Abstract
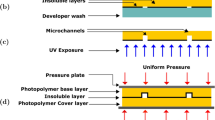
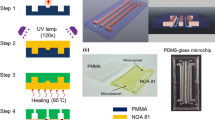
We report a simple and cost-effective method for fabricating integrated electronic-microfluidic devices with multilayer configurations. A CO2 laser plotter was employed to directly write patterns on a transferred polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) layer, which served as both a bonding and a working layer. The integration of electronics in microfluidic devices was achieved by an alignment bonding of top and bottom electrode-patterned substrates fabricated with conventional lithography, sputtering and lift-off techniques. Processes of the developed fabrication method were illustrated. Major issues associated with this method as PDMS surface treatment and characterization, thickness-control of the transferred PDMS layer, and laser parameters optimization were discussed, along with the examination and testing of bonding with two representative materials (glass and silicon). The capability of this method was further demonstrated by fabricating a microfluidic chip with sputter-coated electrodes on the top and bottom substrates. The device functioning as a microparticle focusing and trapping chip was experimentally verified. It is confirmed that the proposed method has many advantages, including simple and fast fabrication process, low cost, easy integration of electronics, strong bonding strength, chemical and biological compatibility, etc.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ai Y, Park S, Zhu J, Xuan X, Beskok A, Qian S (2010) DC electrokinetic particle transport in an L-shaped microchannel. Langmuir 26(4):2937–2944
Alexe M, Gösele U (2004) Wafer bonding: applications and technology. Springer, Berlin
Chen DF, Du H, Li WH, Shu C (2005) Numerical modeling of dielectrophoresis using a meshless approach. J Micromech Microeng 15:1040–1048
Chen DF, Du H, Li WH (2006) A 3D paired microelectrode array for accumulation and separation of microparticles. J Micromech Microeng 16:1162–1169
Cheng I-F, Chang H-C, Hou D, Chang H-C (2007) An integrated dielectrophoretic chip for continuous bioparticle filtering, focusing, sorting, trapping, and detecting. Biomicrofluidics 1:021503. doi:10.1063/1.2723669
Cheng Y, Sugioka K, Midorikawa K (2004) Microfluidic laser embedded in glass by three-dimensional femtosecond laser microprocessing. Opt Lett 29(17):2007–2009
Cheng Y, Xu J, Xu Z, Sugioka K, Midorikawa K (2008) Femtosecond laser integration for biophotonic applications-A “magic brush” in the micro/nano-world. In: Optical fiber communication and optoelectronic exposition and conference 2008. AOE 2008, Asia
Dürr A, Kentsch J, Muller T, Schnelle T, Stelzle M (2003) Microdevices for manipulation and accumulation of micro- and nanoparticles by dielectrophoresis. Electrophoresis 24:722–731
Eddings MA, Johnson MA, Gale BK (2008) Determining the optimal PDMS–PDMS bonding technique for microfluidic devices. J Micromech Microeng 18:067001. doi:10.1088/0960-1317/18/6/067001
El-Ali J, Sorger PK, Jensen KF (2006) Cells on chips. Nature 442:403–411
Ford SM, Davies J, Kar B, Qi SD, Mcwhorter S, Soper SA, Malek CK (1999) Micromachining in plastics using X-ray lithography for the fabrication of micro-electrophoresis devices. J Biomech Eng 121(1):13–21
Harrison DJ, Manz A, Fan Z, Lüdi H, Widmer HM (1992) Capillary electrophoresis and sample injection systems integrated on a planar glass chip. Anal Chem 64(17):1926–1932
Iyer SS, Auberton-Hervé AJ (2002) Silicon wafer bonding technology for VLSI and MEMS. INSPEC, London
Jacobson SC, Hergenröder R, Koutny LB, Warmack RJ, Ramsey JM (1994) Effects of injection schemes and column geometry on the performance of microchip electrophoresis devices. Anal Chem 66(7):1107–1113
Kang Y, Li D, Kalams SA, Eid JE (2008) DC-dielectrophoretic separation of biological cells by size. Biomed Microdev 10:243–249
