Abstract
The ‘road-effect zone’ is a concept developed to describe the impact of road construction on the surrounding area. Although many aspects of the road-effect zone have been investigated, the road-effect zone on soil properties (pH, bulk density, soil moisture, electrical conductivity, organic matter (%), C (%), total N (%), available Na, Ca, Mg, P, and K), light regimes (leaf area index and canopy cover), and a Raunkiaer’s life-form classification of plants remains poorly understood, especially in oriental beech (Fagus orientalis Lipsky) forests. Hence, the main aims of this research were to estimate the extent of the road-effect zone and to identify the main environmental changes due to forest roads. Specifically, we aimed to evaluate road-effects on: (1) the composition of herbaceous species and tree regeneration (up to 100 m distance from the forest road); (2) the light regime; and (3) soil properties, potentially related to changes in ecosystem functions and composition. We observed that forest roads can have significant impacts on soil, stand characteristics, and vegetation composition. The estimated road-effect zone extended up to 30 m from the road edge. Landscape planners should be aware that road-effect zones can potentially influence the ecology and environmental conditions of an area up to 30 m from the road edge.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbasian P, Attarod P, Sadeghi SMM, Van Stan II JT, Hojjati SM (2015) Throughfall nutrients in a degraded indigenous Fagus orientalis forest and a Picea abies plantation in the of North of Iran. For Syst 24(3):035. https://doi.org/10.5424/fs/2015243-06764
Ahmadi MT (2015) Rainfall interception and nutrient leaching from canopy and organic layers in a natural broad-leaved deciduous forest and a Norway spruce plantation in the Caspian region, Mazandaran province. Ph.D. dissertation, Department of Forestry and Forest Economics, University of Tehran
Amaranthus MP, Rice RM, Barr NR, Ziemer RR (1985) Logging and forest roads related to increased debris slides in southwestern Oregon. J For 83(4):229–233
Ampoorter E, Van Nevel L, De Vos B, Hermy M, Verheyen K (2010) Assessing the effects of initial soil characteristics, machine mass and traffic intensity on forest soil compaction. For Ecol Manag 260:1664–1676
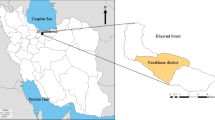
Anonymous, Department of Forestry and Forest Economic (1995) First revision of Forest Management Plan for Namkhaneh District in Kheyrud Educational and Research Forest. Faculty of Natural Resources. University of Tehran, Iran
Ashman MR, Puri G (2002) Essential soil science. Blackwell Science, Oxford
Auerbach NA, Walker MD, Walker DA (1997) Effects of roadside disturbance on substrate and vegetation properties in arctic tundra. Ecol Appl 7:218–235
Avon C, Dumas Y, Bergès L (2013) Management practices increase the impact of roads on plant communities in forests. Biol Conserv 159:24–31
Benítez-López A, Alkemade R, Verweij PA (2010) The impacts of roads and other infrastructure on mammal and bird populations: a meta-analysis. Biol Conserv 143:1307–1316
Bernhardt-Römermann M, Kirchner M, Kudernatsch T, Jakobi G, Fischer A (2006) Changed vegetation composition in coniferous forests near to motorways in Southern Germany: the effects of traffic-born pollution. Environ Pollut 143:572–581
Bignal KL, Ashmore MR, Headley AD, Stewart K, Weigert K (2007) Ecological impacts of air pollution from road transport on local vegetation. Appl Geochem 22:1265–1271
Boissier PE (1867) Flora orientalis, 5 vols. and Suppl. Basel-Geneva-Lyon
Bolling JD, Walker LR (2000) Plant and soil recovery along a series of abandoned desert roads. J Arid Environ 46(1):1–24
Bower CA, Reitemeier RF, Fireman M (1952) Exchangeable cation analysis of saline and alkali soils. Soil Sci 73:251–261
Bremner JM, Mulvaney CS (1982) Nitrogen—total. In: Page AL, Miller RH, Keeney RR (eds) Methods of soil analysis, part 2, 2nd edn. American Society of Agronomy, Madison, pp 595–624
