Abstract
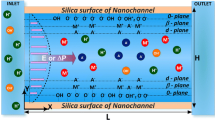
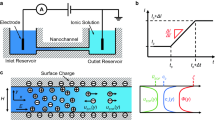
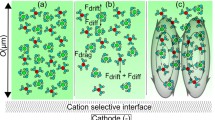
This study fabricates a cross-form microchip in which the two side channels are attached to the main channel via a nanochannel bridge. Ionic depletion and enrichment zones are established on the anodic and cathodic sides of the nanochannel. Results show that the low conductivity within the depletion zone induces a rapid electroosmotic flow, which in turn prompts the generation of vortex flow structures within the depletion zone. Both the lengthening of the depletion bulk charge layer and decrease in length of the diffusion layer as the applied voltage is increased are also demonstrated in this study.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ben Y, Chang HC (2002) Nonlinear Smoluchowski slip velocity and micro-vortex generation. J Fluid Mech 461:229–238
Chang C-C, Yang R-J (2004) Computational analysis of electrokinetically driven flow mixing in microchannels with patterned blocks. J Micromech Microeng 14:550–558
Chen C-H, Lin H, Lele SK, Santiago JG (2005) Convective and absolute electrokinetic instability with conductivity gradients. J Fluid Mech 524:263–303
Cheng L-J, Guo LJ (2007) Rectified ion transport through concentration gradient in homogeneous silica. Nanochannels. Nano Lett 7:3165–3171
Daiguji H, Yang P, Szeri AJ, Majumdar A (2004) Electrochemomechanical energy conversion in nanofluidic channels. Nano Lett 4:2315–2321
Dukhin SS (1991) Electrokinetic phenomena of the second kind and their applications. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 35:173–196
Dukhin SS, Mishchuk NA (1993) Intensification of electrodialysis based on electroosmosis of the second kind. J Memb Sci 79:199–210
Huang K-D, Yang R-J (2007) Electrokinetic behaviour of overlapped electric double layers in nanofluidic channels. Nanotech 18:115701
Hunter RJ (1981) Zeta potential in colloid science. Academic Press, New York
Karnik R, Fan R, Yue M, Li D, Yang P, Majumdar A (2005) Electrostatic control of ions and molecules in nanofluidic transistors. Nano Lett 5:943–948
Kim SJ, Wang Y-C, Lee JH, Jang H, Han J (2007) Concentration polarization and nonlinear electrokinetic flow near a nanofluidic channel. Phys Rev Lett 99:044501
Kirby BJ, Hasselbrink Jr EF (2004) Zeta potential of microfluidic substrates: 1. theory, experimental techniques, and effects on separations. Electrophoresis 25:187–202
Kuo TC, Cannon Jr DM, Shannon MA, Bohn PW, Sweedler JV (2003) Hybrid three-dimensional nanofluidic/microfluidic devices using molecular gates. Sens Actuators A 102:223–233
Mishchuk NA (1999) The role of water dissociation in concentration polarization of disperse particles. Colloids Surf A 159:467–475
Pan Y-J, Lin J-J, Luo W-J, Yang R-J (2006) Sample flow switching techniques on microfluidic chips. Biosens Bioelectron 21:1644–1648
Plecis A, Schoch RB, Renaud P (2005) Ionic transport phenomena in nanofluidics: experimental and theoretical study of the exclusion-enrichment effect on a chip. Nano Lett 5:1147–1155
Probstein RF (1994) Physicochemical hydrodynamics: an introduction. Wiley, New York
Pu Q, Yun J, Temkin H, Liu S (2004) Ion-enrichment and ion-depletion effect of nanochannel structures. Nano Lett 4:1099–1103
Rubinstein I, Shtilman L (1979) Voltage against current curves of cation exchange membranes. J Chem Soc Faraday Trans 75:231–246
Stein D, Kruithof M, Dekker C (2004) Surface-charge-governed ion transport in nanofluidic channels. Phys Rev Lett 93:035901
Takhistov P, Duginova K, Chang HC (2003) Electrokinetic mixing vortices due to electrolyte depletion at microchannel junctions. J Colloid Interface Sci 263:133–143
Wang Y-C, Stevens AL, Han J (2005) Million-fold preconcentration of proteins and peptides by nanofluidic filter. Anal Chem 77:4293–4299
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support provided to this study by the National Science Council of Taiwan under Grant no. NSC-96-2628-E-006-162-MY3.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM1 (MPG 6940 kb)
ESM2 (MPG 5970 kb)
ESM3 (MPG 7273 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, KD., Yang, RJ. Formation of ionic depletion/enrichment zones in a hybrid micro-/nano-channel. Microfluid Nanofluid 5, 631–638 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-008-0281-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-008-0281-9