Kang Y, Li D (2009) Electrokinetic motion of particles and cells in microchannels. Microfluid Nanofluid 6:431–460
Khoshmanesh K, Nahavandi S, Baratchi S, Mitchell A, Kalantar-zadeh K (2010) Dielectrophoretic platforms for bio-microfluidic systems. Biosens Bioelectron 26(5):1800–1814
Kovacs GTA (1998) Micromachined transducers sourcebook. McGraw-Hill, New York
Liu H-B, Gong H-Q (2009) Templateless prototyping of polydimethylsiloxane microfluidic structures using a pulsed CO2 laser. J Micromech Microeng 19:037002. doi:10.1088/0960-1317/19/3/037002
Maharbiz MM, Cohn MB, Howe RT, Horowitz R, Pisano AP (1999) Batch micropackaging by compression-bonded wafer-wafer transfer. In: Proceedings of MEMS Orlando, FL, USA, pp 482–489. doi:10.1109/MEMSYS.1999.746876
McDonald JC, Duffy DC, Anderson JR, Chiu DT, Wu H, Schueller OJA, Whitesides GM (2000) Fabrication of microfluidic systems in poly(dimethylsiloxane). Electrophoresis 21:27–40
Pethig R (2010) Review article—dielectrophoresis: status of the theory, technology, and applications. Biomicrofluidics 4:022811. doi:10.1063/1.3456626
Plecis A, Chen Y (2007) Fabrication of microfluidic devices based on glass–PDMS–glass technology. Microelectron Eng 84:1265–1269
Quake SR, Scherer A (2000) From micro- to nanofabrication with soft materials. Science 290:1536–1540
Roberts MA, Rossier JS, Bercier P, Girault H (1997) UV laser machined polymer substrates for the development of microdiagnostic systems. Anal Chem 69(11):2035–2042
Schmidt H, Ihlemann J, Luther K, Troe J (1999) Modeling of velocity and surface temperature of the moving interface during laser ablation of polyimide and poly (methylmethacrylate). Appl Surf Sci 138–139:102–106
Schmidt MA (1998) Wafer-to-wafer bonding for microstructure formation. Proc IEEE 86(8):1575–1585
Snakenborg D, Klank H, Kutter JP (2004) Microstructure fabrication with a CO2 laser system. J Micromech Microeng 14:182–189
Song H, Bennett DJ (2010) A semi-analytical approach using artificial neural network for dielectrophoresis generated by parallel electrodes. J Electrostat 68:49–56
Sparks D, Queen G, Weston R, Woodward G, Putty M, Jordan L, Zarabadi S, Jayakar K (2001) Wafer-to-wafer bonding of nonplanarized MEMS surfaces using solder. J Micromech Microeng 11:630–634
Tong Q-Y, Gösele U (1999) Semiconductor wafer bonding: science and technology. Wiley, New York
Ueno K, Kitagawa F, Kim H-B, Tokunaga T, Matsuo S, Misawa H, Kitamura N (2000) Fabrication and characteristic responses of integrated microelectrodes in polymer channel chip. Chem Lett 29(8):858–859
Whitesides GM (2006) The origins and the future of microfluidics. Nature 442:368–373
Wu H, Huang B, Zare RN (2005) Construction of microfluidic chips using polydimethylsiloxane for adhesive bonding. Lab Chip 5:1393–1398
Wu H, Odom TW, Chiu DT, Whitesides GM (2003) Fabrication of complex three-dimensional microchannel systems in PDMS. J Am Chem Soc 125(2):554–559
Xia Y, Whitesides GM (1998) Soft lithography. Annu Rev Mater Sci 28:153–184
Zhang M, Wu J, Wang L, Xiao K, Wen W (2010) A simple method for fabricating multi-layer PDMS structures for 3D microfluidic chips. Lab chip 10:1199–1203
Acknowledgments
The author (W.H. Li) wishes to thank Australian government to offer an Australian Endeavour Research Fellowship (1994_2011) to enhance research collaboration with Prof. W. Wen. This project is also partially supported by University of Wollongong through a UIC grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, M., Li, S., Wu, J. et al. A simple and cost-effective method for fabrication of integrated electronic-microfluidic devices using a laser-patterned PDMS layer. Microfluid Nanofluid 12, 751–760 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-011-0917-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-011-0917-z