Abstract
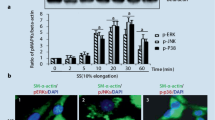
Phenotype transformation of vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) has been reported to be directly influenced by the frequency of mechanical strain. This study explored the effects of different frequencies of mechanical strain on expression of phenotype marker h1-calponin and the possible mechanism. VSMCs were subjected to cyclic strains of 10% elongation at 1 and 2 Hz for 24 h by using a Flexercell strain unit. The protein expression of h1-calponin was assessed by Western blotting and the possible protein kinases involved were evaluated by their specific inhibitor or targeted siRNA ‘knock-down.’ The results showed that cyclic strains modulated the expressions of h1-calponin, phospho-p38, Rac and Rho-guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitor alpha (Rho-GDIα) in nonlinear frequency-dependent manners. This nonlinear frequency-dependent change of h1-calponin expression could be blocked by a specific p38 inhibitor, SB202190. The changed expression of phospho-p38 induced by the frequencies of cyclic strain was reversed by targeted siRNA ‘knock-down’ of Rac, while enhanced by targeted siRNA ‘knock-down’ of Rho-GDIα. These results suggest that the frequency-dependent expression of h1-calponin under cyclic strain is mediated at least partly by the regulation of Rac and Rho-GDIα expression on the activation of p38 pathway.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akhtar N., C. H. Streuli. Rac1 links integrin-mediated adhesion to the control of lactational differentiation in mammary epithelia. J. Cell Biol. 173:781–793, 2006 doi:10.1083/jcb.200601059
Arozarena I., D. Matallanas, P. Crespo Maintenance of CDC42 GDP-bound state by Rho-GDI inhibits MAP kinase activation by the exchange factor Ras-GRF evidence for Ras-GRF function being inhibited by Cdc42-GDP but unaffected by CDC42-GTP. J. Biol. Chem. 276:21878–21884, 2001 doi:10.1074/jbc.M011383200
Bochaton-Piallat M.-L., P. Ropraz, F. Gabbiani, G. Gabbiani. Phenotypic heterogeneity of rat arterial smooth muscle cell clones: implications for the development of experimental intimal thickening. Arterioscler Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 16:815–820, 1996
Brown D. J., E. M. Rzucidlo, B. L. Merenick, R. J. Wagner, K. A. Martin, R. J. Powell. Endothelial cell activation of the smooth muscle cell phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt pathway promotes differentiation. J. Vasc. Surg. 41:509–516, 2005 doi:10.1016/j.jvs.2004.12.024
Bryan B. A., P. A. D’Amore. What tangled webs they weave: Rho-GTPase control of angiogenesis. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 64:2053–2065, 2007 doi:10.1007/s00018-007-7008-z
Cernuda-Morollón E., A. J. Ridley. Rho GTPases and leukocyte adhesion receptor expression and function in endothelial cells. Circ. Res. 98:757–767, 2006 doi:10.1161/01.RES.0000210579.35304.d3
Coso O. A., H. Teramoto, W. F. Simonds, J. S. Gutkind. Signaling from G protein-coupled receptors to c-Jun kinase involves beta gamma subunits of heterotrimeric G proteins acting on a Ras and Rac1-dependent pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 271:3963–3966 1996 doi:10.1074/jbc.271.8.3963
Hori Y., A. Kikuchi, M. Isomura, M. Katayama, Y. Miura, H. Fujioka, K. Kaibuchi, Y. Takai. Post-translational modifications of the C-terminal region of the rho protein are important for its interaction with membranes and the stimulatory and inhibitory GDP/GTP exchange proteins. Oncogene 6:515–522, 1991
Kaspar D., W. Seidl, C. Neidlinger-Wilke, A. Beck, L. Claes, A. Ignatius. Proliferation of human-derived osteoblast-like cells depends on the cycle number and frequency of uniaxial strain. J. Biomech. 35:873–880, 2002 doi:10.1016/S0021-9290(02)00058-1
Kasper B., N. Tidow, D. Grothues, K. Welte. Differential expression and regulation of GTPases (RhoA and Rac2) and GDIs (LyGDI and RhoGDI) in neutrophils from patients with severe congenital neutropenia. Blood 95:2947–2953, 2000
B. A. Kerr, T. Otani, E. Koyama, T. A. Freeman, M. Enomoto-Iwamoto. Small GTPase protein Rac-1 is activated with maturation and regulates cell morphology and function in chondrocytes. Exp. Cell Res. 314: 1301–1312 (2008) doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2007.12.029
Li C., Y. Hu, G. Sturm, G. Wick, Q. Xu. Ras/Rac-dependent activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases in smooth muscle cells stimulated by cyclic strain stress. Arterioscler Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 20:E1–E9, 2000
Li W., Q. Chen, I. Mills, B. E. Sumpio. Involvement of S6 kinase and p38 mitogen activated protein kinase pathways in strain-induced alignment and proliferation of bovine aortic smooth muscle cells. J. Cell Physiol. 195:202–209, 2003 doi:10.1002/jcp.10230
Moldovan L., K. Mythreye, P. J. Goldschmidt-Chermont, L. L. Satterwhite. Reactive oxygen species in vascular endothelial cell motility. Roles of NAD(P)H oxidase and Rac1. Cardiovasc. Res. 71:236–246, 2006 doi:10.1016/j.cardiores.2006.05.003
