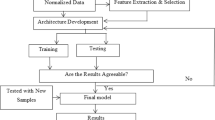
Abstract
Cardiac arrhythmia relating to hypoglycemia is suggested as a cause of death in diabetic patients. This article introduces electrocardiographic (ECG) parameters for artificially induced hypoglycemia detection. In addition, a hybrid technique of swarm-based support vector machine (SVM) is introduced for hypoglycemia detection using the ECG parameters as inputs. In this technique, a particle swarm optimization (PSO) is proposed to optimize the SVM to detect hypoglycemia. In an experiment using medical data of patients with Type 1 diabetes, the introduced ECG parameters show significant contributions to the performance of the hypoglycemia detection and the proposed detection technique performs well in terms of sensitivity and specificity.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexakis, C., et al. Feature extraction and classification of electrocardiogram (ECG) signals related to hypoglycaemia. In: Proceeding of Computers in Cardiology, 2003, pp. 537–540.
Alexakis, C., et al. A knowledge-based electrocardiogram-monitoring system for detection of the onset of nocturnal hypoglycaemia in type 1 diabetic patients. In: Proceeding of Computers in Cardiology, 2006, pp. 5–8.
Astion, M. L., M. H. Wener, R. G. Thomas, G. G. Hunder, and D. A. Bloch. Overtraining in neural networks that interpret clinical data. Clin. Chem. 39:1998–2004, 1993.
Barakat, N. H., A. P. Bradley, and M. N. H. Barakat. Intelligible support vector machines for diagnosis of diabetes mellitus. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 14:1114–1120, 2010.
Batuwita, R., and V. Palade. FSVM-CIL: fuzzy support vector machines for class imbalance learning. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 18:558–571, 2010.
Benhorin, J., et al. Long QT syndrome. New electrocardiographic characteristics. Circulation 82:521–527, 1990.
Burges, C. A tutorial on support vector machines for pattern recognition. Data Min. Knowl. Disc. 2:121–167, 1998.
Can, I., K. Aytemir, S. K¨ose, and A. Oto. Physiological mechanisms influencing cardiac repolarization and QT interval. Card. Electrophysiol. Rev. 6:278–281, 2002.
Christensen, T. F., et al. QT interval prolongation during spontaneous episodes of hypoglycaemia in type 1 diabetes: the impact of heart rate correction. Diabetologia 53:2036–2041, 2010.
Connell, F. A., and J. M. Louden. Diabetes mortality in persons under 45 years of age. Am. J. Public Health 73:1174–1177, 1983.
Darpo, B., et al. Man versus machine: is there an optimal method for QT measurements in thorough QT studies? J. Clin. Pharmacol. 46:598–612, 2006.
del Valle, Y., G. K. Venayagamoorthy, S. Mohagheghi, J. C. Hernandez, and R. G. Harley. Particle swarm optimization: basic concepts, variants and applications in power systems. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 12:171–195, 2008.
Fridericia, L. S. The duration of systole in an electrocardiogram in normal humans and in patients with heart disease. Ann. Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 8:343–351, 2003.
Georgoulas, G., and C. D. Stylios. Predicting the risk of metabolic acidosis for newborns based on fetal heart rate signal classification using support vector machines. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 53:875–884, 2006.
Ghevondian, N., H. T. Nguyen, and S. Colagiuri. A novel fuzzy neural network estimator for predicting hypoglycaemia in insulin-induced subjects. In: Proceeding of the 20th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, 1997, pp. 1371–1374.
Goletsis, Y., C. Papaloukas, D. I. Fotiadis, A. Likas, and L. K. Michalis. Automated ischemic beat classification using genetic algorithms and multicriteria decision analysis. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 51:1717–1725, 2004.
Hastings, G., N. Ghevondian, and H. Nguyen. A self-organising fuzzy estimator for hypoglycaemia monitoring in diabetic patients. In: Proceeding of the 20th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, 1998, pp. 1371–1374.
Heger, G., K. Howorka, H. Thoma, G. Tribl, and J. Zeitlhofer. Monitoring set-up for selection of parameters for detection of hypoglycaemia in diabetic patients. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 34:69–75, 1996.
Ireland, R. H., R. T. C. E. Robinson, S. R. Heller, J. L. B. Marques, and N. D. Harris. Measurement of high resolution ECG QT interval during controlled euglycaemia and hypoglycaemia. Physiol. Meas. 21:295–303, 2000.
Keerthi, S. S., and C.-J. Lin. Asymptotic behaviors of support vector machines with gaussian kernel. Neural Comput. 15:1667–1689, 2003.
Klonoff, D. C. The need for hypoglycemia detection and prevention in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 3:3567–3570, 2001.
Koivikko, M. L., et al. Effects of controlled hypoglycaemia on cardiac repolarisation in patients with type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia 51:426–435, 2008.
Kuo, R. J., S. Y. Hong, and Y. C. Huang. Integration of particle swarm optimization-based fuzzy neural network and artificial neural network for supplier selection. Appl. Math. Model. 34:3976–3990, 2010.