Cain SA (1950) Life forms and phytoclimate. Bot Rev 16:1–32
Christen DC, Matlack GR (2009) The habitat and conduit functions of roads in the spread of three invasive plant species. Biol Invasions 11(2):453–465
Coe D, Tribe NI, Bellingham WA (2004) The hydrologic impacts of roads at varying spatial and temporal scales: a review of published literature as of April 2004. Washington State Department of Natural Resources
Coker GWR (2006) Leaf area index in closed canopies: an indicator of site quality. Master thesis in Forestry Science, University of Canterbury
Cowling SA, Field CB (2003) Environmental control of leaf area production: implications for vegetation and land-surface modeling. Glob Biogeochem Cycles. https://doi.org/10.1029/2002GB001915
Davis PH (1942) Flora of Turkey and the East Aegean Islands. Edinburgh University Press, Edinburgh
Delgado JD, Arroyo NL, Arevalo JR, Fernandez-Palacios JM (2007) Edge effects of roads on temperature, light, canopy cover, and canopy height in laurel and pine forests (Tenerife, Canary Islands). Landsc Urban Plan 81(4):328–340
Deljouei A, Abdi E, Majnounian B (2014) Changes of trees regeneration diversity in main and secondary roads of Hyrcanian forests, Iran. J Inst Nat Appl Sci 19(1–2):30–35
Deljouei A, Abdi E, Marcantonio M, Majnounian B, Amici V, Sohrabi H (2017a) The impact of forest roads on understory plant diversity in temperate hornbeam-beech forests of Northern Iran. Environ Monit Assess. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-6105-1
Deljouei A, Abdi E, Hasanvand M, Sadeghi SMM, Kaybondori S (2017b) Zone effect of secondary forest roads on flora, life forms, and chorology of plants. For Res Dev 3(1):77–89 (In Persian)
Demir M, Makineci E, Yilmaz E (2007) Investigation of timber harvesting impacts on herbaceous cover, forest floor and surface soil properties on skid road in an oak (Quercus petrea L.) stand. Build Environ 42(3):1194–1199
Ehrendorfer F (1965) Uber stammesgeschichtliche Differenzierungsmuster bei den Dipsacaceae. Ber Dtsch Bot Ges 77:83–94
Enoki T, Kusumoto B, Igarashi S, Tsuji K (2014) Stand structure and plant species occurrence in forest edge habitat along different aged roads on Okinawa Island, southwestern Japan. J For Res 19(1):97–104
Flechard CR, Nemitz E, Smith RI, Fowler D, Vermeulen AT, Bleeker A, Erisman JW, Simpson D, Zhang L, Tang YS, Sutton MA (2011) Dry deposition of reactive nitrogen to European ecosystems: a comparison of inferential models across the NitroEurope network. Atmos Chem Phys 11(6):2703–2728
Flory SL, Clay K (2006) Invasive shrub distribution varies with distance to roads and stand age in eastern deciduous forests in Indiana, USA. Plant Ecol 184:131–141
Forman RTT, Alexander LE (1998) Roads and their major ecological effects. Ann Rev Ecol Syst 29(1):207–231
Forman RTT, Deblinger RD (2000) The ecological road-effect zone of a Massachusetts (U.S.A.) Suburban Highway. Conserv Biol 14:36–46
Forman RTT, Lauren AE (1998) Roads and their major ecological effects. Ann Rev Eco Ecol Syst 29:207–231
Forman RTT, Sperling D, Bissonette JA, Clevenger AP, Cutshall AP, Dale VH, Fahrig L, France R, Goldman CR, Heanue K, Jones JA, Swanson FJ, Turrentine T, Winter TC (2003) Road ecology-science and solutions. Island Press, Washington, p 504
Frazer GW, Canham CD, Lertzman KP (1999) Gap light analyzer (GLA), version 2.0: imaging software to extract canopy structure and gap light transmission indices from true-colour fisheye photographs, users manual and program documentation, vol 36. Simon Fraser Univ Burn Br Columbia Inst Ecosyst Stud, Millbrook New York. http://rem.sfu.ca/forestry/downloads/Files/GLAV2UsersManual.pdf. Accessed 20 Dec 2016
Godefroid S, Koedam N (2004) The impact of forest paths upon adjacent vegetation: effects of the path surfacing material on the species composition and soil compaction. Biol Conserv 119(3):405–419
