Abstract
Purpose
Real-time monitoring is important for the safety and effectiveness of high-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) therapy. Magnetic resonance imaging is the preferred imaging modality for HIFU monitoring, with its unique capability of temperature imaging. For real-time temperature imaging, higher temporal resolution and larger spatial coverage are needed. In this study, a sequence based on the echo-shifted RF-spoiled gradient echo (GRE) with simultaneous multi-slice (SMS) imaging was designed for fast temperature imaging.
Methods
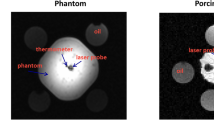
A phantom experiment was conducted to evaluate the accuracy of the echo-shifted sequence using a fluorescent fiber thermometer as reference. The temperature uncertainty of the echo-shifted sequence was compared with the traditional GRE sequence at room temperature through the ex vivo porcine muscle. Finally, the ex vivo porcine liver tissue experiment using HIFU heating was performed to demonstrate that the spatial coverage was increased without decreasing temporal resolution.
Results
The echo-shifted sequence had a better temperature uncertainty performance compared with the traditional GRE sequence with the same temporal resolution. The ex vivo heating experiment confirmed that by combining the SMS technique and echo-shifted sequence, the spatial coverage was increased without decreasing the temporal resolution while maintaining high temperature measurement precision.
Conclusion
The proposed technique was validated as an effective real-time method for monitoring HIFU therapy.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jang HJ, Lee JY, Lee DH, Kim WH, Hwang JH (2010) Current and future clinical applications of high-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) for pancreatic cancer. Gut Liver 4(Suppl 1):S57–S61
Napoli A, Anzidei M, Ciolina F, Marotta E, Cavallo Marincola B, Brachetti G, Di Mare L, Cartocci G, Boni F, Noce V, Bertaccini L, Catalano C (2013) MR-guided high-intensity focused ultrasound: current status of an emerging technology. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 36(5):1190–1203
Celicanin Z, Auboiroux V, Bieri O, Petrusca L, Santini F, Viallon M, Scheffler K, Salomir R (2014) Real-time method for motion-compensated MR thermometry and MRgHIFU treatment in abdominal organs. Magn Reson Med 72(4):1087–1095
Zhao WP, Chen JY, Zhang L, Li Q, Qin J, Peng S, Li KQ, Wang ZB, Chen WZ (2013) Feasibility of ultrasound-guided high intensity focused ultrasound ablating uterine fibroids with hyperintense on T2-weighted MR imaging. Eur J Radiol 82(1):e43–e49
Elias WJ, Huss D, Voss T, Loomba J, Khaled M, Zadicario E, Frysinger RC, Sperling SA, Wylie S, Monteith SJ, Druzgal J, Shah BB, Harrison M, Wintermark M (2013) A pilot study of focused ultrasound thalamotomy for essential tremor. N Engl J Med 369(7):640–648
Roujol S, Ries M, Quesson B, Moonen C, Denis de Senneville B (2010) Real-time MR-thermometry and dosimetry for interventional guidance on abdominal organs. Magn Reson Med 63(4):1080–1087
Zou C, Shen H, He M, Tie C, Chung YC, Liu X (2013) A fast referenceless PRFS-based MR thermometry by phase finite difference. Phys Med Biol 58(16):5735–5751
Rieke V, Butts Pauly K (2008) MR thermometry. J Magn Reson Imaging 27(2):376–390
Yuan J, Mei CS, Panych LP, McDannold NJ, Madore B (2012) Towards fast and accurate temperature mapping with proton resonance frequency-based MR thermometry. Quant Imaging Med Surg 2(1):21–32
Moonen CT, Liu G, van Gelderen P, Sobering G (1992) A fast gradient-recalled MRI technique with increased sensitivity to dynamic susceptibility effects. Magn Reson Med 26(1):184–189
Weidensteiner C, Quesson B, Caire-Gana B, Kerioui N, Rullier A, Trillaud H, Moonen CT (2003) Real-time MR temperature mapping of rabbit liver in vivo during thermal ablation. Magn Reson Med 50(2):322–330
Duyn JH, Mattay VS, Sexton RH, Sobering GS, Barrios FA, Liu G, Frank JA, Weinberger DR, Moonen CT (1994) 3-dimensional functional imaging of human brain using echo-shifted FLASH MRI. Magn Reson Med 32(1):150–155
Voit D, Frahm J (2005) Echo train shifted multi-echo FLASH for functional MRI of the human brain at ultra-high spatial resolution. NMR Biomed 18(8):481–488
de Zwart JA, van Gelderen P, Kelly DJ, Moonen CT (1996) Fast magnetic-resonance temperature imaging. J Magn Reson B 112(1):86–90
Harth T, Kahn T, Rassek M, Schwabe B, Schwarzmaier HJ, Lewin JS, Modder U (1997) Determination of laser-induced temperature distributions using echo-shifted TurboFLASH. Magn Reson Med 38(2):238–245
Chung YC, Duerk JL, Shankaranarayanan A, Hampke M, Merkle EM, Lewin JS (1999) Temperature measurement using echo-shifted flash at low field for interventional MRI. J Magn Reson Imaging 10(1):108
Ma YJ, Liu W, Zhao X, Tang W, Li H, Fan Y, Tang X, Zhang Y, Gao JH (2016) 3D interslab echo-shifted FLASH sequence for susceptibility weighted imaging. Magn Reson Med 76(1):222–228
Schmitz AC, van den Bosch MA, Loo CE, Mali WP, Bartelink H, Gertenbach M, Holland R, Peterse JL, Rutgers EJ, Gilhuijs KG (2010) Precise correlation between MRI and histopathology—exploring treatment margins for MRI-guided localized breast cancer therapy. Radiother Oncol 97(2):225–232
