Abstract
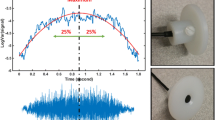
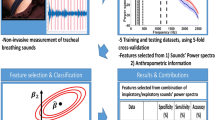
In this article, a novel technique for assessment of obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) during wakefulness is proposed; the technique is based on tracheal breath sound analysis of normal breathing in upright sitting and supine body positions. We recorded tracheal breath sounds of 17 non-apneic individuals and 35 people with various degrees of severity of OSA in supine and upright sitting positions during both nose and mouth breathing at medium flow rate. We calculated the power spectrum, Kurtosis, and Katz fractal dimensions of the recorded signals and used the one-way analysis of variance to select the features, which were statistically significant between the groups. Then, the maximum relevancy minimum redundancy method was used to reduce the number of characteristic features to two. Using the best two selected features, we classified the participant into severe OSA and non-OSA groups as well as non-OSA or mild vs. moderate and severe OSA groups; the results showed more than 91 and 83% accuracy; 85 and 81% specificity; 92 and 95% sensitivity, for the two types of classification, respectively. The results are encouraging for identifying people with OSA and also prediction of OSA severity. Once verified on a larger population, the proposed method offers a simple and non-invasive screening tool for prediction of OSA during wakefulness.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Canosa, M. C., E. H. Pereira, and V. M. Bonillo. Intelligent diagnosis of sleep apnea syndrome. IEEE Trans. Eng. Med. Biol. Mag. 23(2):72–81, 2004.
Caseiro, P., R. Fonseca-Pinto, and A. Andrade. Screening of obstructive sleep apnea using Hilbert-Huang decomposition of oronasal airway pressure recordings. J. Med. Eng. Phys. 32(6):561–568, 2010.
Chesson, A. L., R. A. Ferber, J. M. Fry, et al. Practice parameters for the indications for polysomnography and related procedures. J. Sleep 20:406–422, 1997.
Collop, N. A. Scoring variability between polysomnography technologists in different sleep laboratories. J. Sleep Med. 3(1):43–47, 2002.
Duda, R. O., P. E. Hart, and D. G. Stork. Pattern Classification. New York: Wiley, 2001.
Eastwood, P., I. Szollosi, P. Platt, and D. Hillman. Comparison of upper airway collapse during general anaesthesia and sleep. Lancet 359(9313):1207–1209, 2002.
Fiz, J., J. Morera, J. Abad, et al. Acoustic analysis of vowel emission in obstructive sleep apnea. Chest 104(4):1093–1096, 1993.
Fogel, R., A. Malhotra, and D. White. Pathophysiology of obstructive sleep apnoea/hypopnoea syndrome. Thorax 59(2):159–163, 2004.
Fogel, R., J. Trinder, D. White, et al. The effect of sleep onset on upper airway muscle activity in patients with sleep apnoea versus controls. J. Physiol. 564(2):549–562, 2005.
Gami, A. S., D. E. Olson, and V. K. Somers. Day night pattern of sudden death in obstructive sleep apnea. J. Med. 352(12):1206–1214, 2005.
Gibson, G. J. Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome: underestimated and undertreated. Br. Med. Bull. 72(1):49–65, 2004.
Gnitecki, J., Z. Moussavi, and H. Pasterkamp. Diagnostic potential in state space parameters of lung sounds. J. Med. Biol. Eng. Comp. 46(1):93–99, 2008.
Han, J., Z. Moussavi, T. Szturm, and V. Goodman. Application of nonlinear dynamics to human postural control system. In: Proc. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Conf., 2005, pp. 6885–6888.
Horner, R., S. Shea, J. Mcivor, and A. Guz. Pharyngeal size and shape during wakefulness and sleep in patients with obstructive sleep apnoea. QJM Int. J. Med. 72(2):719–735, 1989.
Huq, S., and Z. Moussavi. Automatic acoustic breath sound detection using only tracheal sounds. In: Proc. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Conf., 2010, pp. 272–275.
Isono, S., J. Remmers, A. Tanaka, Y. Sho, J. Sato, and T. Nishino. Anatomy of pharynx in patients with obstructive sleep apnea and in normal subjects. J. Appl. Physiol. 82(4):1319–1326, 1997.