Grace IIIJM, Clinton BD (2007) Protecting soil and water in forest road management. Trans ASABE 50(5):1579–1584
Greenberg CH, Crownover SH, Gordon DR (1997) Roadside soils: a corridor for invasion of xeric scrub by nonindigenous plants. Nat Areas J 17:99–109
Guariguata MR, Dupuy JM (1997) Forest regeneration in abandoned logging roads in Lowland Costa Rica. Biotropica 29(1):15–28
Härdtle W, Von Oheimb G, Westphal C (2003) The effects of light and soil conditions on the species richness of the ground vegetation of deciduous forests in northern Germany (Schleswig–Holstein). For Ecol Manag 182:327–338
Harper KA, Mascarua-Lopez L, Macdonald SE, Drapeau P (2007) Interaction of edge influence from multiple edges: examples from narrow corridors. Plant Ecol 192:71–84
Heninger R, Scott W, Dobkowski A, Miller R, Anderson H, Duke S (2002) Soil disturbance and 10-year growth response of coast Douglas-fir on nontilled and tilled skid trails in the Oregon Cascades. Can J For Res 32:233–246
Hill W, Pickering CM (2006) Vegetation associated with different walking track types in the Kosciuszko alpine area, Australia. J Environ Manag 78:24–34
Homer CD, Pratt PF (1961) Methods of analysis for soils, plants and waters. University of California, Agricultural Sciences Publications, Berkeley
Honnay O, Verheyen K, Hermy M (2002) Permeability of ancient forest edges for weedy plant species invasion. For Ecol Manag 161:109–122
Horn HS (1971) The adaptive geometry of trees. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Houssard C, Escarré J, Bomane F (1980) Development of species diversity in some Mediterranean plant communities. Vegetation 43(1–2):59–72
Kapos V (1989) Effects of isolation on the water status of forest patches in the Brazilian Amazon. J Trop Ecol 5(2):173–185
Knapp HD (2005) Die globale Bedeutung der Kaspischen Wälder. In: Nosrati K, Marvie Mohadjer R, Bode W, Knapp HD (eds) Schutz der Biologischen Vielfalt und integriertes Management der Kaspischen Wälder (nordiran). Bundesamt für Naturschutz, Bonn, pp 45–70
Kucharik CJ, Norman JM, Gower ST (1999) Characterization of radiation regimes in nonrandom forest canopies: theory, measurements, and a simplified modeling approach. Tree Physiol 19:695–706
Lamont BB, Whitten VA, Witkowski ETF, Rees RG, Enright NJ (1994) Regional and local (road verge) effects on size and fecundity in Banksia menziesii. Aust J Ecol 19:197–205
Laurance WF, Cochrane MA, Bergen S, Fearnside PM, Delamonica P, Barber C, D’Angelo S, Fernandes T (2001) The future of the Brazilian Amazon. Science 291(5503):438–439
Lavoie C, Jodoin Y, de Merlis AG (2007) How did common ragweed (Ambrosia artemisiifolia L.) spread in Quebec? A historical analysis using herbarium records. J Biogeogr 34(10):1751–1761
Lee MA, Davies L, Power SA (2012) Effects of roads on adjacent plant community composition and ecosystem function: an example from three calcareous ecosystems. Environ Pollut 163:273–280
Levey DJ, Bolker BM, Tewksbury JJ, Sargent SS, Haddad NM (2005) Effects of landscape corridors on seed dispersal by birds. Science 309(5731):146–148
Li YH, Hu YM, Chang Y, Li XZ, Bu RC, Hu CH, Wang CL (2010) Effect zone of forest road on plant species diversity in Great Hing’an Mountians. Chin J Appl Ecol 21(5):1112–1119
Lloyd RA, Lohse KA, Ferré TPA (2013) Influence of road reclamation techniques on forest ecosystem recovery. Front Ecol Environ 11(2):75–81
Lonsdale WM, Lane AM (1994) Tourist vehicles as vectors of weed seeds in Kakadu National Park, northern Australia. Biol Conserv 69:277–283
Lotfalian M, RiahiFar N, Fallah A, Hodjati SM (2012) Effects of roads on understory plant communities in a broadleaved forest in Hyrcanian zone. J For Sci 58(10):446–455
Luo T, Pan Y, Ouyang H, Shi P, Luo J, Yu Z, Lu Q (2004) Leaf area index and net primary productivity along subtropical to alpine gradients in the Tibetan Plateau. Glob Ecol Biogeogr 13(4):345–358
