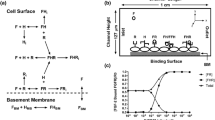
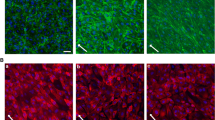
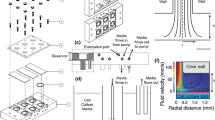
Abstract
The rational design of drug delivery systems requires the ability to predict the environment-specific responses of target cells to the delivered drug. Here we describe the in vitro effects of fluid shear stress, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), and sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) on the migration of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC). Endothelial cell migration into a scrape wound was enhanced in S1P- or VEGF-stimulated HUVEC by the addition of fluid shear stress. In both cases, scrape wound closure rates were near a maximal value that was not exceeded when cells were exposed to all three factors. We also found that cell migration into a scrape wound due to S1P stimulation was correlated with the S1P1 mRNA concentration, in systems where cell migration was not already near maximal. The present work represents our initial steps toward predicting cell migration based upon the activation state of the receptors and enzymes involved in the chemokinetic response. These results also illustrate the importance of context-dependent analysis of cell signaling cascades.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albuquerque, M. L., C. M. Waters, U. Savla, H. W. Schnaper, and A. S. Flozak. Shear stress enhances human endothelial cell wound closure in vitro. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 279:H293–H302, 2000.
Baum, O., L. Da Silva-Azevedo, G. Willerding, A. Wockel, G. Planitzer, R. Gossrau, A. R. Pries, and A. Zakrzewicz. Endothelial NOS is main mediator for shear stress-dependent angiogenesis in skeletal muscle after prazosin administration. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 287:H2300–H2308, 2004.
Bayless, K. J., and G. E. Davis. Sphingosine-1-phosphate markedly induces matrix metalloproteinase and integrin-dependent human endothelial cell invasion and lumen formation in three-dimensional collagen and fibrin matrices. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 312:903–913, 2003.
Borges, E., Y. Jan, and E. Ruoslahti. Platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 bind to the beta 3 integrin through its extracellular domain. J. Biol. Chem. 275:39867–39873, 2000.
Byzova, T. V., C. K. Goldman, N. Pampori, K. A. Thomas, A. Bett, S. J. Shattil, and E. F. Plow. A mechanism for modulation of cellular responses to VEGF: Activation of the integrins. Mol. Cell 6:851–860, 2000.
Callow, A. D., E. T. Choi, J. D. Trachtenberg, S. L. Stevens, D. T. Connolly, C. Rodi, and U. S. Ryan. Vascular permeability factor accelerates endothelial regrowth following balloon angioplasty. Growth Factors 10:223–228, 1994.
Claesson-Welsh, L. Signal transduction by vascular endothelial growth factor receptors. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 31:20–24, 2003.
Davies, P. F., A. Remuzzi, E. J. Gordon, C. F. Dewey, Jr., and M. A. Gimbrone, Jr. Turbulent fluid shear stress induces vascular endothelial cell turnover in vitro. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 83:2114–2117, 1986.
Diamond, S. L., S. G. Eskin, and L. V. McIntire. Fluid flow stimulates tissue plasminogen activator secretion by cultured human endothelial cells. Science 243:1483–1485, 1989.
Dimmeler, S., E. Dernbach, and A. M. Zeiher. Phosphorylation of the endothelial nitric oxide synthase at ser-1177 is required for VEGF-induced endothelial cell migration. FEBS Lett. 477:258–262, 2000.
Dixit, P., D. Hern-Anderson, J. Ranieri, and C. E. Schmidt. Vascular graft endothelialization: Comparative analysis of canine and human endothelial cell migration on natural biomaterials. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 56:545–555, 2001.
Eichholtz, T., K. Jalink, I. Fahrenfort, and W. H. Moolenaar. The bioactive phospholipid lysophosphatidic acid is released from activated platelets. Biochem. J. 291 (3):677–680, 1993.
Elbert, D. L., and J. A. Hubbell. Conjugate addition reactions combined with free-radical cross-linking for the design of materials for tissue engineering. Biomacromolecules 2:430–441, 2001.
Endo, A., K. Nagashima, H. Kurose, S. Mochizuki, M. Matsuda, and N. Mochizuki. Sphingosine 1-phosphate induces membrane ruffling and increases motility of human umbilical vein endothelial cells via vascular endothelial growth factor receptor and CrkII. J. Biol. Chem. 277:23747–23754, 2002.