Morgan K.G., S. S. Gangopadhyay. Invited review: cross-bridge regulation by thin filament-associated proteins. J. Appl. Physiol. 91:953–962, 2001
Morrow D., A. Scheller, Y. A. Birney, C. Sweeney, S. Guha, P. M. Cummins, R. Murphy, D. Walls, E. M. Redmond, P. A. Cahill. Notch-mediated CBF-1/RBP-J{kappa}-dependent regulation of human vascular smooth muscle cell phenotype in vitro. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 289:C1188–C1196, 2005 doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00198.2005
Neuville P., A. Geinoz, G. Benzonana, M. Redard, F. Gabbiani, P. Ropraz, G. Gabbiani. Cellular retinol-binding protein-1 is expressed by distinct subsets of rat arterial smooth muscle cells in vitro and in vivo. Am. J. Pathol. 150:509–521, 1997
Nishimura K., W. Li, Y. Hoshino, T. Kadohama, H. Asada, S. Ohgi, B. E. Sumpio. 2006 Role of AKT in cyclic strain-induced endothelial cell proliferation and survival. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 290:C812–C821 doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00347.2005
Qu M. J., B. Liu, H. Q. Wang, Z. Q Yan, B. R. Shen, Z. L. Jiang. Frequency-dependent phenotype modulation of vascular smooth muscle cells under cyclic mechanical strain. J. Vasc. Res. 44:345–353, 2007 doi:10.1159/000102278
Riha G. M., P. H. Lin, A. B. Lumsden, Q. Yao, C. Chen. Roles of hemodynamic forces in vascular cell differentiation. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 33:772–779, 2005 doi:10.1007/s10439-005-3310-9
Santos M. F., S. A. McCormack, Z. Guo, J. Okolicany, Y. Zheng, L. R. Johnson, G. Tigyi. Rho proteins play a critical role in cell migration during the early phase of mucosal restitution. J. Clin. Invest. 100:216–225, 1997 doi:10.1172/JCI119515
Sotoudeh M., Y. S. Li, N. Yajima, C. C. Chang, T. C. Tsou, Y. Wang, S. Usami, A. Ratcliffe, S. Chien, J. Y. Shyy. Induction of apoptosis in vascular smooth muscle cells by mechanical stretch. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 282: H1709–H1716, 2002
Stegemann J. P., R. M. Nerem. Phenotype modulation in vascular tissue engineering using biochemical and mechanical stimulation. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 31:391–402, 2003 doi:10.1114/1.1558031
Takahashi K., K. Hiwada, T. Kokubu. Isolation and characterization of a 34,000-dalton calmodulin- and F-actin-binding protein from chicken gizzard smooth muscle. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 141:20–26. 1986 doi:10.1016/S0006-291X(86)80328-X
Takano H., I. Komuro, T. Oka, I. Shiojima, Y. Hiroi, T. Mizuno, Y. Yazaki. The Rho family G proteins play a critical role in muscle differentiation. Mol. Cell Biol. 18:1580–1589 1998
Tang L., Z. Lin, Y. M. Li. Effects of different magnitudes of mechanical strain on osteoblasts in vitro. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 344:122–128. 2006 doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.03.123
Tock J., V. Van Putten, K. R. Stenmark, R. A. Nemenoff. Induction of SM-alpha-actin expression by mechanical strain in adult vascular smooth muscle cells is mediated through activation of JNK and p38 MAP kinase. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 301:1116–1121 2003 doi:10.1016/S0006-291X(03)00087-1
Wang H. Q., L. X. Huang, M. J. Qu, Z. Q. Yan, B. Liu, B. R. Shen, Z. L. Jiang. Shear stress protects against endothelial regulation of vascular smooth muscle cell migration in a coculture system. Endothelium 2006 13:171–180 doi:10.1080/10623320600760282
Wang J., H. Chen, A. Seth, C. A. McCulloch. Mechanical force regulation of myofibroblast differentiation in cardiac fibroblasts. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 285:H1871–H1881, 2003
Wille J. J., E. L. Elson, R. J. Okamoto. Cellular and matrix mechanics of bioartificial tissues during continuous cyclic stretch. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 34:1678–1690. 2006 doi:10.1007/s10439-006-9153-1
Wolf A., B. Ackermann, J. Steinmeyer. Collagen synthesis of articular cartilage explants in response to frequency of cyclic mechanical loading. Cell. Tissue. Res. 327:155–166 2007 doi:10.1007/s00441-006-0251-z
Woods A., G. Wang, H. Dupuis, Z. Shao, F. Beier. Rac1 signaling stimulates N-cadherin expression, mesenchymal condensation, and chondrogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 282:23500–23508, 2007 doi:10.1074/jbc.M700680200
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Nos. 30570459 and 10732070.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Ming-Juan Qu and Bo Liu contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qu, MJ., Liu, B., Qi, YX. et al. Role of Rac and Rho-GDI Alpha in the Frequency-dependent Expression of h1-calponin in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells under Cyclic Mechanical Strain. Ann Biomed Eng 36, 1481–1488 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-008-9521-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-008-9521-0