Ma Y, Van Dam RL, Jayawickreme DH (2014) Soil moisture variability in a temperate deciduous forest: insights from electrical resistivity and throughfall data. Environ Earth Sci 72:1367–1381
Makineci E, Demir M, Yilmaz E (2007) Long-term harvesting effects on skid road in a fir (Abies bornmulleriana Mattf.) plantation forest. Build Environ 42:1538–1543
Marcantonio M, Rocchini D, Geri F, Bacaro G, Amici V (2013) Biodiversity, roads, & landscape fragmentation: two Mediterranean cases. Appl Geogr 42:63–72
Mehlich A (1976) New buffer pH method for rapid estimation of exchangeable acidity and lime requirement of soils. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 7:637–652
Mera AG, Hagen MA, Oreliana JAV (1999) Aerophyte, a new life form in Raunkiaer’s classification? J Veg Sci 10:65–68
Metzger F, Schultz J (1984) Understory response to 50 years of management of a northern hardwood forest in Upper Michigan. Am Midl Nat 112:209–223
MRUD (Ministry of Road and Urban Development) (2014) Assessment of road construction in Iran (in Persian)
Munguía-Rosas MA, Montiel S (2014) Patch size and isolation predict plant species density in a naturally fragmented forest. PLoS ONE 9(10):e111742
Muskett CJ, Jones MP (1981) Soil respiratory activity in relation to motor vehicle pollution. Water Air Soil Pollut 23:231–242
Naghdi R, Bagheri I, Basiri R (2010) Soil disturbances due to machinery traffic on steep skid trail in the north mountainous forest of Iran. J For Res 21:497–502
Neher DA, Asmussen D, Lovell ST (2013) Roads in northern hardwood forests affect adjacent plant communities and soil chemistry in proportion to the maintained roadside area. Sci Total Environ 449:320–327
Nepstad D, Carvalho G, Barros AC, Alencar A, Capobianco JP, Bishop J, Moutinho P, Lefebvre P, Silva UL, Prins E (2001) Road paving, fire regime feedbacks, and the future of Amazon forests. For Ecol Manag 154(3):395–407
Normandin V, Kotuby-Amacher J, Miller RO (1998) Modification of the ammonium acetate extractant for the determination of exchangeable cations in calcareous solis. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 29(11–14):1785–1791
Olander LP, Scatena FN, Silver WL (1998) Impacts of disturbance initiated by road construction in a subtropical cloud forest in the Luquillo experimental forest, Puerto Rico. For Ecol Manag 109:33–49
Osma E, Özyiğit İİ, Altay V, Serin M (2010) Urban vascular flora and ecological characteristics of Kadıköy district, Istanbul, Turkey. Maejo Int J Sci Technol 4(1):64–87
Pauchard A, Alaback PB (2006) Edge type defines alien plant species invasions along Pinus contorta burned, highway and clearcut forest edges. For Ecol Manag 223(1):327–335
Pec GJ, Karst J, Sywenky AN, Cigan PW, Erbilgin N, Simard SW, Cahill JF (2015) Rapid increases in forest understory diversity and productivity following a mountain pine beetle (Dendroctonus ponderosae) outbreak in pine forests. PLoS ONE 10:e0124691
Planchais I, Sinoquet H (1998) Foliage determinants of light interception in sunny and shaded branches of Fagus sylvatica (L.). Agric For Meteorol 89:241–253
Raunkiaer C (1934) The life forms of plants and statistical plant geography. Clarendon Press, Oxford
Rechinger KH (1963–1998) Flora Iranica, vol 1–173. Akademisch Druck-U Verlagsanstalt, Graz
Rentch JS, Fortney RH, Stephenson SL, Adams HS, Grafton WN, Anderson JT (2005a) Vegetation-site relationships of roadside plant communities in West Virginia, USA. J Appl Ecol 42:129–138
Rentch JS, Fortney RH, Stephenson SL, Adams HS, Grafton WN, Anderson JT (2005b) Vegetation-site relationships of roadside plant communities in West Virginia, USA. J Appl Ecol 42(1):129–138
Roovers P, Baeten S, Hermy M (2004) Plant species variation across path ecotones in a variety of common vegetation types. Plant Ecol 170:107–119
Ross DS, Ketterings Q (1995) Recommended methods for determining soil cation exchange capacity. In: Recommended soil testing procedures for the northeastern United States, vol 2, pp 62–70