English, D., Z. Welch, A. T. Kovala, K. Harvey, O. V. Volpert, D. N. Brindley, and J. G. Garcia. Sphingosine 1-phosphate released from platelets during clotting accounts for the potent endothelial cell chemotactic activity of blood serum and provides a novel link between hemostasis and angiogenesis. FASEB J. 14:2255–2265, 2000.
Frangos, J. A., L. V. McIntire, and S. G. Eskin. Shear stress induced stimulation of mammalian cell metabolism. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 32:1053–1060, 1988.
Garcia-Cardena, G., J. Comander, K. R. Anderson, B. R. Blackman, and M. A. Gimbrone, Jr. Biomechanical activation of vascular endothelium as a determinant of its functional phenotype. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 98:4478–4485, 2001.
Gliki, G., C. Wheeler-Jones, and I. Zachary. Vascular endothelial growth factor induces protein kinase C (PKC)-dependent Akt/PKB activation and phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase-mediates PKC delta phosphorylation: Role of PKC in angiogenesis. Cell Biol. Int. 26:751–759, 2002.
Gudi, S. R., C. B. Clark, and J. A. Frangos. Fluid flow rapidly activates G proteins in human endothelial cells. Involvement of G proteins in mechanochemical signal transduction. Circ. Res. 79:834–839, 1996.
Igarashi, J., P. A. Erwin, A. P. Dantas, H. Chen, and T. Michel. VEGF induces S1P1 receptors in endothelial cells: Implications for cross-talk between sphingolipid and growth factor receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 100:10664–10669, 2003.
Jin, Z. G., H. Ueba, T. Tanimoto, A. O. Lungu, M. D. Frame, and B. C. Berk. Ligand- independent activation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 by fluid shear stress regulates activation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Circ. Res. 93:354–363, 2003.
Kwon, Y. G., J. K. Min, K. M. Kim, D. J. Lee, T. R. Billiar, and Y. M. Kim. Sphingosine 1-phosphate protects human umbilical vein endothelial cells from serum-deprived apoptosis by nitric oxide production. J. Biol. Chem. 276:10627–10633, 2001.
Lee, H., E. J. Goetzl, and S. An. Lysophosphatidic acid and sphingosine 1-phosphate stimulate endothelial cell wound healing. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 278:C612–C618, 2000.
Lee, M. J., J. R. Van Brocklyn, S. Thangada, C. H. Liu, A. R. Hand, R. Menzeleev, S. Spiegel, and T. Hla. Sphingosine-1-phosphate as a ligand for the G protein-coupled receptor EDG-1. Science 279:1552–1555, 1998.
Lee, M. J., S. Thangada, J. H. Paik, G. P. Sapkota, N. Ancellin, S. S. Chae, M. Wu, M. Morales-Ruiz, W. C. Sessa, D. R. Alessi, and T. Hla. Akt-mediated phosphorylation of the G protein-coupled receptor EDG-1 is required for endothelial cell chemotaxis. Mol. Cell 8:693–704, 2001.
Lee, O. H., Y. M. Kim, Y. M. Lee, E. J. Moon, D. J. Lee, J. H. Kim, K. W. Kim, and Y. G. Kwon. Sphingosine 1-phosphate induces angiogenesis: Its angiogenic action and signaling mechanism in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 264:743–750, 1999.
Lindner, V., and M. A. Reidy. Expression of VEGF receptors in arteries after endothelial injury and lack of increased endothelial regrowth in response to VEGF. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 16:1399–1405, 1996.
Liu, F., A. D. Verin, P. Wang, R. Day, R. P. Wersto, F. J. Chrest, D. K. English, and J. G. Garcia. Differential regulation of sphingosine-1-phosphate- and VEGF-induced endothelial cell chemotaxis. Involvement of G(ialpha2)-linked Rho kinase activity. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 24:711–719, 2001.
Liu, Y., R. Wada, T. Yamashita, Y. Mi, C. X. Deng, J. P. Hobson, H. M. Rosenfeldt, V. E. Nava, S. S. Chae, M. J. Lee, C. H. Liu, T. Hla, S. Spiegel, and R. L. Proia. Edg-1, the G protein-coupled receptor for sphingosine-1-phosphate, is essential for vascular maturation. J. Clin. Invest. 106:951–961, 2000.
McVerry, B. J., and J. G. Garcia. Endothelial cell barrier regulation by sphingosine 1-phosphate. J. Cell. Biochem. 92:1075–1085, 2004.
Murata, N., K. Sato, J. Kon, H. Tomura, M. Yanagita, A. Kuwabara, M. Ui, and F. Okajima. Interaction of sphingosine 1-phosphate with plasma components, including lipoproteins, regulates the lipid receptor-mediated actions. Biochem. J. 352(Pt 3):809–815, 2000.