Deckers R, Merckel LG, Denis de Senneville B, Schubert G, Kohler M, Knuttel FM, Mali WP, Moonen CT, van den Bosch MA, Bartels LW (2015) Performance analysis of a dedicated breast MR-HIFU system for tumor ablation in breast cancer patients. Phys Med Biol 60(14):5527–5542
Bankson JA, Stafford RJ, Hazle JD (2005) Partially parallel imaging with phase-sensitive data: increased temporal resolution for magnetic resonance temperature imaging. Magn Reson Med 53(3):658–665
Cao Z, Oh S, Otazo R, Sica CT, Griswold MA, Collins CM (2015) Complex difference constrained compressed sensing reconstruction for accelerated PRF thermometry with application to MRI-induced RF heating. Magn Reson Med 73(4):1420–1431
Barth M, Breuer F, Koopmans PJ, Norris DG, Poser BA (2016) Simultaneous multislice (SMS) imaging techniques. Magn Reson Med 75(1):63–81
Zahneisen B, Ernst T, Poser BA (2015) SENSE and simultaneous multislice imaging. Magn Reson Med 74(5):1356–1362
Borman PT, Bos C, de Boorder T, Raaymakers BW, Moonen CT, Crijns SP (2016) Towards real-time thermometry using simultaneous multislice MRI. Phys Med Biol 61(17):N461–N477
Boyacioglu R, Schulz J, Norris DG (2017) Multiband echo-shifted echo planar imaging. Magn Reson Med 77(5):1981–1986
De Poorter J, De Wagter C, De Deene Y, Thomsen C, Stahlberg F, Achten E (1995) Noninvasive MRI thermometry with the proton resonance frequency (PRF) method: in vivo results in human muscle. Magn Reson Med 33(1):74–81
Conturo TE, Smith GD (1990) Signal-to-noise in phase angle reconstruction: dynamic range extension using phase reference offsets. Magn Reson Med 15(3):420–437
Breuer FA, Blaimer M, Heidemann RM, Mueller MF, Griswold MA, Jakob PM (2005) Controlled aliasing in parallel imaging results in higher acceleration (CAIPIRINHA) for multi-slice imaging. Magn Reson Med 53(3):684–691
Denolin V, Azizieh C, Metens T (2005) New insights into the mechanisms of signal formation in RF-spoiled gradient echo sequences. Magn Reson Med 54(4):937–954
Setsompop K, Gagoski BA, Polimeni JR, Witzel T, Wedeen VJ, Wald LL (2012) Blipped-controlled aliasing in parallel imaging for simultaneous multislice echo planar imaging with reduced g-factor penalty. Magn Reson Med 67(5):1210–1224
Pruessmann KP, Weiger M, Scheidegger MB, Boesiger P (1999) SENSE: sensitivity encoding for fast MRI. Magn Reson Med 42(5):952–962
Salomir R, Viallon M, Kickhefel A, Roland J, Morel DR, Petrusca L, Auboiroux V, Goget T, Terraz S, Becker CD (2012) Reference-free PRFS MR-thermometry using near-harmonic 2-D reconstruction of the background phase. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 31(2):287–301
Dietrich O, Raya JG, Reeder SB, Reiser MF, Schoenberg SO (2007) Measurement of signal-to-noise ratios in MR images: influence of multichannel coils, parallel imaging, and reconstruction filters. J Magn Reson Imaging 26(2):375–385
Kohler MO, Mougenot C, Quesson B, Enholm J, Le Bail B, Laurent C, Moonen CTW, Ehnholm GJ (2009) Volumetric HIFU ablation under 3D guidance of rapid MRI thermometry. Med Phys 36(8):3521–3535
Holbrook AB, Santos JM, Kaye E, Rieke V, Pauly KB (2010) Real-time MR thermometry for monitoring HIFU ablations of the liver. Magn Reson Med 63(2):365–373
Fuentes D, Walker C, Elliott A, Shetty A, Hazle JD, Stafford RJ, North American Hyperthermia Group (2011) Magnetic resonance temperature imaging validation of a bioheat transfer model for laser-induced thermal therapy. Int J Hyperthermia 27(5):453–464
Corea J, Ye P, Seo D, Butts-Pauly K, Arias AC, Lustig M (2018) Printed receive coils with high acoustic transparency for magnetic resonance guided focused ultrasound. Sci Rep 8(1):3392
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Key Laboratory for Magnetic Resonance and Multimodality Imaging of Guangdong Province (no. 2014B030301013), the National Natural Science Foundation (nos. 81327801, 81527901, 11574039, and 11504401), and the Shenzhen Science and Technology Research Program (nos. JCYJ20150630114942317 and JCYJ20150521094519487). The authors sincerely thank Jianhong Wen, De Meng, Chao Wang, and Zongwei Xu for their technical support in the experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YP: protocol development, data collection, and analysis. CZ: sequence design test, protocol development, and data analysis. YQ: data analysis. CT and QW: data collection and analysis. RJ: data collection or management. CC: data analysis. DL: data analysis. HZ: data analysis. FL: protocol development and data analysis. XL: protocol development and data analysis.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical standards
The study was performed in compliance with ethical standards.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, Y., Zou, C., Qiao, Y. et al. Fast MR thermometry using an echo-shifted sequence with simultaneous multi-slice imaging. Magn Reson Mater Phy 31, 771–779 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-018-0692-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-018-0692-x