Sadeghi SMM, Attarod P, Van Stan JT, Pypker TG (2016) The importance of considering rainfall partitioning in afforestation initiatives in semiarid climates: a comparison of common planted tree species in Tehran, Iran. Sci Tot Environ 568:845–855
Sadeghi SMM, Van Stan JT, Pypker TG, Friesen J (2017) Canopy hydrometeorological dynamics across a chronosequence of a globally invasive species, Ailanthus altissima (Mill., tree of heaven). Agric For Meteorol 240:10–17
Sadeghi SMM, Van Stan JT, Pypker TG, Tamjidi J, Friesen J, Farahnaklangroudi M (2018) Importance of transitional leaf states in canopy rainfall partitioning dynamics. Eur J For Res 137:121–130
Safari A, Kavian A, Parsakhoo A (2013) Assessment of effect of road or road construction on soil physical and chemical properties in northern forests of Iran. Int J Adv Biol Biomed Res 1(8):835–850
Sagheb Talebi K, Pourhashemi M, Sajedi T (2014) Forests of Iran: a treasure form the past, a hope for the future. Springer, Dordrecht
Smethurst PJ, Baillie C, Cherry M, Holz G (2003) Fertilizer effects on LAI and growth of four Eucalyptus nitens plantations. For Ecol Manag 176:531–542
Spellerberg IF (1998) Ecological effects of roads and traffic: a literature review. Glob Ecol Biogeogr Lett 7:317–333
Sriyaraj K, Shutes RB (2001) An assessment of the impact of motorway runoff on a pond, wetland and stream. Environ Geochem Trop Subtrop 26:433–439
Tarvirdizadeh H, Nikooy M, Pourbabaei H, Naghdi R (2014) Effects of road construction on biodiversity and composition of herbaceous species cover, Asalem Forest, Northern Iran. For Ideas 20(2):157–169
R Core Team (2017) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna. https://www.R-project.org/. Accessed 20 Jan 2017
Tikka PM, Hogmander H, Koski PS (2001) Road and railway verges serve as dispersal corridors for grassland plants. Landsc Ecol 16(7):659–666
Trombulak SC, Frissell CA (2000) Review of ecological effects of roads on terrestrial and aquatic communities. Conserv Biol 14:18–30
Vockenhuber EA, Scherber C, Langenbruch C, Meißner M, Seidel D, Tscharntke T (2011) Tree diversity and environmental context predict herb species richness and cover in Germany’s largest connected deciduous forest. Perspect Plant Ecol Evolut Syst 13:111–119
Walkley A, Black IA (1934) An examination of Degtjareff method for determining soil organic matter and a proposed modification of the chromic acid titration method. Soil Sci 37:29–37
Watkins RZ, Chen J, Pickens J, Brosofske KD (2003) Effects of forest roads on understory plants in a managed hardwood landscape. Conserv Biol 17(2):411–419
Wei L, Villemey A, Hulin F, Bilger I, Yann D, Chevalier R, Archaux F, Gosselin F (2015) Plant diversity on skid trails in oak high forests: a matter of disturbance, micro-environmental conditions or forest age? For Ecol Manag 338:20–31
Wilson EJ, Wells TCE, Sparks TH (1995) Are calcareous grasslands in the UK under threat from nitrogen deposition? An experimental determination of a critical load. J Ecol 83:823–832
Zielinska K (2007) The influence of roads on the species diversity of forest vascular flora in Central Poland. Biodivers Res Conserv 5–8:71–80
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the staff in Kheyrud’s Forest Station for assistance in the field (in alphabetical order: Rahmatollah Qomi and Habib Zalnezhad). The authors would like to thank two anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions that improved the quality of this paper.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or non-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Eric R. Labelle.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deljouei, A., Sadeghi, S.M.M., Abdi, E. et al. The impact of road disturbance on vegetation and soil properties in a beech stand, Hyrcanian forest. Eur J Forest Res 137, 759–770 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10342-018-1138-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10342-018-1138-8