Laitinen, T., et al. Electrocardiographic alterations during hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia in healthy subjects. Ann. Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 13:97–105, 2008.
Lee, S. P., et al. Influence of autonomic neuropathy on QTc interval lengthening during hypoglycemia in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 53:1535–1542, 2004.
Lin, C.-J., and M.-H. Hsieh. Classification of mental task from EEG data using neural networks based on particle swarm optimization. Neurocomputing 72:1121–1130, 2009.
Ling, S. H., N. Nuryani, and H. T. Nguyen. Evolved fuzzy reasoning model for hypoglycaemic detection. In: Proceeding of the 32th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, 2010, pp. 4662–4665.
Ling, S. S. H., and H. T. Nguyen. Genetic-algorithm-based multiple regression with fuzzy inference system for detection of nocturnal hypoglycemic episodes. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 15:308–315, 2011.
Lipponen, J. A., et al. Dynamic estimation of cardiac repolarization characteristics during hypoglycemia in healthy and diabetic subjects. Physiol. Meas. 32:649–660, 2011.
Lubinskj, A., et al. New insight into repolarization abnormalities in patients with congenital long QT syndrome: the increased transmural dispersion of repolarization. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 21:172–175, 1998.
Manriquez, A. I., and Q. Zhang. An algorithm for QRS onset and offset detection in single lead electrocardiogram records. In: Proceeding of the 29th Annual International Conference of the IEEE EMBS, 2007, pp. 541–544.
Marques, J. L. B., et al. Altered ventricular repolarization during hypoglycaemia in patients with diabetes. Diabet. Med. 14:648–654, 1997.
Melgani, F., and Y. Bazi. Classification of electrocardiogram signals with support vector machines and particle swarm optimization. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 12:667–677, 2008.
Moss, A. J. Measurement of the QT interval and the risk associated with QTc interval prolongation: a review. Am. J. Cardiol. 72:B23–B25, 1993.
Murphy, N. P., et al. Prolonged cardiac repolarisation during spontaneous nocturnal hypoglycaemia in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia 47:1940–1947, 2004.
Nasiri, J. A., M. Naghibzadeh, H. S. Yazdi, and B. Naghibzadeh. ECG arrhythmia classification with support vector machines and genetic algorithm. In: 2009 Third UKSim European Symposium on Computer Modeling and Simulation, 2009, pp. 187–192.
Nguyen, H. T., N. Ghevondian, and T. W. Jones. Detection of nocturnal hypoglycemic episodes (natural occurrence) in children with type 1 diabetes using an optimal bayesian neural network algorithm. In: Proceeding of the 30th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, 2008, pp. 1311–1314.
Robinson, R. T. C. E., N. D. Harris, R. H. Ireland, I. A. Macdonald, and S. R. Heller. Changes in cardiac repolarization during clinical episodes of nocturnal hypoglycaemia in adults with Type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia 47:312–315, 2004.
Robinson, R. T. C. E., et al. Mechanisms of abnormal cardiac repolarization during insulin induced hypoglycemia. Diabetes 52:1469–1474, 2003.
Schneider, R., A. Bauer, P. Barthel, and G. Schmidt. Challenge 2006: QT interval measurement. In: Proceeding of Computers in Cardiology, 2006, pp. 325–328.
Schultes, B., et al. Defective awakening response to nocturnal hypoglycemia in patients with Type 1 diabetes mellitus. PLoS Med 4:e69, 2007.
Sophia, H. Z., D. H. Eric, M. L. James, E. G. Richard, and Q. F. Dirk. Philips QT interval measurement algorithms for diagnostic, ambulatory, and patient monitoring ECG Applications. Ann. Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 14:S3–S8, 2009.
Tunbridge, W. M. G. Occasional Survey. Factors contributing to deaths of diabetics under fifty years of age. On behalf of the Medical Services Study Group and British Diabetic Association. Lancet 318:569–572, 1981.
Xue, C. X., R. S. Zhang, M. C. Liu, Z. D. Hu, and B. T. Fan. Study of the quantitative structure-mobility relationship of carboxylic acids in capillary electrophoresis based on support vector machines. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 44:950–995, 2004.
Yan, G.-X., and C. Antzelevitch. Cellular basis for the normal T wave and the electrocardiographic manifestations of the long-QT syndrome. Circulation 98:1928–1936, 1998.
Zhao, L., F. Qian, Y. Yang, Y. Zeng, and H. Su. Automatically extracting T–S fuzzy models using cooperative random learning particle swarm optimization. Appl. Soft. Comput. 10:938–944, 2010.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a grant from the Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation. The authors would like to thank Dr. Nejhdeh Ghevondian, and Assoc. Prof. Timothy Jones for their contribution.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest related to this study and the manuscript presented in this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Leonidas D. Iasemidis oversaw the review of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nuryani, N., Ling, S.S.H. & Nguyen, H.T. Electrocardiographic Signals and Swarm-Based Support Vector Machine for Hypoglycemia Detection. Ann Biomed Eng 40, 934–945 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-011-0446-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-011-0446-7