 (2017)
Dang, N.H., Du, N.H., Yin, G.: Existence of stationary distributions for Kolmogorov systems of competitive type under telegraph noise. J. Differ. Equ. 257, 2078–2101 (2014)
DeAngelis, D.L., Goldstein, R.A., O’Neill, R.V.: A model for trophic interaction. Ecology 56, 881–892 (1975)
Dieu, N.T., Nguyen, D.H., Du, N.H., Yin, G.: Classification of asymptotic behavior in a stochastic SIR model. SIAM J. Appl. Dyn. Syst. 15(2), 1062–1084 (2016)
Dieu, N.T., Nguyen, D.H., Du, N.H., Yin, G.: Protection zones for survival of species in random environment. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 76, 1382–1402 (2016)
Du, N.H., Nhu, N.N.: Permanence and extinction of certain stochastic SIR models perturbed by a complex type of noises. Appl. Math. Lett. 64, 223–230 (2017)
Du, N.H., Dang, N.H., Yin, G.: Conditions for permanence and ergodicity of certain stochastic predator-prey models. J. Appl. Probab. 53(1), 187–202 (2016)
Hening, A., Nguyen, D.H.: Coexistence and extinction for stochastic Kolmogorov systems. Ann. Appl. Probab. 28, 1893–1942 (2018)
Hening, A., Nguyen, D.H., Yin, G.: Stochastic population growth in spatially heterogeneous environments: the density-dependent case. J. Math. Biol. 76, 697–754 (2018)
Hethcote, H.W.: The mathematics of infectious diseases. SIAM Rev. 42, 599–653 (2000)
Hieu, N.T.; Du, N.H.; Auger, P.; Dang, N.H.: Dynamical behavior of a stochastic SIRS epidemic model. Math. Model. Nat. Phenom. 10, 56–73 (2015)
Huang, G., Wanbiao, M., Yasuhiro, T.: Global properties for virus dynamics model with Beddington-DeAngelis functional response. Appl. Math. Lett. 22(11), 1690–1693 (2009)
Ichihara, K., Kunita, H.: A classification of the second order degenerate elliptic operators and its probabilistic characterization. Z. Wahrscheinlichkeitstheor. Verw. Geb. 39, 81–84 (1977)
Ikeda, N., Watanabe, S.: Stochastic Differential Equations and Diffusion Processes, 2nd edn. North-Holland Publishing Co., Amsterdam (1989)
Jurdjevic, V.: Geometric Control Theory. Cambridge Studies in Advanced Mathematics, vol. 52. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1997)
Kaddar, A.: On the dynamics of a delayed SIR epidemic model with a modified saturated incidence rate. Electron. J. Differ. Equ. 2009, 133 (2009)
Kaddar, A.: Stability analysis in a delayed SIR epidemic model with a saturated incidence rate. Nonlinear Anal. Model. Control 15(3), 299–306 (2010)
Khas’minskii, R.A.: Ergodic properties of recurrent diffusion processes and stabilization of the Cauchy problem for parabolic equations. Theory Probab. Appl. 5, 179–196 (1960)
Khas’minskii, R.A.: Stochastic Stability of Differential Equations. Springer, Berlin (2012)
Kliemann, W.: Recurrence and invariant measures for degenerate diffusions. Ann. Probab. 15(2), 690–707 (1987)
Lahrouz, A., Settati, A.: Qualitative study of a nonlinear stochastic SIRS epidemic system. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 32(6), 992–1008 (2014)
Lin, Y., Jiang, D., Jin, M.: Stationary distribution of a stochastic SIR model with saturated incidence rate and its asymptotic. Acta Math. Sci. 35(3), 619–629 (2015)
Liu, Z.: Dynamics of positive solutions to SIR and SEIR epidemic models with saturated incidence rates. Nonlinear Anal., Real World Appl. 14, 1286–1299 (2013)
Liu, Q., Chen, Q.: Analysis of the deterministic and stochastic SIRS epidemic models with nonlinear incidence. Physica A 428, 140–153 (2015)
Liu, X., Yang, L.: Stability analysis of an SEIQV epidemic model with saturated incidence rate. Nonlinear Anal., Real World Appl. 13, 2671–2679 (2012)
Lu, Q.: Stability of SIRS system with random perturbations. Physica A 288, 3677–3686 (2009)
Meyn, S.P., Tweedie, R.L.: Stability of Markovian processes III: Foster-Lyapunov criteria for continuous-time processes. Adv. Appl. Probab. 25, 518–548 (1993)
Skorohod, A.V.: Asymptotic Methods in the Theory of Stochastic Differential Equations, vol. 78. Am. Math. Soc., Providence (1989)
Stettner, L.: On the existence and uniqueness of invariant measure for continuous time Markov processes. Technical Report LCDS 86-18, Brown University, Providence, RI (1986)
Yang, Q., Jiang, D., Shi, N., Ji, C.: The ergodicity and extinction of stochastically perturbed SIR and SEIR epidemic models with saturated incidence. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 388(1), 248–271 (2012)
Yorke, J.A., London, W.P.: Recurrent outbreaks of measles, chickenpox and mumps II. Am. J. Epidemiol. 98, 469–482 (1973)
Zhang, T., Zhidong, T.: Pulse vaccination delayed SEIRS epidemic model with saturation incidence. Appl. Math. Model. 32(7), 1403–1416 (2008)
Zhao, Y., Jiang, D.: The threshold of a stochastic SIRS epidemic model with saturated incidence. Appl. Math. Lett. 34, 90–93 (2014)
Zhou, Y., Zhang, W., Yuan, S., Hu, H.: Persistence and extinction in stochastic SIRS models with general nonlinear incidence rate. Electron. J. Differ. Equ. 2014, 42 (2014)
Acknowledgements
We gratefully thank the reviewers and the editor for their positive and helpful suggestions, which help to improve the presentation of the paper. Authors would like to express our gratitude to Nguyen Hai Dang for his valuable comments which helped to improve the paper. This research is funded by Vietnam National Foundation for Science and Technology Development (NAFOSTED) under grant number 101.03-2017.23.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Authors would like to thank Vietnam Institute for Advance Study in Mathematics (VIASM) for supporting and providing a fruitful research environment and hospitality.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Du, N.H., Dieu, N.T. & Nhu, N.N. Conditions for Permanence and Ergodicity of Certain SIR Epidemic Models. Acta Appl Math 160, 81–99 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10440-018-0196-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10440-018-0196-8