Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the efficacy of vitrectomy with internal limiting membrane (ILM) peeling and SF6 gas tamponade for macular holes without face-down positioning.
Methods
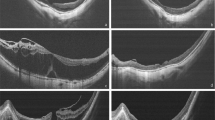
Twenty-one eyes of 21 consecutive patients undergoing pars plana vitrectomy with indocyanine green-assisted ILM peeling and 20% SF6 gas tamponade without face-down positioning were included in this study. Biomicroscopy and optical coherence tomography were used to assess macular hole closure. Pre- and postoperative visual acuities (VAs) were compared.
Results
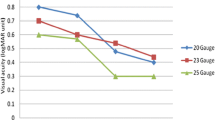
Among the 21 eyes, five (23.8%) had stage 2, 11 (52.4%) stage 3, and five (23.8%) stage 4 macular holes. Mean macular hole size was 0.35 disc diameters. The macular holes had been present for an average of 2.3 months. Twenty eyes (95.2%) were phakic, and one (4.8%) was pseudophakic. Nineteen of the 21 holes (90.5%) initially closed. The final closure rate was 100%, and no eyes showed reopening. Preoperative mean VA (logMAR) was 0.65, and mean VA had significantly improved to 0.46 at 1 month and to 0.42 at 3 months after surgery (P < 0.0001, repeated measures analysis of variance).
Conclusion
Vitrectomy with ILM peeling and SF6 gas tamponade for macular holes without face-down positioning achieved favorable anatomical and functional results.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kelly NE, Wendel RT. Vitreous surgery for idiopathic macular holes. Result of a pilot study. Arch Ophthalmol 1991;109:654–659.
Holekamp NM, Meredith TA, Landers MB, et al. Ulnar neuropathy as a complication of macular hole surgery. Arch Ophthalmol 1999;117:1607–1610.
Treister G, Wygnanski T. Pressure sore in a patient who underwent repair of a retinal tear with gas injection. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 1996;234:657–658.
Park DW, Sipperley JO, Sneed SR, et al. Macular hole surgery with internal-limiting membrane peeling and intravitreous air. Ophthalmology 1999;106:1392–1398.
Merkur AB, Tuli R. Macular hole repair with limited nonsupine positioning. Retina 2007;27:365–369.
Tranos PG, Peter RN, Nath R, et al. Macular hole surgery without prone positioning. Eye 2007;21:802–806.
Rubinstein A, Ang A, Patel CK. Vitrectomy without postoperative posturing for idiopathic macular holes. Clin Experiment Ophthalmol 2007;35:458–461.
Gass JDM. Reappraisal of biomicroscopic classification of stages of development of macular hole. Am J Ophthalmol 1995;119:752–759.
Tornambe PE, Poliner LS, Grote K. Macular hole surgery without face-down positioning. A pilot study. Retina 1997;17:179–185.
Simcock PR, Scalia S. Phacovitrectomy without prone posture for full thickness macular holes. Br J Ophthalmol 2001;85:1316–1319.
Hasler PW, Prünte C. Early foveal recovery after macular hole surgery. Br J Ophthalmol 2008;92:645–649.
Sato Y, Isomae T. Macular hole surgery with internal limiting membrane removal, air tamponade, and 1-day prone positioning. Jpn J Ophthalmol 2003;47:503–506.
Guillaubey A, Malvitte L, Lafontaine PO, et al. Comparison of face-down and seated position after idiopathic macular hole surgery: a randomized clinical trial. Am J Ophthalmol 2008;146:128–134.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Yagi, F., Sato, Y., Takagi, S. et al. Idiopathic macular hole vitrectomy without postoperative face-down positioning. Jpn J Ophthalmol 53, 215–218 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10384-008-0642-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10384-008-0642-7