Nomura, H., C. Ishikawa, T. Komatsuda, J. Ando, and A. Kamiya. A disk-type apparatus for applying fluid shear stress on cultured endothelial cell. Biorheology 25:461–470, 1988.
Okamoto, H., N. Takuwa, K. Gonda, H. Okazaki, K. Chang, Y. Yatomi, H. Shigematsu, and Y. Takuwa. EDG1 is a functional sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor that is linked via a Gi/o to multiple signaling pathways, including phospholipase C activation, Ca2+ mobilization, Ras-mitogen-activated protein kinase activation, and adenylate cyclase inhibition. J. Biol. Chem. 273:27104–27110, 1998.
Paik, J. H., S. Chae, M. J. Lee, S. Thangada, and T. Hla. Sphingosine 1-phosphate- induced endothelial cell migration requires the expression of EDG-1 and EDG-3 receptors and Rho-dependent activation of alpha vbeta3- and beta 1-containing integrins. J. Biol. Chem. 276:11830–11837, 2001.
Pintucci, G., S. Froum, J. Pinnell, P. Mignatti, S. Rafii, and D. Green. Trophic effects of platelets on cultured endothelial cells are mediated by platelet-associated fibroblast growth factor-2 (FGF-2) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). Thromb. Haemost. 88:834–842, 2002.
Richardson, T. P., M. C. Peters, A. B. Ennett, and D. J. Mooney. Polymeric system for dual growth factor delivery. Nat. Biotechnol. 19:1029–1034, 2001.
Swanson, N., K. Hogrefe, Q. Javed, N. Malik, and A. H. Gershlick. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-eluting stents: In vivo effects on thrombosis, endothelialization and intimal hyperplasia. J. Invasive Cardiol. 15:688–692, 2003.
Takada, Y., C. Kato, S. Kondo, R. Korenaga, and J. Ando. Cloning of cDNAs encoding G protein-coupled receptor expressed in human endothelial cells exposed to fluid shear stress. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 240:737–741, 1997.
Tanimoto, T., Z. G. Jin, and B. C. Berk. Transactivation of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptor Flk-1/KDR is involved in sphingosine 1-phosphate-stimulated phosphorylation of Akt and endothelial nitric-oxide synthase (eNOS). J. Biol. Chem. 277:42997–43001, 2002.
Tolkovsky, A. M., and A. Levitzki. Mode of coupling between the beta-adrenergic receptor and adenylate cyclase in turkey erythrocytes. Biochemistry 17:3795, 1978.
Tolkovsky, A. M., S. Braun, and A. Levitzki. Kinetics of interaction between beta-receptors, GTP protein, and the catalytic unit of turkey erythrocyte adenylate cyclase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 79:213–217, 1982.
Traub, O., B. P. Monia, N. M. Dean, and B. C. Berk. PKC-epsilon is required for mechano-sensitive activation of ERKl/2 in endothelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 272:31251–31257, 1997.
Tzima, E., M. A. del Pozo, S. J. Shattil, S. Chien, and M. A. Schwartz. Activation of integrins in endothelial cells by fluid shear stress mediates Rho-dependent cytoskeletal alignment. EMBO J. 20:4639-4647, 2001.
Tzima, E., M. A. Del Pozo, W. B. Kiosses, S. A. Mohamed, S. Li, S. Chien, and M. A. Schwartz. Activation of Rac1 by shear stress in endothelial cells mediates both cytoskeletal reorganization and effects on gene expression. EMBO J. 21:6791–6800, 2002.
Windh, R. T., M.-J. Lee, T. Hla, S. An, A. J. Barr, and D. R. Manning. Differential coupling of the sphingosine 1-phosphate receptors Edg-1, Edg-3, and H218/Edg-5 to the Gi, Gq, and G12 families of heterotrimeric G proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 274:27351–27358, 1999.
Zeng, H., S. Sanyal, and D. Mukhopadhyay. Tyrosine residues 951 and 1059 of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 (KDR) are essential for vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor-induced endothelium migration and proliferation, respectively. J. Biol. Chem. 276:32714–32719, 2001.
Zeng, H., D. Zhao, and D. Mukhopadhyay. KDR stimulates endothelial cell migration through heterotrimeric G protein Gq/11-mediated activation of a small GTPase RhoA. J. Biol. Chem. 277:46791–46798, 2002.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hughes, S.K., Wacker, B.K., Kaneda, M.M. et al. Fluid Shear Stress Modulates Cell Migration Induced by Sphingosine 1-Phosphate and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor. Ann Biomed Eng 33, 1003–1014 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-005-5756-1
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-005-5756-1