Johns, M. W. Daytime sleepiness, snoring, and obstructive sleep apnea: the Epworth sleepiness scale. Chest 103:30–36, 1993.
Kashyap, R., L. M. Hock, and T. J. Bowman. Higher prevalence of smoking in patients diagnosed as having obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep Breath. 5(4):167–172, 2001.
Leung, R. S., and T. D. Bradley. Sleep apnea and cardiovascular disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 164:2147–2165, 2001.
Lucas, J., J. Golish, G. Sleeper, and J. A. O’ryan. Home Respiratory Care. Englewood Cliffs: NJ: Appleton & Lange, 1988.
Mcnicholas, W. T. Diagnosis of obstructive sleep apnea in adults. Proc. Am. Thoracic Soc. 5(2):154–160, 2008.
Montazeri, A., and Z. Moussavi, Acoustical screening for obstructive sleep apnea during wakefulness. In: Proc. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Conf., 2010, pp. 3662–3665.
Montgomery, D. C. Design and Analysis of Experiments. John Wiley & Sons Inc, 2008.
Partinen, M., A. Jamieson, and C. Guilleminault. Long-term outcome for obstructive sleep apnea syndrome patients mortality. Chest 94:1200–1204, 1988.
Pasterkamp, H., J. Schäfer, and G. Wodicka. Posture-dependent change of tracheal sounds at standardized flows in patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Chest 110(6):1493–1498, 1996.
Peng, H., F. Long, and C. Ding. Feature selection based on mutual information: criteria of max-dependency, max-relevance, and min-redundancy. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intel. 27(8):1226–1238, 2005.
Ryan, C., and T. D. Bradley. Pathogenesis of obstructive sleep apnea. J. Appl. Physiol. 99(6):2440–2450, 2005.
Ryan, C., A. Lowe, D. Li, and J. Fleetham. Three-dimensional upper airway computed tomography in obstructive sleep apnea. A prospective study in patients treated by uvulopalatopharyngoplasty. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 144(2):428–432, 1991.
Salisbury, J., and Y. Sun. Rapid screening test for sleep apnea using a nonlinear and nonstationary signal processing technique. Med. Eng. Phys. 29(3):336–343, 2007.
Stauffer, J., C. Zwillich, R. Cadieux, et al. Pharyngeal size and resistance in obstructive sleep apnea. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 136(3):623–627, 1987.
Suto, Y., T. Matsuo, T. Kato, et al. Evaluation of the pharyngeal airway in patients with sleep apnea: value of ultrafast MR imaging. Am. J. Roentgenol. 160(2):311–314, 1993.
Varady, P., T. Micsik, S. Benedek, and Z. Benyo. A novel method for the detection of apnea and hypopnea events in respiration signals. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 49(9):936–942, 2002.
West, B., Complexity, Scaling, and Fractals in Biological Signals. Wiley Encyclopedia of Biomedical Engineering, 2006.
Yadollahi, A., and Z. Moussavi. Detailed analysis of the relationship between tracheal breath sounds and airflow in relation to OSA during wake and sleep. In: Proc. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Conf., 2011, pp. 6797–6800.
Yadollahi, A., E. Giannouli, and Z. Moussavi. Sleep apnea monitoring and diagnosis based on pulse oximetry and tracheal sound signals. J. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 48(11):1087–1097, 2010.
Yadollahi, A., and Z. Moussavi. Acoustical flow estimation: review and validation. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Magazine 26(1):56–61, 2007.
Yamauchi, M., S. Tamaki, M. Yoshikawa, et al. Differences in breathing patterning during wakefulness in patients with mixed apnea-dominant vs. obstructive-dominant sleep apnea. Chest 140(1):54–61, 2011.
Younes, M. Role of respiratory control mechanisms in the pathogenesis of obstructive sleep disorders. J. Appl. Physiol. 105(5):1389–1405, 2008.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported in part by the Tele-Communication Research Labs (TRLabs). The authors would like to thank the Misericordia Sleep Disorder Lab’s (Winnipeg, Canada) staff for the invaluable help and assistance in data recording.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor John H. Linehan oversaw the review of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Montazeri, A., Giannouli, E. & Moussavi, Z. Assessment of Obstructive Sleep Apnea and its Severity during Wakefulness. Ann Biomed Eng 40, 916–924 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-011-0456-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-011-0456-5